2051
Right ventriclar myocardial strain in chronic total occlusion patients by cardiac magnetic resonance tissue tracking: a polit study
Xin Li 1, Zhiyong Li1, Qingwei Song1, and Ailian Liu1
1First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
1First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
We try to valuate right ventricular myocardial strain in CTO patients using cardiac magnetic resonance tissue tracking. In this study we found that in CTO patients, even though the structural and functional parameters of right ventricle were normal, the strain condition had already compensated. Besides,compared with LGE area, strain is more correlated with LVEF.
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate right ventricular myocardial strain in CTO patients using cardiac magnetic resonance tissue tracking.Introduction
Coronary chronic total occlusion (CTO) are defined as an occluded coronary segment with thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) flow 0 for ≥ 3 months duration[1]. At present, studies have proved that left ventricular myocardial strain decreased in CTO patients compared with normal people, but few studies focus on right ventricle.Materials and methods
69 CTO patients(50 males, mean age 62.03±10.66 years) were recruited and underwent on a 1.5 T MR scanner(HDxt; General Electric Medical Systems, Waukesha, WI,USA).The scan was completed by using the 8-channel phased array receiver coil for the heart under the control of electrocardiography and respiration. Scanning parameters included: TR/TE = 3.6/1.6 ms, flip angle = 50°, FOV = 350×350 mm2, matrix size = 192×224, bandwidth = 125kHz, slice thickness = 1.0 mm, and slice gap = 0 mm.The RV myocardial deformation was quantified using a CVI42 Tissue Tracking software (cvi42 v5.10.0, Circle Cardiovascular Imaging, Alberta, Canada). We traced the LV and RV endocardial and epicardial borders at the end diastolic (ED) phase in both short-axis and long-axis cine images(papillary muscles and muscle column were excepted in myocardium). Conventional structural and fuctional parameters included LVEF(left ventricular ejection fraction), RVEF(right ventricular ejection fraction), RVEDV(right ventricular end diastolic volume), RVESV(right ventricular end systolic volume), RVSV(right ventricular stroke volume)、HR (heart rate), RVM(right ventricular mass). Then strain parameters were automatically derived by the software, including GRS(global radial peak strain), GCS(global circumferential peak strain),GLS(global longitudinal peak strain), SRSR(global systolic radial strain rate), SCSR (global systolic circumferential strain rate), SLSR (global systolic longitudinal strain rate), DRSR(global diastolic radial strain rate), DCSR (global diastolic circumferential strain rate), DLSR (global diastolic longitudinal strain rate)(Figure 1). The area of late gadolinium enhanced (LGE) was manually outlined by the software.
Independent sample t test or Mann Whithey U test were used for comparison between the CTO and noraml group according to whether it conforms to a normal distribution. Pearson correlation analysis was used to observe the correlation between LVEF, LGE area and srain parameters. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
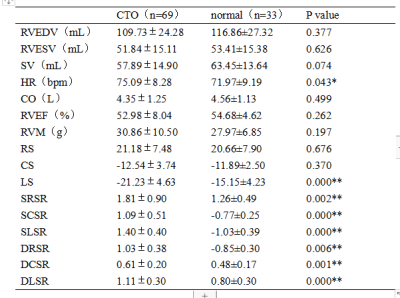
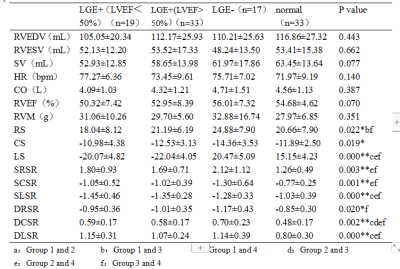
In terms of structural and functional parameters of the right ventricle, except HR, RVEDV, RVESV, SV, CO, RVEF and RVM in the CTO group and the normal group showed no significant difference. In terms of RV strain parameters, RS and CS showed no statistical difference between the two groups, but LS in the CTO group were increased (-21.23±4.63 vs -15.15±4.23). Besides, SRSR, SCSR, SLSR, DRSR, DCSR and DLSR were also significantly increased in the CTO group (P ≤0.001)(Table 1).We further the CTO patients into three groups, LGE (-), LGE (+) and LVEF < 50%, LGE (+) and LVEF > 50%, and the normal control group. Analysis found that RVEDV, RVESV, RVSV, HR, CO, RVEF, RVM had no statistical difference between the four groups, but right ventricular strain and strain rate all had significant statistical differences. In addition to this, we observed more strain values in LGE (-) group were statistically different than those in LGE (+) group compared with normal group(Table 2).
For CTO patients, RVSV, RVEF, RS, CS, DRSR were significantly positively correlated with LVEF. However, all RV function and strain parameters had no significant correlation with LGE area.