2027
Compressed-SENSE accelerated fast comprehensive eight minutes MR based stroke protocol including non-contrast imaging of ischemic penumbra1Philips Health Systems, Philips India Limited, Gurugram, India, 2Department of Radiology, Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram, India, 3Department of Interventional Neuroradiology, Fortis Memorial research Institute, Gurugram, India, 4Department of Neurology, Fortis Memorial research Institute, Gurugram, India
Synopsis
In this study, we propose a modified fast MR 8-minutes stroke protocol including Flair-TSE, DWI, SWI, 3D-pCASL and 3D-non-contrast-MRA that can provide complete information covering the whole spectrum of core-infarct, hemorrhagic-components, vessel-occlusion and ischemic-penumbra. The time duration of this protocol is sufficiently shorter with the benefit of using Compressed-SENSE acceleration algorithm. This MR based stroke protocol does not involve any harmful radiation and contrast media. In our study, this protocol is validated in clinical setting and benefits the therapy-planning of about 70% of patients presented acute ischemic stroke. This protocol has the potential to be adapted for acute-stroke management strategies.
Introduction
Imaging is the main stay in acute stroke management. If thrombolytic-therapy and intervention are performed within right time window, it can help in stroke patient survival and minimize long-term disabilities [1]. CT has earlier been modality of choice due to fast acquisition, low cost and higher availability. For past few years, MRI stroke protocols are being explored on priority as MRI extracts the maximum diagnostic information required for stroke therapies [2]. The challenge is to make a balance between faster acquisitions to preserve the time window, as well as not to compromise on the information. In a recent study [3], compressed-SENSE-accelerated six minutes stroke protocol was reported that used FLAIR, DWI, single-shot T2, T1, SWIp and non-contrast 3D MRA ;however, this fast protocol lacks the ischemic penumbra information. Stroke penumbra extent is a critical information for stroke-therapy planning that can be obtained by either CT or MR-based-perfusion methods. Perfusion is avoided commonly due to contrast injection and compromised patient situation in acute-ischemic-stroke, thus making the diagnosis incomplete. Following the 6 min stroke protocol, in this study, we propose a modified fast MR stroke protocol including Flair-TSE, DWI, SWI, 3D pCASL and 3D non-contrast-MRA within eight minutes period that can provide complete information covering the whole spectrum of core-infarct, hemorrhagic-components, vessel-occlusion and ischemic-penumbra. The time duration of this protocol is sufficiently shorter with the benefit of using Compressed-SENSE-acceleration algorithm. This fast protocol has been run in clinical setup and its utility has been evaluated in this study of real-time acute stroke imaging.Materials and method:
Under this EC approved study, thirty patients presented with acute stroke symptoms underwent MRI at 3.0T (Ingenia, Philips, The Netherlands) with a 15-channel head coil. All of them were scanned with the proposed fast compressed-SENSE accelerated (CSA) stroke protocol. The protocol and parameter details are mentioned in Table-1. DWI was used for infarct-core detection, susceptibility-weighted-imaging (SWI) and 3D-non-contrast-MRA in routine-stroke-protocol aided detection of early hemorrhagic transformations and arterial occlusion respectively. Compressed-SENSE technique, used in 3D-SWI and 3D-Non-contrast-MRA is benefitting from the variable-density-incoherently under-sampling of k-space. Compressed-SENSE factors used for each sequence were optimized to achieve possible scan duration reduction while keeping the visual image quality comparable with previously used non-compressed-SENSE protocols. 3D-pCASL was used for performing non-contrast-perfusion scans and the parameters were optimized and restricted to only 14 slices to make the acquisition-time shorter to about 1.30 minutes . Post-label-delay was 2000 ms, with a label-duration of 1800. 3D pCASL provided the information on stroke penumbra extent. T1 and T2 sequences are omitted from the previous 6 min protocol as these do not add any additional information to the stroke evaluation. The scans were qualitatively assessed by two experienced senior neuroradiologist (with more than 40 years of experience). Manual ROI were drawn on ADC and 3D pCASL to analyze core and penumbra area. The patients were taken to stroke therapy based on MRI findings. Cases having a mismatch between stroke penumbra (assessed in pCASL) and core-infarct (DWI), were treated with necessary thrombolyzation/recanalization therapy. The post therapy images were acquired to validate the progress. The stroke therapist validated penumbra finding from pCASL qualitatively.Results and Discussion
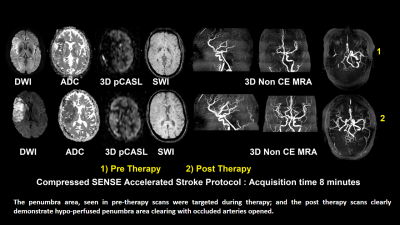
A total of thirty patients with a mean age of 69.8 (range, 36-94) years had been evaluated in this study. For 21 patients, the stroke penumbra information provided by 3D pCASL was utilized for and validated by therapy planning. A total of 70% of cases have been benefitted by this tailored protocol design. These 70% of cases had a mismatch between stroke-penumbra (assessed in pCASL) and core-infarct (DWI) which was re-confirmed in stroke therapies, and the post-therapy scans confirmed the progress of the cases qualitatively. In rest 30% of cases, either no penumbra was seen (old infarct) or the penumbra area were matching with the core-infarct (no mismatch). An example of stroke case is shown in Figure 1, where pre-therapy and post-therapy scans clearly demonstrated the utility of 3D-pCASL. The penumbra area, seen in pre-therapy scans were targeted during therapy; and the post therapy scans clearly demonstrate hypo-perfused penumbra area clearing with occluded arteries opened. SWIP and non-contrast 3D-MRA sequences, specially benefitted from Compressed-SENSE in terms of high acceleration-factors to reduce scan time, without any potential loss of image quality for stroke screening. Utility of 3D-pCASL is often debated in case of tumor or encephalopathies. In acute stroke, 3D-pCASL indicated the hypo-perfusion of penumbra extent reliably, as found in pre and post-therapy study. This proposed protocol and study is a qualitative way to validate the protocol benefits in clinical scenario. Further studies are being formulated to quantify the DWI-pCASL mismatch ratio and subsequent validation. The 3D-pCASL sequence also gives quantitative CBF information which can further be explored.Conclusion
Proposed fast Compressed-SENSE-accelerated eight minutes protocol is short and generates comprehensive clinical information required for efficient stroke management. Moreover, this MR based stroke protocol does not involve any harmful radiation and contrast-media used in CT. In our study, this protocol is validated in clinical setting and benefits the therapy planning of about 70% of patients presented acute ischemic stroke . This protocol has the potential to be adapted for acute stroke management strategies.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Jansen O, von Kummer R, Forsting M, Hacke W, Sartor K. Thrombolytic therapy in acute occlusionof the intracranial internal carotid artery bifurcation. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology.1995; 16(10):1977–1986. [PubMed: 8585483]
[2] Schellinger PD, Bryan RN, Caplan LR, et al. Evidence-based guideline: The role of diffusion andperfusion MRI for the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke: report of the Therapeutics andTechnology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology.2010; 75(2):177–185. [PubMed: 20625171]
[3] Bhattacharjee
R, Raj RK, Verma RK, Gupta RK Comprehensive stroke protocol of less than six
minutes: using Compressed-SENSE with valued addition of SWIp and Non-Contrast-3D-MRA. ISMRM 2019, Montreal,
Canada ( Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 27 (2019), Page Nu-1188).