1846
Fast APTw imaging with Compress Sense technique in Glioma
Cong Xie1, Yaou Liu1, Rongkai Ju2, Zhiwei Shen2, Zhizheng Zhuo1, Yunyun Duan1, Xiaobo Wang1, Qiong Qiu1, and Fenglian Zheng1
1Department of Radiology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Philips,healthcare,China, Beijing, China
1Department of Radiology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Philips,healthcare,China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
explorer the performance of in APTw with Compress Sense (CS) in the evaluation of glioma with high grade and low grade.
Objective: to explorer the performance of in APTw with Compress Sense (CS) in the evaluation of glioma with high grade and low grade. Methods APT imaging was performed using a 3D TSE DIXON sequence on a 3.0 T MRI system (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands), using 32 channel head coil. Three different APTw sequences (the original sequence, with high resolution and with CS 4.0) were performed and scan parameters of APT sequences are shown in Table 1. Nine phantoms with different concentrations of free amino acids and one with pure water were firstly test to prove the feasibility of APTw with CS 4. 36 histologically confirmed glioma patients were enrolled in this retrospective study. Two groups of high-grade glioma (astrocytoma, n=10; oligodendroglioma, n=6; oligodend astrocytoma, n=3) and low grade glioma (meta-degeneration astrocytoma, n=8; glioblastoma, n=8; diffuse-midline glioma, n=1) were perform. 30 patients were scanned with three different types of APTw sequence at one time. The CNR of tumor and normal tissue was calculated, and paired t test was used to evaluate the difference comparing original sequence and high-resolution sequence, or original sequence and fast sequence with CS 4. The difference of APT value between high grade group and low grade group was also detected by t-test. All data was analysis by SPSS17.0. Results The APT signal curves of phantom by three sequences show a good uniformity, and three APTw values are all approximately linear with the contents of free proteins in different concentrations (Figure 1), which indicates that APTw values can effectively reflect the contents of free proteins. All the subjects were scanned by APTw sequences with CS 4. Furthermore, patients were scanned with three different types of APTw sequence at one time (Figure 2). The apt values were measured from console. With tumor CNR in APTw mapping, there was no significant difference among the three groups (P > 0.05). Compared with pathology, it was found that the apt values is more than 4.0% in high grade glioma, and when APTw values is less than 4.0%, it needs to be diagnosed in combination with clinical and other images (Table 2). 4.Discussion and Conclusion With CS technique, the scan time of APT sequence was effectively reduced without significant image quality degradation and APT value change. During scanning, we found it is not suitable for saddle area, subsaddle and head and neck junction lesions for the inhomogeneity of B0. Therefore, APTw is ideal in meningoma and glioma, but not ideal in cavernous angioma. In this study, the feasibility and accuracy of APTw with CS 4 was proven In water phantom test and patients with gliomas, provides a fast new method to tumor detect and the classification of gliomas by APT value. Key words: CS free protein water phantom glioma grade
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
Accelerating chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI by combining compressed sensing and sensitivity encoding techniques.Heo HY, Zhang Y, Lee DH, Jiang S, Zhao X, Zhou J.Magn Reson Med. 2017 Feb;77(2):779-786.
Prospective acceleration of parallel RF transmission-based 3D chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging with compressed sensing.Heo HY, Xu X, Jiang S, Zhao Y, Keupp J, Redmond KJ, Laterra J, van Zijl PCM, Zhou J.Magn Reson Med. 2019 Nov;82(5):1812-1821.
Figures
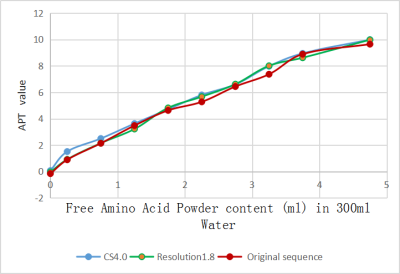
Figure 1. The APT signal curves of phantom by three sequences show a good uniformity, and three APTw values are all approximately linear with the contents of free proteins in different concentrations
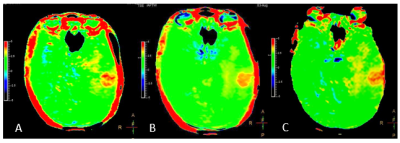
Figure 2. A 43-year-old woman with glioma. APTw image with original APT sequence (a), with highresolution (b) and with CS 4.0 (c) showed APT with CS 4sequence was fast without significant image quality degradation and tumor CNRchange.
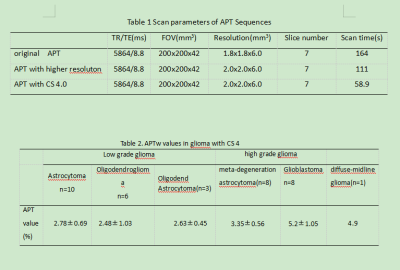
Table 1 Scan parameters of APT Sequences
Table 2. APTw values in glioma with CS 4