1711
Simultaneous Fast and Slow DCE: temporal multiresolution and spatial high resolution T1 dynamics of the whole brain from a single continuous scan1University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 2Medical University Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 3University of Vienna, Wien, Austria
Synopsis
We present DCE acquisition with high spatial resolution that excels the guidelines of the ACR for spatial resolution, maintaining whole brain coverage at all times, while at the same time providing a temporal sampling rate of fast enough to make accurate flow and permeability measurements from T1-weighted DCE MRI in a clinical neuro-oncology setting possible.Furthermore we demonstrate the use of radial spoke aggregation in GRASP reconstruction for DCE perfusion imaging of the brain and show preliminary results on the impact of variable temporal resolution on estimating pharmacokinetic models.
INTRODUCTION and MOTIVATION
Dynamic Contrast Enhanced (DCE) MRI, i.e. dynamic T1-weighted imaging is a well establised technique that is widly considered gold standard for measuring blood-brain-barrier integrity. [1]Different pharmacokinetic models are used to extract quantitative parameters representing tissue characteristics. For this work we chose the widely used 'extended Tofts' (eT) and the (full) 'two compartment exchange' (2CX) model. The eT comprises 3 parameters, including the volume transfer constant Ktrans, while the latter 2CX comprises 4 parameters, including the plasma flow Fp. [1][2][3] These derived parameters allow a characterization of brain pathology. [4] For both models it is assumed that the duration of the bolus passage is small compared to the typical timescale of the model and the duration of the bolus passage through the tissue of interest. [1] The typical mean transit time of contrast agent through the capillary bed in healthy brain parenchyma is in the order of a few seconds while in brain tumors it is in the order of tens of secounds. [1][2]
It has been demonstrated that temporal resolution and acquisition length significantly affect model parameters and accuracy. [5] The accurate estimation of kinetic parameters such as the blood flow (Fp, 2CX) or Ktrans (eT) requires an adequate sampling rate of at least similar magnitude.
The Arterial Input Function (AIF) enters in both models and is crucial for the accuracy of the parameter estimates. [1]
Previously available MRI sequences resulted in the necessity of making a trade-off between either slow sampling with good resolution, slow sampling with good coverage or fast sampling potentially loosing both. [3]
It is the aim of this paper to present a solution and show that we can sample fast enough and spatially fine enough the fullfill all the aforementioned contraints while maintaining whole brain coverage.
Furthermore we will present data comprising multiple temporal resolutions from the same continious scan via aggregating radial spokes in k-space and use this to investigate the influence of temporal resolution on the DCE models.
METHODS
The measurement of 20 brain tumor patients was carried out by injecting 8mL of Gadoteridol solution by a pressure injector 30s after start of the DCE acquisition followed by a saline flush.All measurements were performed an a 3T Siemens Magnetom Vida 128XT using a 64 channel Head-Neck Coil.
Prior to contrast agent injection a Variable Flip Angle T1 mapping was performed using the vendor provided radial stack-of-stars 3d RF-spoiled gradient-echo sequence with parameters closely matching the DCE sequence. The T1 mappings were postprocessed directly on the scanner incorporating a B1-inhomogenity correction.
DCE imaging was performed using the vendor provided Compressed Sensing (CS) Golden-angle RAdial SParse (GRASP) dynamic T1-weighted radial stack-of-stars 3d RF-spoiled gradient-echo sequence (FoV 220mm, resolution 192px, 3046 radial spokes, 3.7ms/1.75ms TR/TE, FA 12deg, partial fourier 6/8 (slice), 20% gap) with 1.1mm x 1.1mm x 3mm resolution and 42 axial slices over 06:00 min.
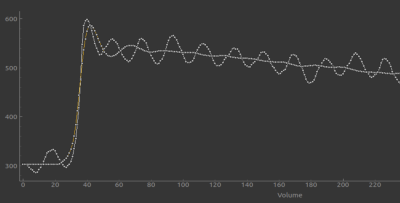
The data was postprocessed retrospectively on the MRI-reconstruction-system (NumarisX VA11B&VA20A) using the vendor provided iterative reconstruction by aggregating 13, 21, 34, 56, 89, 92 radial spokes resulting in 233, 144, 89, 54, 33 timepoints per series with resolutions of approximately 1.5s, 2.5s, 4s, 6.5s, 10.5s and CS -acceleration-factors of 23.2, 14.4, 8.9, 5.5, 3.4, 2.1, 1.3 as well as a static image comprising all spokes used for coil sensitvity calibration.
This approach is possible due to the high uniformity of k-space coverage in GRASP. [6][7][8]
Following rigid body registration of the dynamic data and the T1 mappings to the aforementioned all-spoke image using FSL [9] the data was evaluated with the Bayesian model fitting framework FABBER [10][11].
RESULTS and DISCUSSION
The resulting time series were suitable for pharmacokinetic modeling and show decreasing undersampling artefact levels with increasing numbers of aggregated spokes consitent with previous results in other organ systems. [6][7]The estimation of the AIF does benefit from high temporal and spatial resolution.
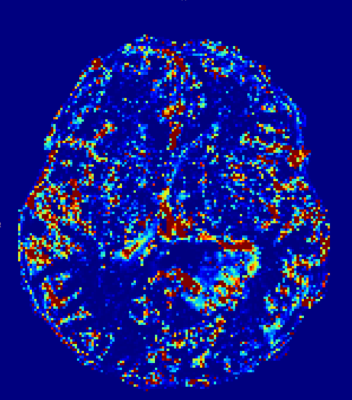
The fastest sampling (1.5s) proofed best for 2CX, providing a significant difference in Fp for healthy parenchyma compared to highly perfused tumor and showed good correlation with CBF from DSC imaging. (A prototypical case is shown.)
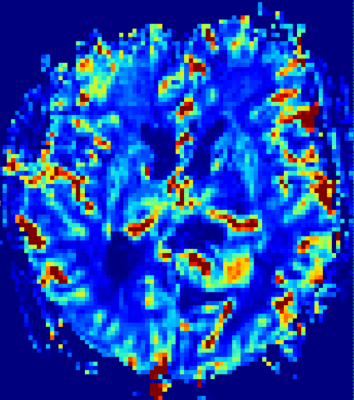
Conversely eT gave the most convincing results with least variability for healthy parenchyma when using slower temporal resolutions (6.5s, 10.5s) with less streaking artefcts. A trend of decreasing Ktrans with decreasing temporal resolution can be seen. This preliminary finding is in accorance with previous results using image space temporal averaging [5]
The observed variability in the pharmacokinetic parameter estimates emphasizes the need for standardization.
CONCLUSION
We present a DCE acquisition for brain tumors that excels the guidelines of the ACR [1] for spatial resolution, maintaining whole brain coverage at all times, while at the same time providing a temporal sampling rate fast enough to make accurate flow and permeability measurements from T1-weighted DCE MRI in a clinical neuro-oncology setting possible.Furthermore we demonstrate the use of radial spoke aggregation in GRASP reconstruction for DCE perfusion imaging of the brain and show preliminary results on the impact of variable temporal resolution on estimating pharmacokinetic models.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Cercignani, M., Dowell, N.G. and Tofts, P.S. eds., 2018. Quantitative MRI of the brain: principles of physical measurement. CRC Press.
[2] Sourbron, S., Ingrisch, M., Siefert, A., Reiser, M. and Herrmann, K., 2009. Quantification of cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume, and blood–brain‐barrier leakage with DCE‐MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 62(1), pp.205-217.
[3] Sourbron, S.P. and Buckley, D.L., 2013. Classic models for dynamic contrast‐enhanced MRI. NMR in Biomedicine, 26(8), pp.1004-1027.
[4] Anzalone, N., Castellano, A., Cadioli, M., Conte, G.M., Cuccarini, V., Bizzi, A., Grimaldi, M., Costa, A., Grillea, G., Vitali, P. and Aquino, D., 2018. Brain gliomas: multicenter standardized assessment of dynamic contrast-enhanced and dynamic susceptibility contrast MR images. Radiology, 287(3), pp.933-943.
[5] Larsson, C., Kleppestø, M., Rasmussen Jr, I., Salo, R., Vardal, J., Brandal, P. and Bjørnerud, A., 2013. Sampling requirements in DCE‐MRI based analysis of high grade gliomas: Simulations and clinical results. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 37(4), pp.818-829.
[6] Block, K.T., Chandarana, H., Milla, S., Bruno, M., Mulholland, T., Fatterpekar, G., Hagiwara, M., Grimm, R., Geppert, C., Kiefer, B. and Sodickson, D.K., 2014. Towards routine clinical use of radial stack-of-stars 3D gradient-echo sequences for reducing motion sensitivity. Journal of the Korean Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 18(2), pp.87-106.
[7] Feng, L., Grimm, R., Block, K.T., Chandarana, H., Kim, S., Xu, J., Axel, L., Sodickson, D.K. and Otazo, R., 2014. Golden‐angle radial sparse parallel MRI: combination of compressed sensing, parallel imaging, and golden‐angle radial sampling for fast and flexible dynamic volumetric MRI. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 72(3), pp.707-717.
[8] Winkelmann, S., Schaeffter, T., Koehler, T., Eggers, H. and Doessel, O., 2006. An optimal radial profile order based on the Golden Ratio for time-resolved MRI. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 26(1), pp.68-76.
[9] M. Jenkinson, C.F. Beckmann, T.E. Behrens, M.W. Woolrich, S.M. Smith. FSL. NeuroImage, 62:782-90, 2012
[10] Chappell, M.A., Groves, A.R., Woolrich, M.W., “Variational Bayesian inference for a non-linear forward model”, IEEE Trans. Sig. Proc., 2009, 57(1), 223–236.
[11] Groves, A. R., Chappell, M. A., & Woolrich, M. W. (2009). “Combined spatial and non-spatial prior for inference on MRI time-series.” NeuroImage, 45(3), 2009.doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.12.027