1701
Application of Half-Dose Contrast-Enhanced T2-Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery (T2 FLAIR) Sequence in Brain Metastasis1Radiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2Department of Radiology, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
For reducing the gadolinium dose of patients with metastasis, we seek a valuable tool to lower contrast agent doses but keep MR image quality, which is important for patients’ healthcare. We analyzed the optimum scanning time for 1/2 dose CE-T2FLAIR, and compared the CR value of metastases and enhancement degree among the 1/2 dose CE-T2 FLAIR, 1/2 dose CE-T1WI and full dose CE-BRAVO sequence. Our team further analyzed the relationship between enhancement pattern, lesion size and image quality. Our study not only reduced the harm from GBCA administrations but also improved detection rate of brain metastases.
Objective
To explore the clinical value of half-dose contrast-enhanced T2-fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequence (1/2-dose CE-T2 FLAIR) in intracranial metastases.Materials and Methods
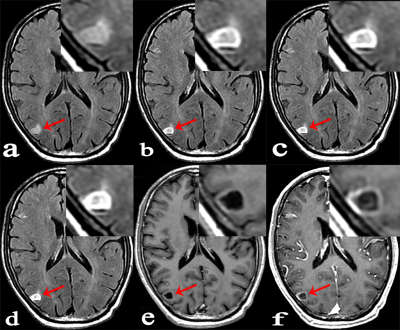
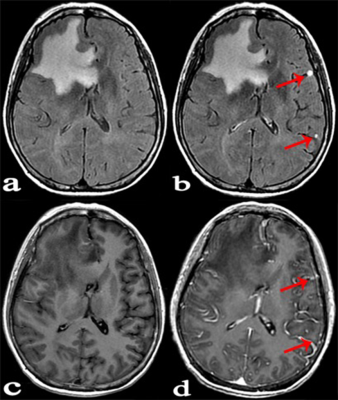
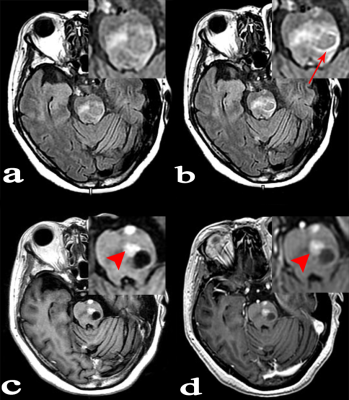
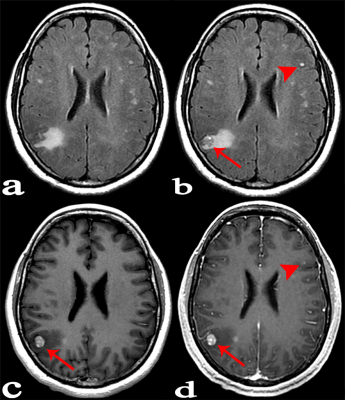
Forty-six patients with known cancers and brain metastasis were prospectively enrolled, they underwent 3.0 T MR examinations which mainly including: 1/2-dose CE-T2 FLAIR (continuous scanning for three phases: phase1, phase2 and phase3), 1/2-dose CE-T1WI and routine-dose CE-3D-BRAVO. All lesions were divided into three groups according to the diameter and enhancement pattern: Group A, solid-enhanced with a diameter ≥5mm; Group B, ring-enhanced with a diameter ≥5mm; Group C, lesion diameter <5mm. The lesion enhancement degree was scored in 1/2-dose CE-T2 FLAIR (phase3), 1/2-dose CE-T1WI and routine-dose CE-BRAVO respectively. The scoring criteria was as follows: 3 point, enhancement degree was good; 2 point, enhancement degree was moderate; 1 point, enhancement degree was poor (Lesions that were initially misdiagnosed were also scored 1 point). I) The CR values of lesions in three consecutive phases of 1/2-dose CE-T2 FLAIR were compared; (II) The percentage increase (PI) of 1/2-dose CE-T2 FLAIR in groups A, B, and C were measured respectively for comparisons; (III) Statistical analysis was performed to compare the enhancement degree on three enhanced-sequences in each group.Results:
A total of 89 metastases were confirmed, including 27 in group A, 23 in group B, and 39 in group C. (I) The mean values of CR in 1/2-dose CE-T2 FLAIR for the three consecutive phases were CRphase1=63.64±32.19, CRphase2=77.34±40.19, and CRphase3=83.05±46.65, wherein CRphase1<CRphase2<CRphase3 (P=0.001). (II) The PI values of 1/2-dose CE-T2 FLAIR in groups A, B, and C were PIA=31.42±11.65, PIB= 58.60±27.79, and PIC=61.05±29.55, respectively. PIA<PIB (P=0.001) and PIA<PIc (P<0.001). (III) Group A: the enhancement degree of metastases on 1/2-dose CE-T2 FLAIR was lower than that on 1/2-dose CE-T1WI (P=0.001) and routine dose CE-BRAVO (P<0.001); Group B: there was no significant difference between 1/2-dose CE-T2 FLAIR and routine-dose CE-BRAVO (P=0.122); Group C: the enhancement degree on 1/2-dose CE-T2 FLAIR was obviously higher than that on 1/2-dose CE-T1WI (P<0.001) and routine-dose CE-BRAVO (P<0.001)Conclusion
Compared with routine-dose CE-BRAVO, half dose CE-T2 FLAIR has unique advantages in detecting ring-enhanced metastases and small metastases at early phase.Acknowledgements
Funding: This work was supported by Bracco international B.V. as an investigator initiated trial. The funders had no roles in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.References
1. Fok JS, Smith WB. Hypersensitivity reactions to gadolinium-based contrast agents[J]. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 17(4): 241-261.
2. Liisrto F, alsini G, Bolognese L. The clinical burden of contrast media-induced nephropathy[J]. Ital Heart J, 2003, 4(10): 668-676.
3. Tedechi E, Caranci F, GiordanoF, et al. Gadolinium retention in the body: what we know and what we can do[J]. Raiol Med, 2017, 122(8): 589-600.
4. Semelka RC, Ramalho J, Vakharia A, et al. Gadolinium deposition disease: Initial description of a disease that has been around for a while[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2016, 34(10): 1383-1390.
5. Lord ML, Chettle DR, Grafe JL, et al. Observed Deposition of Gadolinium in Bone Using a New Noninvasive in Vivo Biomedical Device: Results of a Small Pilot Feasibility Study[J]. Radiology, 2018, 287(1): 96-103.
6. Lee EK, lee EJ, Kim S, et al. Importance of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Various Intracranial Pathologic Conditions[J]. Korean J Radiol, 2016, 17(1): 127-141.
7. Mathews VP, Caldemeyer KS, Lowe MJ, et al. Brain: gadolinium-enhanced fast fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery MR imaging[J]. Radiology, 1999, 211(1): 257–263.
8. Jackson EF, Hayman LA. Meningeal enhancement on fast FLAIR images[J]. Radiology, 2000, 215(3): 922-924.
9. Oguz KK, Cila A. Rim enhancement of meningiomas on fast FLAIR imaging[J]. Neuradiology, 2003, 45(2): 78-81.
10. Namba Y, Kijima T, Yokota S, et al. Gefitinib in patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer: review of 15 clinical cases[J]. Clin Lung Cancer, 2004, 6(2): 123-128.
11. Kermode A, Tofts P, Thompson A, et al. Heterogeneity of blood-brain barrier changes in multiple sclerosis: an MRI study with gadolinium-DTPA enhancement[J]. Neurology, 1990, 40(2): 229-235.
Figures