1650
Whole-Brain Brain Oxygen Metabolism in Adult Sickle-Cell Patients Using Two Different Quantitative MRI Approaches1University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA, United States
Synopsis
Silent cerebral infarcts are the most common neurologic injury in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). In this study, we compared T2 -relaxation under spin tagging (TRUST) and susceptibility-based oximetry (SBO) techniques in a cohort of SCD patients compared to healthy control subjects. We observed opposite trends in oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) and cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) in SCD patients compared to controls using TRUST and SBO methods. High OEF measured by TRUST technique lead to very high supraphysiologic CMRO2 values. We conclude that SBO method is more reliable in measuring OEF and CMRO2 in patients with SCD.
Quantitative MRI based methods have been employed to study oxygen metabolism in sickle cell disease (SCD) patients. T2 -relaxation under spin tagging (TRUST) sequence uses spin labeling to isolate pure venous blood signals and measures its T2 value, which is converted to venous oxygenation (Yv) with a calibration plot1. However, there exists some controversy on the impact of HbS on the calibration curve and oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) parameters from TRUST MRI method2. The purpose of the present study was to compute the values of OEF and cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) from SCD patients using both TRUST and susceptibility-based oximetry (SBO) methods3 and to compare those with that of healthy controls.
Methods:
A cohort of 18 patients with SCD [males/females: 8/10; mean age: 28.52 ± 5.24 years; mean hematocrit:30.92 ± 6.73%] and 12 age-matched healthy control subjects underwent MR imaging on a 3T MR system equipped with 64 channel head phased array coil. The imaging protocol included T1-weighted 3D magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo (MPRAGE) sequence, SBO sequence comprising of an interleaved, high temporal resolution 2D-gradient-recalled echo images and TRUST MRI with a single slice EPI intersecting the lower superior sagittal sinus region4. All data were processed using in-house developed MATLAB scripts. Using Non-parametric Mann-Whitney U tests, OEF= (Ya-Yv)/Ya) and CMRO2 were compared between healthy control and SCD patients as obtained from TRUST and SBO methods. Additionally, CBF values as obtained from the SBO sequence were also compared between the two groups.
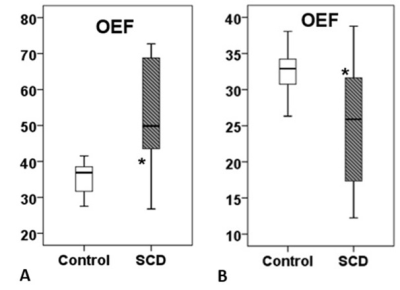
Results:
Higher global CBF was observed in SCD patients compared to control (84.8 ± 16.1 vs 46.0 ± 5.6 ml/min/100g; p< 0.001). Using TRUST, higher OEF (52.7 ± 15.3 vs 35.5 ± 4.1; p< 0.001) were observed in SCD patients compared to the healthy control group. On the other hand, lower OEF (26.4 ± 7.1 vs. 32.7 ± 3.3, p= 0.007) were observed in SCD patients compared to healthy controls using SBO method. CMRO2 was significantly lower in SCD patients when measured by SBO technique compared to TRUST (127.2 ± 41.6 vs. 251.8±75.4 µmol/100 g/min, p<0.000).
Conclusion:
We observed opposite trends in OEF and CMRO2 in SCD patients compared to controls using TRUST and SBO methods. High OEF measured by TRUST technique lead to very high supraphysiologic CMRO2 values. SBO method that does not depend upon the morphologic and hematologic changes of sickle cell is more reliable in measuring OEF and CMRO2 in patients with SCD.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Lu H, Ge Y. Quantitative evaluation of oxygenation in venous vessels using T2-Relaxation-Under-Spin-Tagging MRI. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 2008;60(2):357-63.
2. Bush AM, Coates TD, Wood JC. Diminished cerebral oxygen extraction and metabolic rate in sickle cell disease using T2 relaxation under spin tagging MRI. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 2018;80(1):294-303.
3. Jain V, Langham MC, Wehrli FW. MRI estimation of global brain oxygen consumption rate. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 2010;30(9):1598-607.
4. Barhoum
S, Rodgers ZB, Langham M, Magland JF, Li C, Wehrli FW. Comparison of MRI
methods for measuring whole-brain venous oxygen saturation. Magnetic resonance
in medicine. 2015;73(6):2122-8.