1634
Investigation of collateral circulation compensatory capacity of Willis ring using vessel selective arterial spin labeling1radiology, The first hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2The third people's hospital of Datong, Datong, China, 3GE Healthcare, MR Research China,Beijing, Beijing, China
Synopsis
The Willis ring plays an important role in the collateral circulation especially in patients with internal carotid artery (ICA) stenosis. However conventional time of flight (TOF) MR angiography may only offer limited knowledge of the compensatory blood flow attributed to collateral circulation for patients with stenosis. Vessel selective arterial spin labeling allows the assessment of blood flow of a specific vessel. The purpose of this study was to quantify the influence of various anatomical types on the compensatory capacity of the Willis ring for patients with severe stenosis or occlusion using combined TOF MRA and vessel selective ASL method.
Introduction
The Willis ring plays an important role in the collateral circulation especially in patients with internal carotid artery (ICA) stenosis. However conventional time of flight (TOF) MR angiography may only offer limited knowledge of the compensatory blood flow attributed to collateral circulation for patients with stenosis. Vessel selective arterial spin labeling allows the assessment of blood flow of a specific vessel. The purpose of this study was to quantify the influence of various anatomical types on the compensatory capacity of the Willis ring for patients with severe stenosis or occlusion using combined TOF MRA and vessel selective ASL method.METHODS
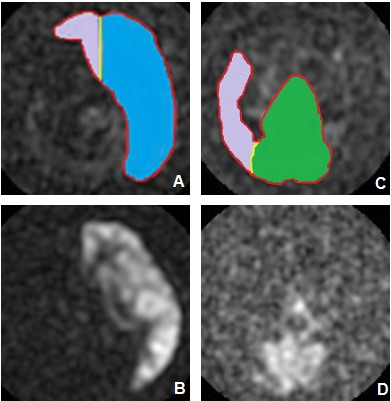
40 patients with severe stenosis or occlusion of the unilateral ICA confirmed by TOF-MRA, CTA, and TCD and 30 normal volunteers were prospectively collected from 2018-01 to 2019-01 in the Department of Neurosurgery, First Hospital of Jilin University. All participants were scanned with the TOF-MRA and vessel selective arterial spin labeling using the GE Discovery750 3.0T MRI scanner. The results were separately evaluated by two imaging physicians. All image data were processed as follows: (1) Estimate the circle condition of anterior communicating artery (AcoA) and posteior communicating artery (PcoA) through TOF-MRA and measure the diameter of P1 segment on A1 segment, PcoP and posterior cerebral artery(PCA)of bilateral anterior cerebral artery (ACA)by RadiAnt DICOM Viewer software; (2) With MATLAB (Mathworks, Natick, Mass), the affected-side ICA and vertebral-basilar artery (VBA) were semi-automatically segmented and defined as the cerebral hemisphere compensation range of the affected side, and the compensatory volume ratios of the unaffected-side ICA and VBA were calculated, as illustrated by a case in Figure 1. In this study, patients were divided into the transient ischemic attack (TIA) group and the cerebral infarction (CI) group according to clinical manifestations. The diameters of Willis ring between the affected and unaffected side in the patient group as well as between the patient group and the normal volunteers were compared. The differences in diameter of each component of the ring, the effects of AcoA and PcoP with or without opening branches and of the diameters of the Willis ring on the compensatory capacity in the healthy ICA and VBA.RESULTS
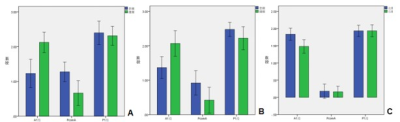
31 males (77.5%) with an average of 61.28 ± 8.735 years in the TIA group and 14 patients (46.7%) with an average age of 54.18±13.17 in 30 healthy controls were enrolled in this study. 23 patients (57.5%) in the TIA group and 17 patients (42.5%) in the cerebral infarction group were discovered. The diameters of the blood vessels in A1 segment and PcoP were statistically different between the affected and unaffected side of the Willis ring in the TIA (P<0.05), and the diameter of the unaffected-side A1 segment (2.12±0.682) was larger than the affected-side one (P<0.05) while PcoP diameter in the affected side (1.27 ± 0.652) was greater than the healthy side. Only the diameter of the A1 segment (2.06±0.725) was larger than the healthy side (1.36±0.615) in the cerebral infarction group (P<0.05). Compared to the normal control group, significant larger A1 segment, bilateral PcoP and bilateral P1 segments in both the TIA and CI group were found (P<0.05). The unaffected-side A1 segment and PcoP as well as the bilateral P1 segments in the cerebral infarction group were significantly larger than in the normal group (P<0.05) (Table 1, Table 2 and Figure2). The compensation range of ICA was significantly larger in the CI group when the AcoA with the opening branch (0.294±0.144) than without the opening branch (0.177±0.189). The compensation volume of unaffected-side ICA was significantly smaller when the PcoP with the opening branch (0.208±0.171) than without the opening branch (0.338±0.130) (P<0.05) (Table3 and Figure 3). The compensation range of unaffected-side VBA was significantly larger when the PcoP with the opening branch (0.223) than without the opening branch (0.056 ± 0.042) (P<0.05) (Table 4 and Figure 4). The linear correlation coefficient between the diameters of unaffected-side A1 segment and the corresponding compensatory ability in the ICA group and between the diameters of unaffected-side PcoP and corresponding compensatory ability in the VBA group was 0.581 and 0.727, respectively.Discussion and CONCLUSIONS
Severe stenosis or occlusion of ICA might change the arterial diameter of the Willis ring, and the opening conditions and anatomical structure of the Willis circle has different effects on the post-circulation compensation capability of healthy-side ICA. Previously, the assessment of collateral circulation is either based on MRA or perfusion, however neither method alone may offer complete picture of the compensatory blood flow. This preliminary study show the compensatory blood flow attributed by collateral circulation may be quantitatively assessed by the simultaneous use of TOF-MRA and vessel selective ASL. Further study with a larger patient cohort and other clinical complications would be needed for the clinical application of this method.Acknowledgements
References
[1]Otite FO, Khandelwal P, Malik AM,et al. National Patterns of Carotid Revascularization Before and After the Carotid Revascularization Endarterectomy vs Stenting Trial (CREST)[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2018,75(1): 51-57. [2]Malhotra K, Goyal N, Tsivgoulis G. Internal Carotid Artery Occlusion: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management[J]. Curr Atheroscler Rep,2017,19(10): 41. [3]Ginsberg MD. The cerebral collateral circulation: Relevance to pathophysiology and treatment of stroke[J]. Neuropharmacology,2018,134(Pt B): 280-292. [4]Ito K, Sasaki M, Kobayashi M, et al. Noninvasive evaluation of collateral blood flow through circle of Willis in cervical carotid stenosis using selective magnetic resonance angiography[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,2014,23(5): 1019-23. [5]Jung S, Wiest R, Gralla J,et al. Relevance of the cerebral collateral circulation in ischaemic stroke: time is brain, but collaterals set the pace[J]. Swiss Med Wkly,2017,147: w14538. [6]Hartkamp MJ, van Der Grond J, van Everdingen KJ, et al. Circle of Willis collateral flow investigated by magnetic resonance angiography[J]. Stroke,1999,30(12): 2671-8. [7] Shuaib A, Butcher K, Mohammad AA, et al. Collateral blood vessels in acute ischaemic stroke: a potential therapeutic target[J]. Lancet Neurol,2011,10(10): 909-21. [8]Alastruey J, Parker KH, Peiró J,et al. Modelling the circle of Willis to assess the effects of anatomical variations and occlusions on cerebral flows[J]. J Biomech,2007,40(8): 1794-805. [9]Hendrikse J, Eikelboom BC, van der Grond J.Magnetic resonance angiography of collateral compensation in asymptomatic and symptomatic internal carotid artery stenosis[J].J Vasc Surg.2002,36(4):799-805. [10]Hendrikse J, Hartkamp MJ, Hillen B,et al. Collateral ability of the circle of Willis in patients with unilateral internal carotid artery occlusion: border zone infarcts and clinical symptoms[J]. Stroke, 2001,32(12): 2768-73. [11]Faber JE, Zhang H, Rzechorzek W, et al. Genetic and Environmental Contributions to Variation in the Posterior Communicating Collaterals of the Circle of Willis[J]. Transl Stroke Res,2018. [12]Orosz L, Hoksbergen AW, Molnár C,et al.Clinical applicability of a mathematical model in assessing the functional ability of the communicating arteries of the circle of Willis[J].J Neurol Sci.2009,287(1-2):94-9. [13]Manninen H,Mäkinen K,Vanninen R,et al.How often does an incomplete circle of Willis predispose to cerebral ischemia during closure of carotid artery? Postmortem and clinical imaging studies[J].Acta Neurochir (Wien),2009,151(9):1099-105. [14]van Laar PJ, Hendrikse J, Klijn CJ,et al.Symptomatic Carotid Artery Occlusion_ Flow Territories of Major Brain-Feeding Arteries[J].Radiology,2007,242(2):526–534. [15]Hartkamp NS, Petersen ET, Chappell MA, et al. Relationship between haemodynamic impairment and collateral blood flow in carotid artery disease[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2018,38(11): 2021-2032. [16]Wang BH, Leung A, Lownie SP. Circle of Willis Collateral During Temporary Internal Carotid Artery Occlusion II: Observations From Computed Tomography Angiography[J]. Can J Neurol Sci, 2016,43(4): 538-42.109. [17]Lownie SP, Larrazabal R, Kole MK. Circle of Willis Collateral During Temporary Internal Carotid Artery Occlusion I: Observations From Digital Subtraction Angiography[J]. Can J Neurol Sci,2016,43(4): 533-7. [18]张玉忠,张雪林,昌仁民,等.磁共振血管成像willis环的变异及其意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2002,20(3):190-193. [19]Hoksbergen AW, Fülesdi B, Legemate DA,et al. Collateral configuration of the circle of Willis: transcranial color-coded duplex ultrasonography and comparison with postmortem anatomy[J]. Stroke,2000,31(6): 1346-51. [20] Qiu C, Zhang Y, Xue C,et al.MRA Study on Variation of the Circle of Willis in Healthy Chinese Male Adults[J] .Biomed Res Int, 2015;2015:976340. [21]Waaijer A, van Leeuwen MS, van der Worp HB,et al. Anatomic variations in the circle of Willis in patients with symptomatic carotid artery stenosis assessed with multidetector row CT angiography[J]. Cerebrovasc Dis,2007,23(4): 267-74. [22]Varga A, Di Leo G2, Banga PV3,et al.Multidetector CT angiography of the Circle of Willis: association of its variants with carotid artery disease and brain ischemia[J].Eur Radiol,2019 ,29(1):46-56. [23]Banga PV, Varga A, Csobay-Novák C, et al. Incomplete circle of Willis is associated with a higher incidence of neurologic events during carotid eversion endarterectomy without shunting[J]. J Vasc Surg,2018,68(6): 1764-1771. [24]Lal BK, Beach KW, Sumner DS. Intracranial collateralization determines hemodynamic forces for carotid plaque disruption[J]. J Vasc Surg,2011,54(5): 1461-71. [25]Arteaga DF, Strother MK, Davis LT, et al. Planning-free cerebral blood flow territory mapping in patients with intracranial arterial stenosis[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2017,37(6): 1944-1958. .[26]Zhu G, Yuan Q, Yang J,et al.The role of the circle of Willis in internal carotid artery stenosis and anatomical variations: a computational study based on a patient-specific three-dimensional model[J].Biomed Eng Online, 2015,25(14):107.116. [27]Ren Y, Chen Q, Li ZY. A 3D numerical study of the collateral capacity of the Circle of Willis with anatomical variation in the posterior circulation[J]. Biomed Eng Online,2015,14 Suppl 1: S11.
Figures
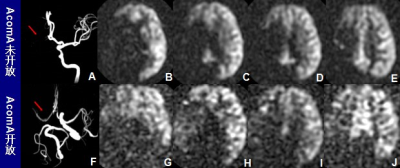
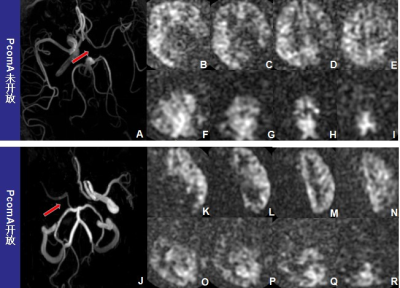
A-I: A patient with opening ACoA, but without PcoP(as indicated by a red arrow). B-E represent the compensation range of the unaffected-side ICA. F-I represent the compensation range of the VBA, and no obvious VBA compensation was seen in this patient. J-R : A patient without opening ACoA ,but with PcoP(as indicated by a red arrow).K-N represent the compensation range of the unaffected-side ICA, and no obvious compensation.O-R represent the compensation range of the VBA.