1626
Clipped cerebral aneurysm evaluation with gradient modulated PETRA, preliminary study1Department of Radiology, Nagasaki University Hospital, Nagasaki, Japan, 2Department of Radioisotope Medicine, Atomic Bomb Disease Institute, Nagasaki University, Nagasaki, Japan, 3Siemens Healthcare K.K., Tokyo, Japan, 4Department of Radiology, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, MN, United States
Synopsis
Gradient modulated pointwise encoding time reduction with radial acquisition sequence (GM-PETRA) is a new sequence, which can minimize metallic artifact caused by surgical clips. The GM-PETRA samples k-space more quickly by increasing the gradient amplitude after excitation while keeping a relatively low excitation bandwidth. GM-PETRA provides decrease the susceptibility artifact caused by a metallic implant such as surgical clip and can demonstrate the patency of parent artery adjacent to the surgical clip more clearly than conventional PETRA and TOF MRA.
INTRODUCTION
Noninvasive imaging follow-up is necessary for picking up of the recurrence or newly developed aneurysm after treatment. Time-of-flight (TOF) MRA depicts inflow in the arteries without requiring contrast media. However, TOF MRA after clipping of cerebral artery aneurysm remains difficult to demonstrate residual aneurysm neck or newly developed aneurysm adjacent to the clip because of a magnetic susceptibility artifact, which can obscure the neck remnant and adjacent structures as a result of signal loss. Newly developed ultrashort TE imaging (UTE) is known to decrease the susceptibility artifacts caused by metallic devices. Gradient modulated pointwise encoding time reduction with radial acquisition sequence (GM-PETRA) is a new sequence developed by Kobayashi N, et al.1, which can minimizes metallic artifact caused by surgical clips. In this study, we evaluate the visualization of cerebral arteries adjacent to surgical aneurysm clip with the GM-PETRA compared to conventional PETRA protocol and TOF MRA.METHODS
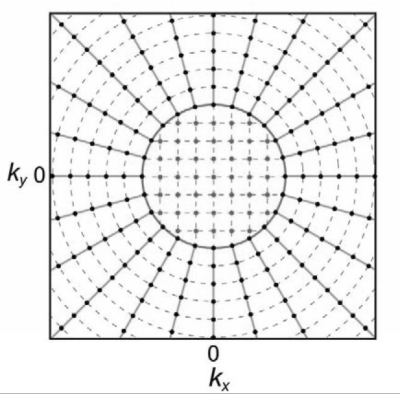
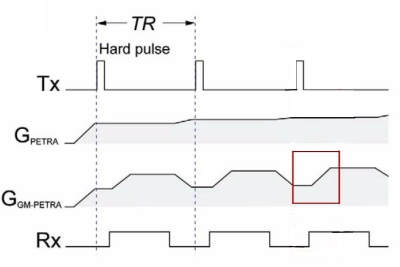
The PETRA sequence is a 3D radial projection based UTE technique2. k-space sampling in PETRA and GM-PETRA is a hybrid of 2 sampling strategies. The center region is sampled with single-point imaging and the peripheral region by radial readout (Fig.1). The GM-PETRA samples k-space more quickly by increasing the gradient amplitude after excitation while keeping a relatively low excitation bandwidth (Fig.2, read box). We used the GM-PETRA optimized for at 3 Tesla scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with a 20-channel head coil. The technique was validated with healthy volunteers (n=3) under a local IRB approved protocol. Conventional PETRA was acquired with the following protocol: FOV200 mm3, 80000 radial spokes; isotropic 0.8mm3; FA 6°; TR/TE 4/0.07 msec; BW 1860 Hz/pixel; total scan time 3.4 min. GM-PETRA was acquired with the following protocol: FOV 256 mm3, 20000 radial spokes; isotropic 0.8mm3; FA 6°; TR/TE 3.3/0.07 msec; BW 1860 Hz/pixel; total scan time 3.5 min. TOF MRA acquired with the following protocol: FOV 200 mm3, 0.5x0.6x0.5 mm3; FA 18°; TR/TE 21/3.6 msec total scan time 4.4 min.RESULTS
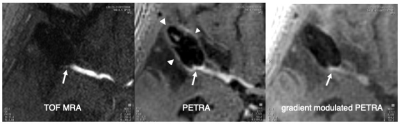
5 cases with clipped aneurysm were examined, and these scans and reconstructions were performed successfully. GM-PETRA was useful for visualizing the patency of parent artery adjacent to a surgical clip, and demonstrated the parent artery more clearly than conventional PETRA (Fig.3). Conventional PETRA showed marginal hyperintensity surrounding surgical clip, which overlapped the parent artery inflow signal, and which may mislead residual aneurysm neck. All TOF MRA were failed to demonstrate the parent artery adjacent to a surgical clip.DISCUSSION
Gradient modulation has been introduced in this GM-PETRA to increase readout bandwidth, which can reduce image-blurring artifacts resulting from T2* signal decay such as a surgical clips. GM-PETRA has some limitation; an increase acoustic noise, drop-off of inflow enhancement in distal portion of artery, and the image-blurring reduction accompanying the reduction of the signal to noise ratio.CONCLUSION
GM-PETRA provides decrease the susceptibility artifact caused by a metallic implant such as surgical clip. GM-PETRA can demonstrate the patency of parent artery adjacent to the surgical clip more clearly than conventional PETRA and 3D-TOF MRA.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1: Kobayashi N, Goerke U, Wang L, Ellermann J, Metzger GJ, Garwood M. Gradient-Modulated PETRA MRI. Tomography. 2015 Dec;1(2):85-90.
2: Grodzki DM, Jakob PM, Heismann B. Ultrashort echo time imaging using pointwise encoding time reduction with radial acquisition (PETRA). Magn Reson Med. 2012 Feb;67(2):510-8.
Figures