1566
Drumming training induces myelin remodelling in Huntington’s disease: a diffusion MRI and quantitative magnetization transfer study1Department of Psychology, Cardiff University Brain Research Imaging Centre, Cardiff, United Kingdom, 2Department of Neurosciences and Mental Health, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3Department of Biosciences, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom, 4Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Bristol, Bristol, United Kingdom
Synopsis
Huntington’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder leading to debilitating cognitive and motor symptoms. It has been proposed that impaired myelination contributes to HD pathogenesis. As well, evidence shows that myelin formation underlies the learning of new motor skills. Here we demonstrate that two months of drumming and rhythm exercises result in an increase in a proxy MRI measure of myelin in patients with early HD relative to healthy controls. This suggests that tailored behavioural stimulation has the potential to result in neural benefits in early HD that could be exploited for future therapeutics aiming to delay disease progression.
Introduction
Huntington’s disease (HD) is a genetic, neurodegenerative disorder leading to debilitating cognitive and motor symptoms. White matter (WM) impairment, due to changes in myelin-associated biological processes at the cellular and molecular level1,2,3,4, may play an important role in HD. Myelin sheaths wrapping axons regulate saltatory conduction and synaptic plasticity, and are hence critical for brain development and healthy brain function5. Currently, no disease modifying treatment exists for HD. However, environmental stimulation and behavioural interventions may have the potential to delay disease onset6. Notably, myelin plasticity has been shown to underpin the learning of new motor skills7,8.The present study investigated whether myelin plasticity and motor sequence learning could be triggered by two months of drumming training in patients with early HD. Moving beyond previously assessed diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)9 indices 10,11,12, which are unspecific measurements of WM microstructural properties13, we investigated training-related changes in the myelin-sensitive macromolecular proton fraction (MPF) from quantitative magnetization transfer (qMT)14 and the restricted signal fraction (Fr) from the Composite and Hindered and Restricted Model of Diffusion (CHARMED)15, a proxy of axonal density13. Fractional anisotropy (FA) and radial diffusivity (RD) from DTI9, were included for comparability with previous training studies10,11,12.
Methods
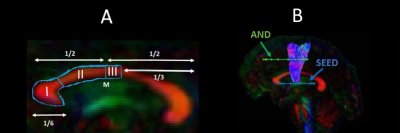
15 early HD patients and 13 age, sex, and education-matched healthy controls took part in the training. Participants trained for 15 min per day, 5 times per week, for 2 months (40 sessions in total)16. Improvements were assessed for easy, medium, and hard levels of task difficulty according to the Trinity College London marking criteria (2016). MRI data were acquired at baseline and post-training on a 3 Tesla General Electric HDx MRI system. The DTI and CHARMED models9,12 were fitted to the diffusion-weighted images. The Ramani’s pulsed MT approximation17 was fitted to the MT-weighted images. Training-related changes in MPF, Fr, FA and RD were studied in WM pathways known to be affected in HD, i.e., tracts between the putamen and the supplementary motor area bilaterally (SMA-Putamen), and within three segments of the corpus callosum (CCI, CCII and CCIII)18 (Fig.1). Tracts were reconstructed using the damped Richardson-Lucy algorithm19 in ExploreDTI20. Median measures of FA, RD, Fr and MPF were derived for each of the reconstructed tracts. Post-training percentage change scores in each measure were calculated in each tract. The dimensionality of the MPF data was reduced with principal component analysis (PCA) as these were highly correlated between tracts21, and group differences in MPF component scores of change were analysed. Training-associated changes in FA, Fr and RD were investigated with permutation analyses separately for each tract as measures did not correlate between tracts. Behavioural training effects on drumming performance were analysed with repeated measure analysis of variance (ANOVA). Finally, tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS)22 was used to investigate baseline differences in MPF between HD subjects and controls across the whole brain, in an unbiased way.Results
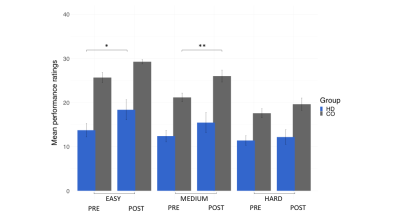
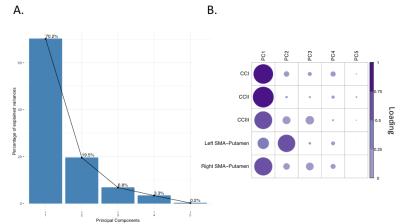
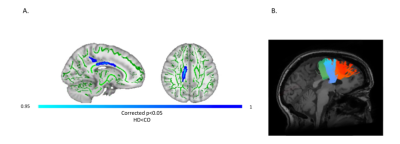
Patients and controls significantly improved in their drumming performance. Patients improved their drumming performance significantly for the easy pattern [t(10) = 2.7, p = 0.02; 95% CI of mean difference: 1.5 – 7.8] and controls for the medium pattern [t(7) = 3.8, p = 0.01; 95% CI of mean difference: 2.8 – 8.5] (Fig. 2). PCA of change scores in MPF revealed one single component explaining 70.2% of the variance. This component presented high loadings from all the tracts investigated (Fig. 3). A significant group difference was present for the MPF component, suggesting that HD patients presented higher changes in MPF in response to training, as compared to controls [t(14) = -1.743, n = 17, p = 0.03]. 5% FDR corrected post-hoc comparisons revealed that the mean difference in MPF change scores was significantly different between the two groups for CCII [ t(14) = -20.72, p=0.04], CCIII [t(14) = -25.87, p=0.04], and the right SMA-putamen pathway [t(14) = -25.48, p=0.04]. No significant changes on any of the other microstructural measures were detected. TBBS analysis revealed significantly lower baseline MPF in HD patients compared to controls, in areas which mostly overlapped with the tracts showing remodelling post-training.Conclusion
These findings suggest that our training intervention influenced motor behaviour in both patients and controls. Furthermore, they show that the drumming training led to a greater change in MPF in HD patients as compared to controls. Histology evidence demonstrates that MPF is highly sensitive to the myelin content of WM22, suggesting that this measure might be a sensitive in vivo proxy measure of myelin plasticity. Our results support the notion that myelin plasticity can be triggered in HD with specifically tailored training programs.Acknowledgements
This research was funded by a Wellcome Trust Institutional Strategic Support Fund Award (ref: 506408) to Claudia Metzler-Baddeley. We would like to thank Candace Ferman and Louise Gethin for collating the patients’ clinical details and Jilu Mole for assistance with data analysis. The authors declare no competing financial interest.References
1. Bartzokis, G., Lu, P. H., Tishler, T. A., Fong, S. M., Oluwadara, B., Finn, J. P., … Perlman, S. (2007). Myelin breakdown and iron changes in Huntington’s disease: Pathogenesis and treatment implications. Neurochemical Research, 32(10), 1655–1664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9352-7
2. Huang, B., Wei, W., Wang, G., Gaertig, M. A., Feng, Y., Wang, W., … Li, S. (2015). Mutant huntingtin downregulates myelin regulatory factor-mediated myelin gene expression and affects mature oligodendrocytes. Neuron, 85(6), 1212–1226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.02.026
3. Jin, J., Peng, Q., Hou, Z., Jiang, M., Wang, X., Langseth, A. J., … Duan, W. (2015). Early white matter abnormalities, progressive brain pathology and motor deficits in a novel knock-in mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Human Molecular Genetics, 24(9), 2508–2527. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddv016
4. Teo, R. T. Y., Hong, X., Yu-Taeger, L., Huang, Y., Tan, L. J., Xie, Y., … Pouladi, M. A. (2016). Structural and molecular myelination deficits occur prior to neuronal loss in the YAC128 and BACHD models of Huntington disease. Human Molecular Genetics, 25(13), 2621–2632. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddw122
5. Martenson, R. E. (1992). Myelin. CRC Press.
6. Yhnell, E., Lelos, M. J., Dunnett, S. B., & Brooks, S. P. (2016). Cognitive training modifies disease symptoms in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Experimental Neurology, 282, 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.05.008
7. McKenzie, I. A., Ohayon, D., Li, H., de Faria, J. P., Emery, B., Tohyama, K., & Richardson, W. D. (2014). Motor skill learning requires active central myelination. Science (New York, N.Y.), 346(6207), 318–322. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254960
8. Sampaio-Baptista, C., Khrapitchev, A. A., Foxley, S., Schlagheck, T., Scholz, J., Jbabdi, S., … Johansen-Berg, H. (2013). Motor Skill Learning Induces Changes in White Matter Microstructure and Myelination. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(50), 19499–19503. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3048-13.2013
9. Pierpaoli, C., & Basser, P. J. (1996). Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 36(6), 893–906.
10. Lövdén, M., Bodammer, N. C., Kühn, S., Kaufmann, J., Schütze, H., Tempelmann, C., … Lindenberger, U. (2010). Experience-dependent plasticity of white-matter microstructure extends into old age. Neuropsychologia, 48(13), 3878–3883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.08.02611.
11. Scholz, J., Klein, M. C., Behrens, T. E. J., & Johansen-Berg, H. (2009). Training induces changes in white matter architecture. Nature Neuroscience, 12(11), 1370-1371.
12. Zatorre, R. J., Fields, R. D., & Johansen-Berg, H. (2012). Plasticity in gray and white: Neuroimaging changes in brain structure during learning. Nature Neuroscience, 15(4), 528-536.
13. De Santis, S., Drakesmith, M., Bells, S., Assaf, Y., & Jones, D. K. (2014). Why diffusion tensor MRI does well only some of the time: Variance and covariance of white matter tissue microstructure attributes in the living human brain. Neuroimage, 89(100), 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.12.003
14. Sled, J. G. (2018). Modelling and interpretation of magnetization transfer imaging in the brain. NeuroImage, 182, 128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.11.065
15. Assaf, Y., & Basser, P. J. (2005). Composite hindered and restricted model of diffusion (CHARMED) MR imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage, 27(1), 48–58.
16. Metzler-Baddeley, C., Cantera, J., Coulthard, E., Rosser, A., Jones, D. K., & Baddeley, R. J. (2014). Improved Executive Function and Callosal White Matter Microstructure after Rhythm Exercise in Huntington’s Disease. Journal of Huntington’s Disease, 3(3), 273–283. https://doi.org/10.3233/JHD-140113
17. Henkelman, R. M., Stanisz, G. J., & Graham, S. J. (n.d.). Magnetization transfer in MRI: A review. NMR in Biomedicine, 14(2), 57–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.683
18. Hofer, S., & Frahm, J. (2006). Topography of the human corpus callosum revisited—Comprehensive fiber tractography using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage, 32(3), 989–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.05.044
19. Dell’acqua, F., Scifo, P., Rizzo, G., Catani, M., Simmons, A., Scotti, G., & Fazio, F. (2010). A modified damped Richardson-Lucy algorithm to reduce isotropic background effects in spherical deconvolution. NeuroImage, 49(2), 1446–1458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.033
20. Leemans, A, Jeurissen, B., Sijbers, J., & Jones, D. K. (n.d.). ExploreDTI: a graphical toolbox for processing, analyzing, and visualizing diffusion MR data. 1.
21. Penke, L., Maniega, S. M., Murray, C., Gow, A. J., Hernández, M. C. V., Clayden, J. D., … Deary, I. J. (2010). A General Factor of Brain White Matter Integrity Predicts Information Processing Speed in Healthy Older People. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(22), 7569–7574. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1553-10.2010
22. Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Rueckert, D., Nichols, T. E., Mackay, C. E., … Behrens, T. E. J. (2006). Tract-based spatial statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage, 31(4), 1487–1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.02.024
23. Ou, X., Sun, S.-W., Liang, H.-F., Song, S.-K., & Gochberg, D. F. (2009). The MT pool size ratio and the DTI radial diffusivity may reflect the myelination in shiverer and control mice. NMR in Biomedicine, 22(5), 480–487. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1358
Figures