1491
Greater BBB permeability change in APOE4 carrier in cognitively normal and mild cognitive impaired subjects: a new imaging phenotype for APOE4
Won-Jin Moon1, Ilheon Ha1, Changmok Lim1, Yaehoon Kim1, Yeolsil Moon2, and Seol-Heui Han2
1Radiology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2Neurology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea
1Radiology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2Neurology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Synopsis
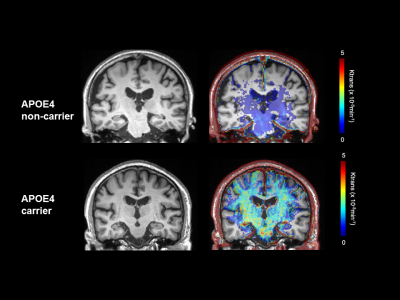
In normal and cogntively impaired subjects, BBB permeability of hippocampus is increased in APOE4 carrier group than in APOE4 non-carrier group. After adjusting for education years, and medial temporal lobar atrophy, the only valuable predicting factor for predicting cognitive function was BBB permeability of hippocampus. Our study indicates that BBB permeability imaging can be a distinct imaging phenotype of APOE4 mutation as well as an early imaging marker for clinical decline in cognitive impaired subjects.
ABSTRACT
PURPOSE:The disruption of BBB integrity, which is modulated by APOE4 mutation, is implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer Disease.The purpose of this study is to test if BBB permeability from DCE permeability imaging differ by APOE4 in subjects with normal cognition (NC) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
METHOD and MATERIALS:
In this prospective study, 106 consecutive particpants were enrolled between June 2018-May 2019. Out of them, we selected 33 age-matched CN subjects and 33 MCI subjects using age-matching procedure with MedCalc for the analysis. All participants underwent 3T brain MRI including 3D MPRAGE, 3D FLAIR, and DCE-T1WI with gadobutrol and 10 min acquisition time. We processed the DCE data using Nordic ICE software to generate the permeability maps. Concentration of the contrast in tissue was calculated by using relative signal chane and T1 mapping. Vascular input function was obtained from superior sagittal sinus by semiautomatic method in Nordic ICE. For calculating the tissue permeability, we used Patlak model to generate the permeability parmater, Ktrans. Region-of interest-analysis was performed on the map to compare the values of the hippocampi. Student t-test and chi-square test was performed for numerical and categorical variables, respectively. the effects of Ktrans on clinical cognitive function were evaluated using multivariate linear regression analysis.
RESULTS:
Between age-matched CN and MCI groups, there was no significant difference in vascular risk factors and the permeability (Ktrans) in the hippocampi. However, medial temporal lobar atrophy tended to be more prominent in MCI compared with CN subjects (p=0.053)In a subgroup analysis of subjects with known APOE4 status (n=34), APOE4 carrier (n=17) and non-carrier (n=17) did not differ in MMSE score, vascular risk factors, Fazekas scale for white matter hyperintensity, number of lacunes and microbleeds. The Ktrans of hippocampus was significantly higher in APOE4 carrier group than in APOE4 non-carrier group (Ktrans = .748±.476 x10-3/min versus Ktrans = .425±.342 x10-3/min)(p=0.034). After adjusting for education years, and medial temporal lobar atrophy, the only valuable predicting factor for predicting cognitive function (CDR-SB) was BBB permeability of hippocampus (beta = 0.698 [95% CI, 0.063-1.333], p=0.033).
CONCLUSION:
BBB permeability of hippocampus is increased in APOE4 carrier subjects than in APOE4 non-carrier subjects. Our study indicates that BBB permeability imaging can be a distinct imaging phenotype of APOE4 mutation in cognitive impaired subjects and can serve an early imaging marker for representing the underlying cause of cognitive decline in AD.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP)(no. 2017R1A2B4010634) and a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number HI18C1038).References
- Montagne A, Barnes SR, Sweeney MD et al. Neuron. 2015 Jan 21;85(2):296-302
- Van de Haar, Burgmans S, Jansen JF et al. Radiology. 2016 Nov;281(2):527-535
- Sweeney MD, Sagare AP, Zlokovic BV. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018 Mar;14(3):133-150.
- Yamazaki Y, Zhao N, Caulfield TR, Liu CC, Bu G. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019 Sep;15(9):501-518