1459
Cognitive Status in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping
Yangyingqiu Liu1, Junyi Dong1, Yanwei Miao1, Ailian Liu1, Qingwei Song1, and Lizhi Xie2
1Department of Radiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2GE healthcare, Beijing, China
1Department of Radiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2GE healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Blood oxygen level of the cerebral vein is quantitatively assessed by magnetic sensitivity value (MSV)using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM), and its’correlation to cognitive scores is also analyzed in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD).The results show that increased MSV value of cerebral vein in AD patients may affect cognitive scores.
Purpose
To quantitatively asses the blood oxygen levels of the cerebral vein using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM), and to analyze the correlation between magnetic sensitivity value (MSV) and cognitive scores in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD).Materials and Methods
Fifty-nine patients (21 males, 38 females) with clinically confirmed AD (AD group) and 22 control subjects (12 males, 10 females; CON group) were enrolled. Ethical approval and consent forms were prior to this study. All patients underwent Mini-mental State Examination, Montreal Cognitive Assessment, Clock Drawing Task and Activity of Daily Living Scale test, as well as MR exam including routine sequences and enhanced gradient echo T2 star weighted angiography (ESWAN).Magnetic sensitivity value (MSV) of bilateral cerebral vein was obtained using signal processing in nuclear magnetic resonance (SPIN) software(MR Innovations Inc., Detroit, MI, USA, Ver:1.4.5). The region of interest(ROI) were manually drawn along the boundary of the full length of the vein at the maximum slice that clearly displayed the vein. Three consecutive slices were then measured at the same location and averaged. Data analysis was performed using the statistical package for social science (SPSS) version 17.0. Kruskal-Wallis test was used for comparison between groups. Pearson and Spearman correlation analysis was performed on the MSV of the AD group, and the MMSE score, the MoCA score, the ADL score and CDT score of the AD group; Pearson correlation analysis was performed between clinical and laboratory data of the AD group and MSV; Spearman correlation analysis was performed between the clinical and laboratory data in the AD group and cognitive scores. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results
The placement of ROIs on the obtained QSM maps are illustrated in Figure 1.The increased MSV in cerebral vein was present in AD group compared to in CON group, and significant differences were observed for bilateral thalamus veins(TV)(pL=0.011, pR=0.014), bilateral dentate nucleus veins(DNV)(pL=0.011, pR=0.029), left basal veins(BV)( p=0.018)and left internal cerebral veins(ICV)(p=0.035)(Figure 2). The correlation analysis results were shown in heat maps in Figure 3 and 4. The MSV of bilateral TV(rL=-0.524, pL=0.000; rR=-0.406, pR=0.002), bilateral ICV(rL=-0.387, pL=0.003; rR=-0.313, pR=0.017) and bilateral DNV(rL=-0.450, pL=0.000; rR=-0.454, pR=0.000) had significant negative correlation with Mini-mental State Examination score(MMSE); the MSV of bilateral TV(rL=-0.455, pL=0.000; rR=-0.380, pR=0.003) and bilateral DNV(rL=-0.517, pL=0.000; rR=-0.464, pR=0.000) had a significant negative correlation with Montreal Cognitive Assessment scores(MoCA); a significant negative correlation between the MSV of bilateral TV(rL=-0.526, pL=0.000; rR=-0.505, pR=0.001), bilateral DNV(rL=-0.398, pL=0.002; rR=-0.281, pR=0.031), right septal veins(SV)(rR=-0.343, pR=0.008)and the Clock Drawing Task score(CDT); the MSV of bilateral TV(rL=-0.588, pL=0.000; rR=-0.491, pR=0.000), bilateral SV(rL=-0.373, pL=0.005; rR=-0.319, pR=0.018) and left BV(r=-0.287, p=0.034) had a significant negative correlation with Activity of Daily Living Scale score(ADL)(Figure 3). The MSV of left DNV(r=0.375, p=0.013) was positively correlated with the course of the disease, while the MSV of right SV(r=0.285, p=0.030)was positively correlated with total cholesterol; the MSV of right DNV(r=0.262, p=0.047) was positively correlated with triglyceride content, and the MSV of left ICV(r=-0.266, p=0.046) was inversely correlated with high-density lipoprotein content(Figure 4).Discussion and Conclusion
The level of QSM is dependent on the amount and concentration of deoxyhemoglobin in tissues and the diameter of blood vessels. Fan et al[1]reported that QSM may reflect the oxygen levels of human cerebral veins, and provide information on oxygen metabolism, the difference of MSV is inversely proportional to the oxygen level of blood, i.e. the higher the vein oxygen, greater the difference of MSV. In this study, it was found that the oxygen level of bilateral cerebral veins in AD group was generally lower than that in CON group.In addition, the significant correlation between MSV of cerebral vein and cognitive score (MMSE,MoCA, CDT, ADL)were observed, and indicated lower venous oxygen level may worse cognitive levelin AD patients.To conclude, increased MSV value measured by QSM in cerebral vein may affect cognitive scores in AD patients.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Fan A, Bilgic B, Gagnon L, et al. Quantitative oxygenation venography from MRI phase[J]. MagnReson Med, 2014, 72(1): 149-159.
Figures
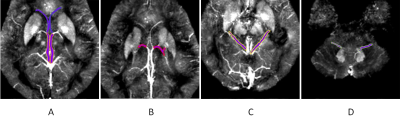
Fig.1 ROI selection of cerebral vein. (A)The SV and ICV are shown front and back. (B)Showing the TV. (C) Showing the BV. (D)Showing the DNV.
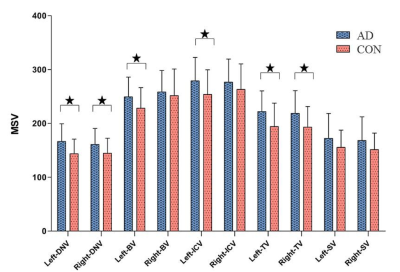
Fig.2 Comparison of cerebral vein MSV between AD group
and CON group. ★P < 0.05.
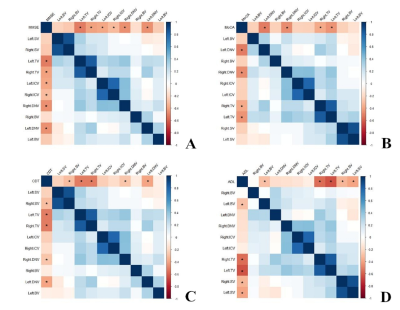
Fig.3 Hot
maps showing the correlation analysis between MSV of cerebral veins and MMSE
score (A), MoCA score (B), CDT score (C) and ADL score (D) in
AD group, respectively. *Significant correlation.
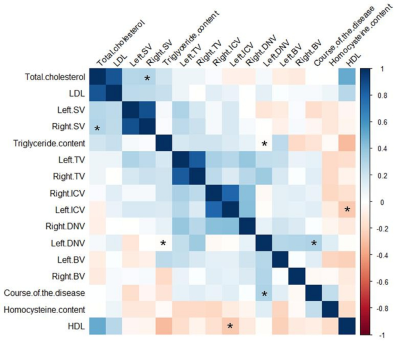
Fig.4 The hot
maps showing the correlation analysis between MSV of cerebral veins and
clinical, laboratory data in AD group.*significant
correlation.