1241
Functional connectivity is associated with radiotherapy-induced vascular injury and cognitive impairment in young brain tumor survivors1Radiology & Biomedical Imaging, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States, 2Department of Pediatrics, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States
Synopsis
While radiation therapy plays an essential role in the management of brain tumor patients, exposure to radiation has been known to lead to declines in neurocognitive performance and vascular injury. As there remains a need for a reliable marker and predictor of patient outcome, this study explores the usefulness of functional connectivity measurements derived from 7T rsfMRI. We found that temporal properties, specifically low-frequency signals of some large-scale brain networks,are associated with more severe cognitive impairment and vascular injury, highlighting the potential benefit of using rsfMRI for treatment planningand prediction of patient outcome after RT.
Introduction
While radiation therapy (RT) plays an essential role in the clinical management of brain tumor patients, exposure to radiation has been known to lead to declines in neurocognitive performance and vascular injury in the form of cerebral microbleeds (CMBs).1,2Although recent evidence from our group suggests that RT-induced CMBs are cross-sectionally and longitudinally associated with performance on specific tasks representing certain cognitive domains (e.g. verbal memory, attention)3,4, the relationship between CMBs and cognitionstill remains largely unexplored. Resting-state functional MRI (rsfMRI) – a technique which infers brain connections through spatiotemporal correlation of spontaneous and synchronous blood oxygen metabolism during rest – can be used to resolve large-scale brain network topology5and ultimately the brain areas and pathways through which many cognitive processes are mediated. As rsfMRI measurements have been able to predict and explain the cognitive impairments experienced by various neurological disease populations6-8, we hypothesized that the strength of rsfMRI-derived functional connections would differ across patients according treatment factors and long-term outcome measures. Thus, this cross-sectional 7T fMRI study explores the relationship between functional connectivity, CMB burden, cognitive performance, age during RT, and treatment strategy (i.e. total brain volume irradiated).Methods
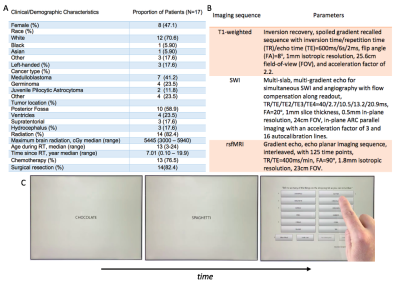
Seventeen pediatric and young adult brain tumor survivors (median age 19; range 13-25) underwent 7T MRI and cognitive assessment. The cohort included 8 patients treated with whole-brain RT, 6 patients treated with focal RT, and 3 non-irradiated control patients with non-supratentorial brain tumors. Patient demographics are listed in Figure 1A. All imaging was performed on a 7T GE scanner with a 32 channel receive head coil to effectively improvesensitivity for CMBs, gray and white matter delineation and to improve estimates of functional connections. Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI), T1-weighted anatomical and rsfMRI time series data were acquired using the sequence parameters listed in Figure 1B. Domain-specific cognitive performance was evaluated using a battery of computerized cognitive tests (Cogstate, Inc.; Newhaven, CT) chosen to elucidate impairment in specific cognitive domains (Figure 1C). Raw scores were converted to z-scores using mean performance scores of healthy control subjects from the Cogstate database. CMBs were detected from SWI images using an in-house semi-automated detection and fully-automated segmentation algorithm.9,10The CONN software11and AFNI toolbox12were used for data preprocessing, group independent component analysis (ICA) and second-level statistical analyses with covariate modelling.Results
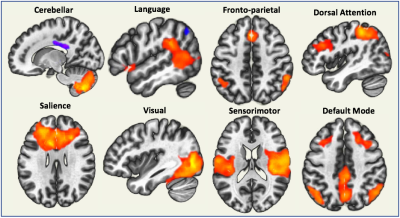
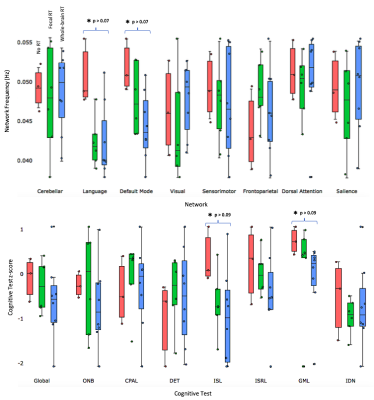
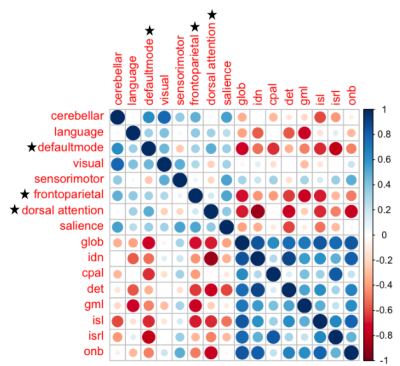
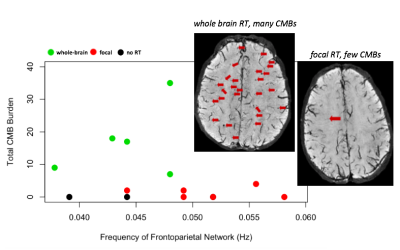
Spatial and temporal properties of eight distinct brain networks were isolated in the group ICA including: the default mode, sensorimotor, visual, salience, dorsal attention, frontoparietal, language, and cerebellar networks (Figure 2). A Kruskal-Wallis test revealed a trend of group differences in the frequency of the language (p < 0.07) and default mode networks (p < 0.07) according to whether patients received a whole-brain or focal RT regimen or no RT (Figure 3). Specifically, patients who received whole-brain RT had the lowest rsfMRI signal frequencies within these networks. Two cognitive tests evaluating verbal memory and executive function also demonstrated significant group differences (both p < 0.09). Frequencies associated with the default mode, frontoparietal, and dorsal attention networks showed the strongest and greatest number of correlations with cognitive test scores (Figure 4). Temporal characteristics of the frontoparietal network were trending towards being associated with total CMB burden amongst the different treatment groups (Figure 5; p < 0.06). When age during RT and time elapsed since RT were included as covariates, two additional ICA components involving brain areas associated with the default mode and sensorimotor networks were moderately associated with CMBs (p < 0.08 andp < 0.09 respectively). Contrasting this was a lack of association between cognitive test scores and CMB burden, with and without covariate modelling.Discussion & Conclusions
This work demonstrates that temporal properties of large-scale rsfMRI brain networks reflect thatthe severity of long-term side effects of RT. Specifically, we found that lower frequency rsfMRI signals in certain spatial networks were a strong indicator of greater cognitive impairment and vascular injury, and that rsfMRI can help elucidate the functional substrates of theglobal side effectsof RT. This finding is not surprising as low-frequency connectivity has been related to the impairments associated with other neurological disorders.13Ongoing work will evaluate how these temporal properties of rsfMRI networks serve as potential markers or predictors of outcome and evolve over time relative to traditional cognitive test scores. As the acquisition of rsfMRI data requires minimal patient cooperation, the technique remains a strong candidate for evaluation of young brain tumor patients.Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge support from the NIH NICHD (RO1HD079568).References
1. Greene-schloesser, D., & Robbins, M. E. (2012). Radiation-induced cognitive impairment- from bench to bedside. Neuro-Oncology, 37–44.
2. Greene-Schloesser, D., Robbins, M. E., Peiffer, A. M., Shaw, E. G., Wheeler, K. T., & Chan, M. D. (2012). Radiation-induced brain injury: A review. Frontiers in Oncology,2(July), 73.
3. Roddy, E., Sear, K., Felton, E., Tamrazi, B., Gauvain, K., Torkildson, J., Buono, B. D., Samuel, D., Haas-Kogan, D. A., Chen, J., Goldsby, R. E., Banerjee, A., Lupo, J. M., Molinaro, A. M., Fullerton, H. J., & Mueller, S. (2016). Presence of cerebral microbleeds is associated with worse executive function in pediatric brain tumor survivors. Neuro-Oncology, 18(11), 1548–1558.
4. Morrison, M., Mueller, S., Felton, E., Jakary, A., Stoller, S., Avadiappan, S., Yuan, J., Molinaro, A.M., Braunstein, S., Banerjee, A., Hess, C.P., Lupo, J.M. Rate of radiation-induced microbleed formation on 7T MRI relates to cognitive impairment in young brain tumor survivors. Submitted to Radiology Oct 2019.
5. van den Heuvel, M.P., Hulshoff Pol, H.E. (2010). Exploring the brain network: A review on resting-state fMRI functional connectivity. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 20(8):519-534.
6. Lin, Q., Rosenberg, M.D., Kwangsun, Y., Hsu, T.W., O’Connell, T.P., Chun, M.M. (2018). Resting-state functional connectivity predicts cognitive impairment related to Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 10:94, Epub.
7. Wolters, A.F., van de Weijer, S.C.F., Leentjens, A.F.G., Duits, A. A., Jacobs, H.I.L., Kuijf, M.L. (2019). Resting-state fMRI in Parkinson’s disease patients with cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord.62:16-27.
8. Kesler, S.R., Ogg, R., Reddick, W.E., Phillips, M., Scoggins, M., Glass, J.O., Cheung, Y.T., Pui, C.H., Robison, L.L., Hudson, M.M., Krull, K.R. (2018). Brain network connectivity and executive function in long-term survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Brain Connect.8(6):333-342.
9. Bian, W., Hess, C.P., Chang, S.M., Nelson, S.J., Lupo, J.M. (2013). Computer-aided detection of radiation-induced cerebral microbleeds on susceptibility-weighted MR images. NeuroImage Clin. 2:282–290.
10. Morrison, M.A., Payabvash, S., Chen, Y., Avadiappan, S., Shah, M., Zou, X., Hess, C.P., Lupo, J.M. (2018). A user-guided tool for semi-automated cerebral microbleed detection and volume segmentation: Evaluating vascular injury and data labelling for machine learning. NeuroImage Clin. 20:498–505.
11. Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Nieto-Castanon A. (2012). Conn:A functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connectivity.2(3):125-41.
12. Cox, R.W. (1996). AFNI: Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Computers and Biomedical Research. 29:162-173.
13. Dunkley, B. T., Da Costa, L., Bethune, A., Jetly, R., Pang, E. W., Taylor, M. J., Doesburg, S. M. (2015). Low-frequency connectivity is associated with mild traumatic brain injury. Neuroimage Clin. 7:611-21
Figures