1058
Correlation between APTw changes and regional cerebral oxygen metabolism in ischemic tissue of patients with subacute ischemic stroke1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
The relationship between APTw and regional cerebral oxygen metabolism levels in the ischemic area is unclear. This study attempts to investigate the mechanism of ischemic tissue pH changes and its influencing factors by measuring the APTw value of ischemic tissue, combined with ASL and SWI. We found that the phase differences of the veins in the infarct (Δφlesion) is positively correlated with APTWmax and APTWmax-min in the ischemic penumbra at PLD1.5.
Introduction
Early diagnosis and evaluation of brain function in patients with ischemic cerebral infarction are particularly important for clinicians to develop reasonable treatment options and assessment of prognosis. As a new type of magnetic resonance technology, APT imaging technology can detect changes in brain metabolites[1]. Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) has important diagnostic value for cerebral infarction. Some scholars believe that the OEF of local tissues can be estimated by measuring the phase difference between the vein and the surrounding tissue[2]. The balance between oxygen supply and oxygen uptake maintains the normal function of brain tissue, and oxygen supply and uptake disorders lead to ischemia and hypoxic infarction in local brain tissue[3]. The phase difference between the vein and the surrounding tissue is measured on the SWI phase diagram to reflect the OEF, which in turn reflects the cerebral oxygen metabolism of the ischemic tissue. This study combined with APT and SWI to study the changes of pH and oxygen metabolism in subacute ischemic tissue for the first time to explore the correlation between pH change and local brain metabolism.Materials and Methods
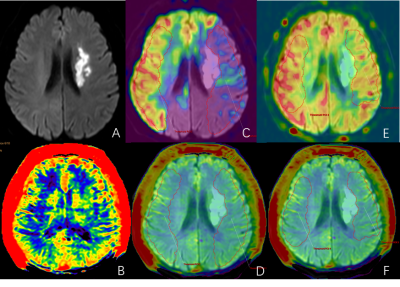
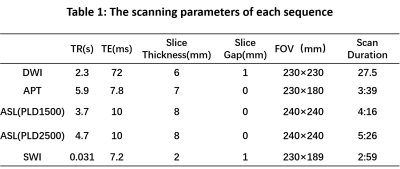
This study has been approved by the local institutional review board. A total of 40 patients (23 males, age 44-87 years) with clinically suspected ischemic stroke was prospectively collected and underwent routine sequence and APT imaging on a 3.0T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands). The scan parameters were described in Table 1. Excluding the scanning artifacts and interrupted scans due to poor patient cooperation, a total of 16 patients (9 males, age 44-86 years) with subacute ischemic stroke in the unilateral middle cerebral artery blood were analyzed. Image data was automatically transmitted to the vender-provided workstation (IntelliSpace Portal, Philips Healthcare), where the data post-processing was independently carried out by two observers. The DWI images were fused with APT and ASL images, then the infarction area and DWI-ASL mismatched area on DWI were delineated by 3D ROI. Based on the ROI, the APTw values of infarct area and ischemic penumbra (IP) were obtained. The SWI phase map was imported into the signal processing in neuroimaging (SPIN) for processing. Combined with DWI and SWImip images, the phase difference value of the vein around the lesion was measured on the phase map, and expressed by Δφ value (unit: spin). The measurement line was placed in the middle of the vein and perpendicular to the vein, and the phase difference of the venous blood vessels in the infarct zone and the contralateral zone wass measured, which was represented by Δφlesion and Δφnormal, respectively. Three veins were measured in each region, and finally the average value was represented. The intra-group correlation coefficient was used to test the consistency of the two observers' measured data. Pearson correlation test was used to analyze the correlation between APTw value and Δφ. For all tests, values of p <0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.Results
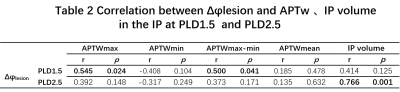
The data measured by the two observers are in good agreement (ICC > 0.75). The phase differences of the veins in the infarct (Δφlesion=426.15±139.59 (spin)) was significantly larger than the contralateral side (Δφnormal=334.15±68.75 (spin)) (t=3.448, p=0.003) (Fig. 1). The venous phase difference Δφlesion in the infarct side was positively correlated with APTWmax and APTWmax-min in the IPat PLD1.5 (p=0.024, r=0.545; p=0.041, r=0.500). There was no correlation between the venous phase difference Δφlesion and APTw in the IP atPLD2.5. However, a significant positive correlation between the venous phase difference Δφlesion with the IP volume was shown at PLD2.5 (p=0.001, r=0.766). (Table 2)Conclusions and discussion
This study found that compared with the normal side, the phase difference of the infarcted drainage vein increased, indicating that the insufficiency side oxygen saturation decreased and OEF increased. In addition, Δφlesion is positively correlated with IP APTWmax and APTWmax-min at PLD1.5. In the subacute infarction, hypoxia is further aggravated with the decrease of blood perfusion, and the APTWmax and APTWmax-min of IP increase, which may indicate that "false normalization" occurs in the subacute APTW or that the acidosis in the ischemic area gradually changes to alkali poisoning over time.The heterogeneity of the APTW signal in the tissue (ie APTWmax-min) can reflect the diversity of the pH value of the ischemic stroke tissue, indicating that the heterogeneous ischemic injury in the tissue becomes more severe with the further aggravation of hypoxia. In conclusion, the oxygen metabolism of ischemic tissue has a certain influence on the change of APTw.Acknowledgements
References
[1]Zhou J, Heo H Y, Knutsson L, et al. APT‐weighted MRI: Techniques, current neuro applications, and challenging issues[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2019.
[2] Przelaskowski A, Sklinda K, Bargieł P, et al. Improved early stroke detection: wavelet-based perception enhancement of computerized tomography exams.[J]. Computers in Biology & Medicine, 2007, 37(4):524-533.
[3] Przelaskowski A, Sklinda K, Bargieł P, et al. Improved early stroke detection: wavelet-based perception enhancement of computerized tomography exams.[J]. Computers in Biology & Medicine, 2007, 37(4):524-533.
Figures