0940
Significance of Perivascular Spaces in Acute Ischemic Stroke and its Predictions of Epileptogenesis1Department of Neurology, The Nanjing Brain Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China, 2Department of Neurology, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Melbourne, Australia, 3Department of Radiology, The Nanjing Brain Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Melbourne, China, 4Department of Neuroscience, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, 5Department of Neurology, Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, Australia, 6Department of Radiology, Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, Australia, 7Department of Radiology, The Nanjing Brain Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China, 8Department of Medicine, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
Synopsis
Around 10% of patients with stroke go on to develop epilepsy, however, imaging biomarkers for post-stroke epilepsy (PSE) are lacking. Perivascular spaces (PVS) are small interstitial fluid filled spaces lining the blood vessels which have a role in waste clearance in the brain. They have been found to be abnormal in epilepsy, and here we investigate whether they could serve as an early predictor of PSE. We found that the overall number and scores of enlarged PVSs were not associated with PSE, but the inter-hemispheric asymmetry was an independently associated biomarker.
Introduction
Stroke is a major cause of adult epilepsy accounting for almost 50% of newly diagnosed epilepsy beyond 60 years old1,2, but the search for simple, objective predictors of post-stroke epilepsy (PSE) remains ongoing3,4.Perivascular spaces (PVS) are interstitial fluid-filled cavities surrounding the small penetrating vessels5. Enlarged PVS (EPVS) can be clearly seen with higher resolution MRI6 and occur in most of patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS)7. Recently, EPVSs have been taken to indicate dysfunction of the brain drainage system, with potential pathological roles in small vessel disease, cognitive impairment, multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease8.
Higher presence of EPVS has been found in the hippocampi of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy9.Several case reports have also showed that EPVS may be associated with the onset of seizures10. Recent studies have found that a significantly asymmetric distribution of PVSs in the brain may be potential biomarker for epilepsy11 and post-traumatic seizures/epilepsy12. But the relationship between brain PVS characteristics and PSE remains uncertain. This study investigated whether brain PVS characteristics could predict epilepsy development after AIS.
Methods
156 AIS patients (96 male, mean age 67.46±11.65) presenting to the Nanjing Brain Hospital of Nanjing Medical University were included in the study and split into two groups:(1) PSE group (n=29) At least a single seizure 30 days after the stroke or ≥2 seizures at least 7 days after the stroke, during the follow-up period of over 1 year from stroke onset13.
(2) no-EP AIS group: (n=127) AIS patients without any seizures or epilepsy during the follow-up period.
T2-weighted MRI scans (resolution=1x1x6mm, TR/TE/FA=7411ms/106ms/600) were performed within 2 weeks after symptom onset of AIS using a 3T (Siemens Verio) MRI scanner.
EPVSs were defined as tubular-linear when parallel or round-ovoid dot-like structures when perpendicular to the imaging plane with a CSF-like signal intensity and a diameter of <3mm. MRI were reviewed manually by two trained raters blinded to clinical details. Total numbers of PVSs (S), in three locations: Basal Ganglia (BG), Centrum Semiovale (CS) and Midbrain (MB) were recorded in the axial slice. All relevant slices were reviewed, but the slice with the highest number of EPVSs was selected for counting. EPVS number in each region was summed to give total EPVS number $$$S_{T}=S_{BG}+S_{CS}+S_{MB}$$$. The number of EPVSs were converted into a EPVS score (0-4) according to14. Inter-hemispheric asymmetry in EPVS in each region was calculated11,12 as:
$$AI_{J} = \left|\frac{S_{JR} - S_{JL}}{S_{JR} + S_{JL}}\right|$$
with 0≤AI≤1, J=region, L/R=left/right
Since an unbalanced distribution of PVS at some level may be observed in healthy controls11,12, we used a threshold of AI≥0.2 to define a significantly high asymmetry in PVS distribution (AI-score).
Between group differences were measured in EPVS characteristics and the following clinical variables: age, sex, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), causes of AIS, treatment after stroke, stroke locations, laterality of stroke lesion, infarct numbers category. A Chi-square test was designed to analyse categorical variables (2*2) and Wilcoxon Rank sum test was used to analyse the ordinal variables.
A multiple logistic regression model was used to identify independent predictors of PSE, with presence of PSE as the dependent variable. The independent variables were PVS characteristics and clinical variables with univariate between-group difference of P<0.05.
Results
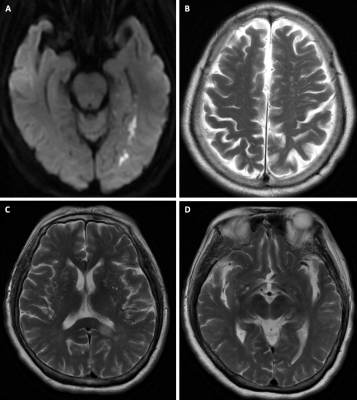
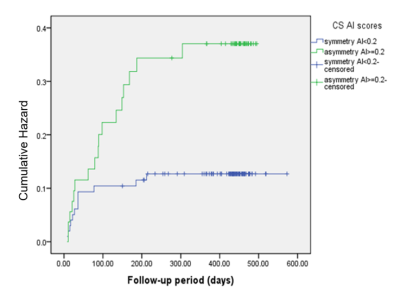
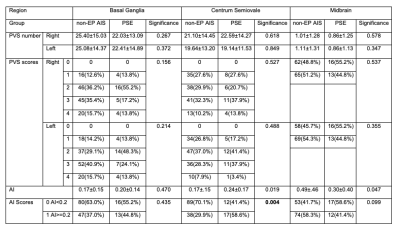
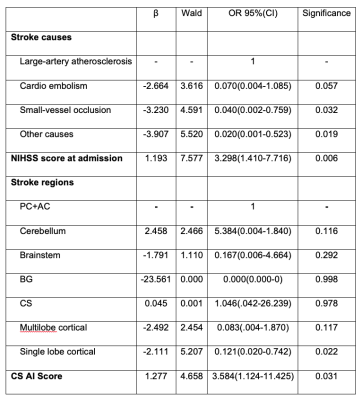
EPVS numbers and scores were not significantly different between PSE group and non-EP AIS group in any region (Table 1) or in the whole brain (p=0.180). A marked difference in AI-score in the CS region was found between PSE group and non-EP AIS group (P=0.004,Table 1). AI-score was not significantly different between groups in the other brain regions (P=0.435 in BG, P=0.099 in MB, Table 1), or in the whole brain (P=0.059). A typical example is shown in Figure 1.Four variables were significantly associated with PSE and were selected for the multivariate logistic regression model (Table 2): large-artery atherosclerosis of stroke causes, NIHSS at admission, stroke location and AI-score. In this model AI-score was a significant independent predictor of PSE (OR=3.584, P=0.031). Kaplan-Meier estimate of time to PSE for AI scores of CS is shown in Figure 2.
Discussion
Our study is the first to demonstrate that an asymmetric distribution of PVSs in CS is independently and significantly associated with PSE.Potential explanations for the link between PVS and PSE are: 1) Inflammatory reactions in the brain can increase the permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to proinflammatory molecules and cells and enhance neuronal excitability to trigger seizures attack15. Impaired PVS could allow leukocytes and antigen-presenting cells to penetrate the glia, then releasing proinflammatory molecules further degrading BBB structures16. 2) PVS are proposed to form part of a complex brain fluid drainage system to support interstitial fluid exchange and facilitate clearance of waste products from the brain. Impaired function of the PVSs may further lead to reduced blood flow, oxidative stress (free radical damage), hypoperfusion and hypoxia, which are linked to PSE17.
An early predictor for PSE will provide better evidence and choice for early anti-epileptic treatment. The EPVS AI score provides a novel imaging biomarker for the understanding of epileptogenesis after stroke.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Feyissa AM, Hasan TF, Meschia JF. Stroke-related epilepsy. Eur J Neurol, 2019, 26(1):18-e3.
[2] Yang H, Rajah G, Guo A, Wang Y, Wang Q. Pathogenesis of epileptic seizures and epilepsy after stroke. Neurol Res, 2018, 40(6):426-432.
[3] Haapaniemi E, Strbian D, Rossi C, Putaala J, Sipi T, Mustanoja S, Sairanen T, Curtze S, Satopää J, Roivainen R, Kaste M. The CAVE score for predicting late seizures after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke, 2014, 45(7):1971-1976.
[4] Galovic M, Döhler N, Erdélyi-Canavese B, Felbecker A, Siebel P, Conrad J, Evers S, Winklehner M, von Oertzen TJ, Haring HP, Serafini A. Prediction of late seizures after ischaemic stroke with a novel prognostic model (the SeLECT score): a multivariable prediction model development and validation study. Lancet Neurol, 2018, 17(2):143-152.
[5] Sun BL, Wang LH, Yang T, Sun JY, Mao LL, Yang MF, Yuan H, Colvin RA, Yang XY. Lymphatic drainage system of the brain: A novel target for intervention of neurological diseases. Prog in neurobiol, 2018, 163:118-143
[6] Cai K, Tain R, Das S, Damen FC, Sui Y, Valyi-Nagy T, Elliott MA, Zhou XJ. The feasibility of quantitative MRI of perivascular spaces at 7 T. J Neurosci Methods, 2015, 256:151-156.
[7] Liang Y, Chan YL, Deng M, Chen YK, Mok V, Wang F, Ungvari GS, Chu CW, Tang WK. Enlarged perivascular spaces in the centrum semiovale are associated with poststroke depression: A 3-month prospective study. Affect Disord, 2018, 228: 166-172.
[8] Benjamin P, Trippier S, Lawrence AJ, Lambert C, Zeestraten E, Williams OA, Patel B, Morris RG, Barrick TR, MacKinnon AD, Markus HS. Lacunar infarcts, but not perivascular spaces, are predictors of cognitive decline in cerebral small-vessel disease. Stroke, 2018, 49(3):586-593.
[9] Öztoprak İ, Sönmez M, Bolayır E, Öztoprak B. The Prevalence of Virchow-Robin Spaces in Hippocampus in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neurology Psychiatry and Brain Research, 2005, 12(1):5-8.
[10] Rawal S, Croul SE, Willinsky RA, Tymianski M, Krings T. Subcortical cystic lesions within the anterior superior temporal gyrus: a newly recognized characteristic location for dilated perivascular spaces. Am J Neuroradiol, 2014, 35(2):317-322.
[11] Feldman RE, Rutland JW, Fields MC, Marcuse LV, Pawha PS, Delman BN, Balchandani P. Quantification of perivascular spaces at 7 T: A potential MRI biomarker for epilepsy. Seizure, 2018, 54:11-8.
[12] Duncan D, Barisano G, Cabeen R, Sepehrband F, Garner R, Braimah A, Vespa P, Pitkänen A, Law M, Toga AW. Analytic Tools for Post-traumatic Epileptogenesis Biomarker Search in Multimodal Dataset of an Animal Model and Human Patients. Front Neuroinform, 2018, 12:86.
[13] Fisher RS, Acevedo C, Arzimanoglou A, Bogacz A, Cross JH, Elger CE, Engel Jr J, Forsgren L, French JA, Glynn M, Hesdorffer DC. ILAE official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia, 2014, 55(4):475-82.
[14] Potter GM, Chappell FM, Morris Z, Wardlaw JM. Cerebral perivascular spaces visible on magnetic resonance imaging: development of a qualitative rating scale and its observer reliability. Cerebrovasc Dis, 2015;39(3-4):224-231.
[15] Rana A, Musto AE. The role of inflammation in the development of epilepsy. J Neuroinflammation, 2018, 15(1):144.
[16] Owens T, Bechmann I, Engelhardt B. Perivascular spaces and the two steps to neuroinflammation. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 2008, 67(12):1113-21.
[17] Li Y, Li M, Yang L, Qin W, Yang S, Yuan J, Jiang T, Hu W. The relationship between blood-brain barrier permeability and enlarged perivascular spaces: a cross-sectional study. Clin Interv Aging, 2019, 14:871-878.
Figures