0922
The usefulness of diffusion tensor imaging in evaluating the neuroprotective effect of LITUS to moderate traumatic brain injury with rat model
Zheng Tao1, Du Juan1, Yuan Yi2, Wu Shuo1, Wang Zhanqiu1, Liu Defeng1, Shi Qinglei3, Wang Xiaohan1, and Liu Lanxiang1
1MRI, Qinhuangdao Municipal No. 1 Hospital, Qinhuangdao, China, 2Institute of Electrical Engineering, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, China, 3Siemens Healthcare, MR Scientific Marketing, Beijing, China
1MRI, Qinhuangdao Municipal No. 1 Hospital, Qinhuangdao, China, 2Institute of Electrical Engineering, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, China, 3Siemens Healthcare, MR Scientific Marketing, Beijing, China
Synopsis
In this study, we verified the feasibility of FA and MD values in evaluating the neuro therapeutic effect of LITUS with rat model. The neuro therapeutic effect of LITUS was attributed to promoting blood flow and the protein expression of BDNF.
Background and Purpose:
Parameters of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) can be used as biomarkers in reflecting the direction and degree of water molecules’ diffusion motion in tissues. In past literatures’ report, they played important roles in disease differential diagnosis, treatment effect evaluation and prediction. The low-intensity transcranial ultrasound stimulation (LITUS) has been proved possess a significant therapeutic effect for cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain injury (TBI). So, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the therapeutic effect of LITUS in moderate TBI with rat model via fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) values.Materials and Methods:
Forty-five male Sprague Dawley rats (pseudo-normal: 15, TBI: 15, LITUS treated: 15, mean age: 3 months; range, 1-4 months) were enrolled and underwent MR imaging on a MAGNETOM Verio 3T MR scanner (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). The images were acquired with a single-shot echo-planar sequence and the parameters were as follows: repetition time/echo time = 1,800/110 ms, field of view = 74 mm × 74 mm, slice thickness = 2 mm, voxel size = 1.5 mm × 1.0 mm × 2.0 mm, sensitivity encoding factor =2, nonlinear directions = 15, b-value = 0/1,000 s/mm2, averages = 9. Maps of FA and MD were reconstructed online automatically. Values of FA and MD were measured on a workstation named Leonardo 3682 (Siemens Healthcare Ltd.). To increase the accuracy in measuring, anatomical images like T2WI, T1WI of similar slices were referenced when drawing ROIs. The results were analyzed using a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) for repeated measures, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. A P < 0.05 was considered significant difference.Results:
At the beginning of the TBI rat model established, the FA value of the LITUS treated group is significantly higher than that of the control group (adjusted P=0.042) on the 1th day, but on 14th, 21th and 35th day, the FA values of the LITUS treated group is significantly lower than those of the TBI group (adjusted P=0.001, 0.006 and 0.017, respectively). At the end of the scanning time, the difference between the two groups didn’t demonstrated statistical significant (adjusted P=0.324). MD values of the LITUS treated group were significantly higher than that in the TBI group at early stage (adjusted P=0.016) but significantly lower than those of the TBI group at the following time points.Discussions:
As literature’s report and the experimental results we did past, reasons of the LITUS’s therapeutic effect for cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain injury (TBI) can be attributed to two mechanisms. One is that LITUS promotes blood flow in the event of TBI. As it is known, if the cerebral blood flow drops below 10–15 mL/100 g/min, the intracellular water volume increases and the water flows from the intercellular spaces into the cells to swell the latter and cause cytotoxicity. The other mechanism is that LITUS promotes the protein expression of BDNF, which can promote the division and differentiation of endothelial cells. Therefore, the effect of LITUS on blood flow and the protein expression of BDNF may be the reason of therapeutic effect. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a technique can display the connectivity of white matter fiber tracts and the pathological changes of gray matter. Lots of studies have revealed that the FA value relates with the degree of demyelination or injury and can reflect the integrity of neurons. MD value can reflect the diffusion movement of water in tissues, and thus reflect the pathological changes of tissues.Conclusions:
The changes of FA and MD values derived from DTI can reflect the pathological changes of TBI in rat model. In clinical situations, they maybe can evaluate the therapeutic effect of LITUS in moderate TBI.Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(grant no.81871029)References
No reference found.Figures
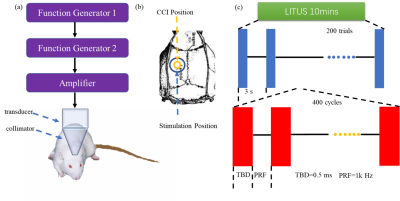
Figure
1: (A) LITUS
system, two connected function generators were used to generate pulsed signals.
The pulsed signal from the second generator was amplified by a linear power
amplifier and transmitted to an unfocused ultrasound transducer. The ultrasound
transducer was connected to the rat skin by a conical collimator with a
diameter of 10 mm that was filled with ultrasound coupling gel. (B) Stimulation
position and CCI position. (C) Time schedule of ultrasound stimulation and the
parameters of the ultrasound.
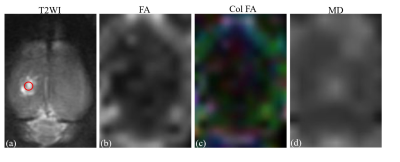
Figure
2: (A) T2-weighted
image. (B) fractional anisotropy map. (C) Color-coded map of the principle
eigenvector of diffusion matrix. D: mean diffusion map. ROI of injury area (red
circle in A) was chosen on coronal T2WI image with which the FA map and T2 WI map
co-registered.
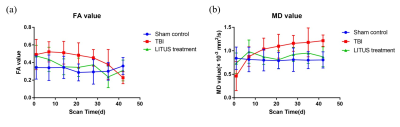
Figure
3: (A) Trends of
FA values in the injury cortex. (B) Trends of MD values in injury cortex.
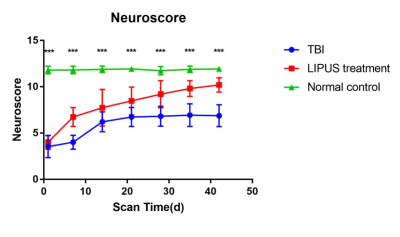
Figure 4: Trends of neuroscores of TBI, LITUS treatment and Sham Control groups.
Unpaired t-test, ***p<0.001. Mean±SD, n=15.
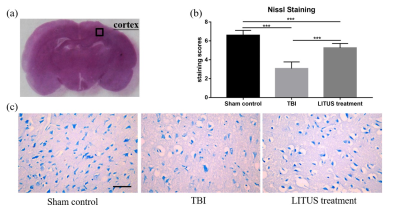
Figure
5: Histopathology in the ipsilateral cortex 42 days
after TBI. Representative images of cresyl violet stained neurons (A). The mean
staining scores of rats in the LITUS treatment group were all between 5 and 6.
The mean staining scores for the Sham Control group were 7, indicating the
structure of a normal nucleus in these cells (B). Nissl staining of rat brains of TBI, LITUS treatment
and Sham Control groups at 42 days after injury(C).