0822
T1 and T2 relaxation time in synthetic MRI for differentiating benign and malignant breast lesions
Shi yun SUN1, Zhuo lin Li1, Ying ying Ding1, Yi fan Liu1, Dong xue ZHANG1, Li sha NIE2, Ke XUE1, and Dian Ke DU1
1Radiology, Yunnan Cancer Hospital,The Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China, China
1Radiology, Yunnan Cancer Hospital,The Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China, China
Synopsis
It is reported that dynamic contrast imaging and T2 relaxation time can be used to differentiate benign and malignant breast lesions. However, few researches have investigated T1 and T2 relaxation time changes before and after contrast injection. But it's important for the diagnosis of breast diseases. Thus, the study aims to utilize the T1 and T2mapping in synthetic MR to differentiate benign and malignant lesions. Our results demonstrated that T1 and T2 mapping could constitute a new adjunct in the MRI diagnosis of breast diseases.
Introduction
With the change of lifestyle, the incidence of breast cancer is on the rise. Previous researches showed that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is more sensitive to the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases than mammography and ultrasonography [1]. Conventional MRI utilizes dynamic contrast imaging to differentiate benign and malignant breast lesions,and the use of T2 relaxation in differential diagnosis has been previously reported[2].However, few researches have investigated T1 and T2 relaxation time changes before and after contrast injection. And these studies always ignored the T1 relaxation time. Synthetic MRI is a novel imaging technique that may offer simultaneously acquired all the quantitative relaxation maps. In this work, the use of the T1 and T2 mapping in synthetic MR before and after contrast injection in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant cancer is investigated.Methods
This study was approved by the institutional review board, and written informed consent was obtained from all patients. 186 patients with breast lesions (age 40.15±12.65years, age range 19~79 years) were prospectively enrolled in this study and underwent both of synthetic MR (magnetic resonance image compilation, MAGiC) and pathological biopsy. All data were acquired on a 3T MRI system (Signa Pioneer, GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, USA). Routine scan were performed firstly and then the MAGIC. Both the scan sequences were performed before and after contrast injection. The scan parameters for synthetic MR were: TR = 4000 ms, TE1=19 and TE2=85.5 ms, slice thickness/gap = 5/0 mm, FOV = 36 cm, data matrix = 260*260, echo length = 10, bandwidth = 27.78 Hz. All the regions of interest (ROI) delineation were placed by two experienced radiologists. Firstly,we delineated the the solid lesions of the T1 and T2 quantitative maps avoiding the cystic,necrotic,and hemorrhagic areas(called as “Tlocal“).And then drawn the outline of the whole tumor(called as“Ttumor“).The mean relaxation values T1、T2、ΔT1、ΔT2(the difference before and after contrast injection)within the ROIs were measured. The “T“ and ”T+“ are used to represent the relaxation time before and after contrast injection respectively. All of the data were recorded as mean ± SD and then analyzed by Wilcoxon signed rank test. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis and the area under the curve (AUC) statistics were applied to evaluate diagnostic performance of MAGIC in benign and malignant cancer.Results
The study included 71 benign lesions (46 of fibroadenomas, 10 of inflammatory lesions, 9 of breast adenosis, 4 of intraductal papilloma, 2 of benign phyllodes), and 115 malignancy lesions(5 of intraductal carcinoma in situ, 10 of intraductal carcinoma in situ with invasive carcinoma, 95 of invasive ductal carcinoma, 2 of invasive lobular carcinoma, and 3 of mucinous adenocarcinoma). The T1local,T1tumor,ΔT1tumor,T2local,T2+local,ΔT2local,T2tumor,T2+tumor, and ΔT2tumor were all statistically significant differences between benign and the malignant lesions(Table 1). The area under the curve(AUC) of T2local was the largest (AUC=0.819, 95CI%: 0.747~0.891). The T2 relaxation time of the malignant lesions was significantly lower than the benign lesions(78.97±16.95 ms vs 111.79±37.15 ms,p<0.001) . Using T2 relaxation time of 90.56 ms as a cut-off between the benign and malignant, a sensitivity of 83.1% and a specificity of 80.6% were obtained.The positive predictive value and negative predictive value were 89.6% and 70.4%.The T1local,T1+local,ΔT1local,T1+tumor,ΔT1tumor and ΔT2tumor all had statistically significant differences between the subgroups of benign lesions (Table 2). However,only the T1local was statistically different between the benign(Table 3). Typical cases of benign and malignant lesions are shown in Figures 1 and 2.Discussion
Our study show that T2 relaxation time is an effective parameter to distinguish benign and malignant breast lesions, which is concordant with previous study[2-3]. Prolongation of the T2 relaxation time indicates tissue water content increasing[4]. Therefore, the higher degree of malignancy, which has the greater density of tumor cells and the less free water content in the the extracellular interstitium will make the T2 relaxation time shorter. However, different to previous studies, our study included the changes between T1 and T2 relaxation times before and after contrast scanning. Compared with benign tumors, malignant tumors have higher capillary network density, greater cell permeability and faster contrast agent outflowing. Therefore, the ΔT value can be used to predict the lesions. In our study, the ΔT1tumor,ΔT2local and ΔT2tumor all have statistically differences between benign and the malignant lesions. Generally speaking, the benign lesions show progressive enhancement and the contrast concentration reaches the peak in the delayed period. Rather, the enhancement pattern of malignant lesions is fast inflow-outflow, and the contrast concentration in the delayed lesions was lower.Therefor, we speculate that the the ΔT values of the malignant lesions are lower than those in the benign lesions in our study, which may be related to the MAGIC scanning in the delayed phase.Conclusion
T1 and T2 quantitative relaxation time offered by synthetic MR may be effective tools for diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions. Our study showed that T2local had the highest diagnostic efficiency. T2local of 90.56ms can be used as a cut-off between the benign and malignant with a sensitivity of 83.1% and a specificity of 80.6%.Acknowledgements
NO AcknowledgementsReferences
1.Bluemke DA, Gatsonis CA, Chen MH, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast prior to biopsy[J]. Jama, 2004, 292(22): 2735-2742. 2.Liu L, Yin B, Shek K, et al. Role of quantitative analysis of T2 relaxation time in differentiating benign from malignant breast lesions[J]. J Int Med Res, 2018, 46(5): 1928-1935. 3.Merchant TE, Thelissen GR, de Graaf PW, et al. Application of a mixed imaging sequence for MR imaging characterization of human breast disease[J]. Acta Radiol, 1993, 34(4): 356-361. 4.Bueno MJ, Mouron S, Quintela-Fandino M. Personalising and targeting antiangiogenic resistance: a complex and multifactorial approach[J]. Br J Cancer, 2017, 116(9): 1119-1125.Figures
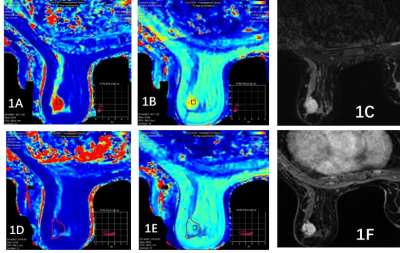
Figure
1: Female, 23y, fibroadenoma, A~F.
Image reconstruction with MAGiC, respectively T1 Mapping (A),T2
Mapping(B),T2WI(C),T1
Contrast Mapping (D),T2 Contrast Mapping(E),T1WI
Contrast(F).T1loacl=2976ms,T2loacl=154ms,T1tumor=2129ms,T2tumor=136ms,T1+
loacl=356ms,T2+
loacl=100ms,T1+
tumor=493ms,T2+
tumor=97ms.
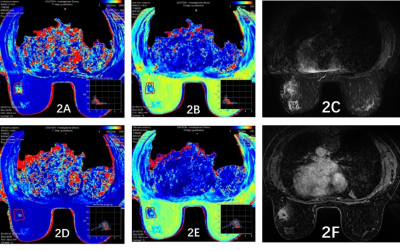
Figure 2: Female, 45y, Invasive ductal
carcinoma,A~F. Image reconstruction with MAGiC, respectively T1 Mapping (A),T2
Mapping(B),T2WI(C),T1
Contrast Mapping (D),T2 Contrast Mapping(E),T1WI
Contrast(F).T1loacl=820ms,T2loacl=88ms,T1tumor=967ms,T2tumor=103ms,T1+
loacl=437ms,T2+ loacl=66ms,T1+
tumor=480ms,T2+ tumor=87ms.
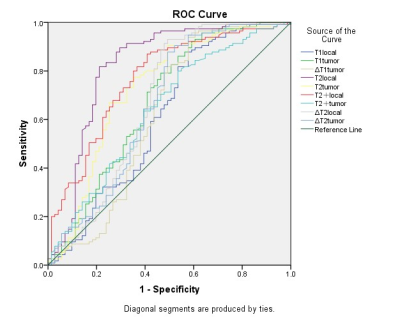
Figure 3: The T2local area
under the curve was 0.815. Using 91.75 ms as the cut-off between benign and malignant
breast lesions, a sensitivity of 90.5% and a specificity of 67.6% was obtained.
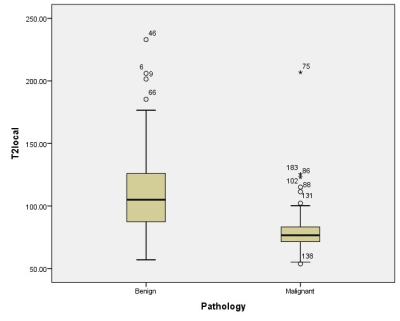
Figure
4: Box-whisker plot showing the T2local relaxation times of benign
and malignant breast lesions. The T2local relaxation times of the
benign lesions were longer than those of the malignant lesions. The black
horizontal lines are medians, the extremities of the boxes are the 25th and
75th