0705
Does Compliance with PIRADSv2 Technical Requirements Guarantee Image Quality or Adequacy in Prostate mpMRI Reads?1Molecular Imaging Program, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, MD, United States, 2National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, MD, United States
Synopsis
High quality MRIs are needed for prostate cancer screening and accurate targeting in MRI guided biopsies. Based on blind image quality assessment by image readers, compliance with the PIRADSv2 Minimum Technical Standards was determined to be neither necessary nor sufficient in ensuring quality in prostate T2 and DWI images.
Purpose:
Multi-parametric MRI imaging using the PIRADSv2 standard has consistently been shown to have a high predictive value in predicting the progression of prostate cancer, allowing physicians to triage patients and avoid biopsies in patients unlikely to have prostate cancer.1, 2 However, variable image quality among centers is potentially a significant threat for the widespread use of multiparametric MRI. Increasingly, as multiparametric MRI disseminates to a wider user-base, scans that are of limited diagnostic value are becoming more common. Low quality prostate MRIs can easily limit the ability to localize lesions, leading to low diagnostic yield in MRI guided biopsies and loss of a potential benefit over standard ultrasound guidance (TRUS). Image quality is notoriously difficult to assess but may be partly responsible for several recent large studies that showed little difference between MRI-guided and TRUS-guided biopsies.1, 3The PI-RADSv2 Minimum Technical Standards (MTS) were created with the goal of standardizing imaging protocols and reducing image quality variance.4 However, Esses et al. found that adherence to the guidelines varied widely across different institutions with some standards only achieving 17% adherence.5 It is reasonable to ask whether adherence to the standards solves the quality problem. Towards this end we measured, the impact each element of the PI-RADSv2 had on subjective image quality.
Methods:
62 prostate MRI examinations including T2W and DWI from 62 different institutions acquired within the last 12 months were included. After training on a different set of high-quality reference images, 6 readers ranked image quality on a 1-5 scale and categorized the images as either adequate or inadequate for use in prostate cancer detection. Beyond the image quality assessment, readers also assessed images according to subjective visual characteristics (bluriness and contrast) and for the presence and severity of perceived artifacts (noise, motion, geometric distortion, and aliasing/ghosting). PIRADSv2 technical requirements were synthesized into sets of 7 and 10 rules for T2W and DWI, respectively. Image compliance was assessed using DICOM metadata. Statistical analysis of survey results and image compliance was performed based on reader quality scoring (Kendall Rank Tau-b) and reader adequate scoring (Wilcoxon test for association) for T2 and DWI quality assessment.Results:
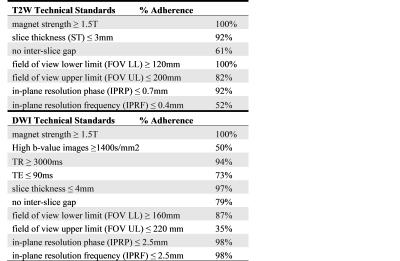
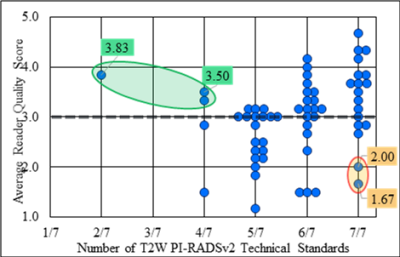
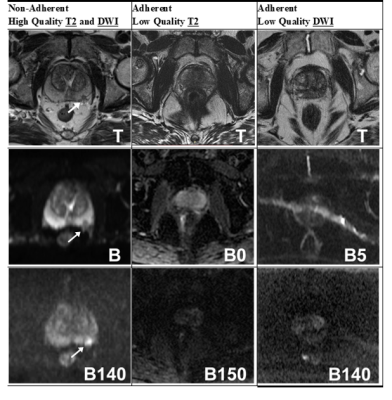
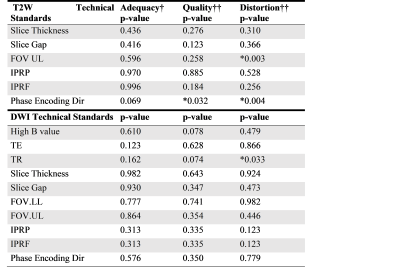
Adherence to PI-RADSv2 MTS varied widely. 18 studies met all 7 T2 standards and 6 studies met all 10 DWI standards. The T2W imaging standards with the lowest rates of adherence were in-plane resolution phase ≤ 0.4mm, and no interslice gap with adherence rates of 52% and 61% respectively. For DW imaging the standards with the lowest rates of adherence were field-of-view ≤ 220mm and high-b value ≥ 1400s/mm2 with adherence rates of 35% and 50% respectively (Figure 1).PI-RADSv2 MTS compliance was loosely correlated with image quality for T2 images (tau-b=0.22, p-value=0.01, Figure 2), however there are prominent examples of both adherent low quality images and non-adherent high quality images (Figure 3). While T2 imaging studies following all PI-RADSv2 T2 rules achieved a higher average quality score than partially noncompliant ones (median avg score = 3.58 for 7 out of 7 rules vs. median avg score = 3 for <7, p=0.012), the only significant statistically significant association for any of the individual PI-RADSv2 MTS T2 rules with image quality was for the upper limit constraint for the FOV (Figure 4). There was also a statistically significant impact on the phase encoding direction on quality (horizontal encoding resulted in higher average quality), however, this is currently not part of the PIRADSv2 MTS.
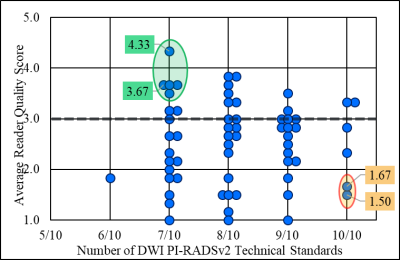
For DWI images, only 9% were scored as high quality by a majority of readers and only 4 studies out of 62 met all 10 DWI rules. For DWI not only was there no significant association between adherence to PI-RADSv2 technical standards and image quality but the tau-b degree of correlation between the two measures was -0.01 (SE 0.08) signifying a near complete absence of correlation (Figure 5).
For T2W images the perceived artifact with the greatest effect on image quality was noise. The tau-b correlation coefficient for noise and image quality was 0.58 (SE 0.09). For DWI both noise and distortion had particularly strong correlations with image quality with tau-b correlation coefficients of 0.61 (SE 0.09) and 0.54 (SE 0.09) respectively.
Conclusions:
Image quality in prostate multi-parametric MRI was highly variable. Adherence to PI-RADSv2 Minimum Technical Standards had a minimal effect in reducing this variability for T2 imaging sequences and no effect for DWI sequences. Noise and distortion emerged as the most obvious sources of problems in most prostate multi-parametric MRI. These results suggest that simply prescribing a set of sequence specifications is unlikely to solve the problem of image quality, as additional physiological factors that are situational and patient specific also exist.6-9 It may be difficult to devise new and better purely technical standards to account for these factors. However, there are other quality assurance methods that can be devised such as standards for patient exams or automatic assessment of image quality based on image statistics.10, 11Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] van der Leest, M., Cornel, E., Israel, B., Hendriks, R., Padhani, A. R., Hoogenboom, M., Zamecnik, P., Bakker, D., Setiasti, A. Y., Veltman, J., van den Hout, H., van der Lelij, H., van Oort, I., Klaver, S., Debruyne, F., Sedelaar, M., Hannink, G., Rovers, M., Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C., and Barentsz, J. O. (2019) Head-to-head Comparison of Transrectal Ultrasound-guided Prostate Biopsy Versus Multiparametric Prostate Resonance Imaging with Subsequent Magnetic Resonance-guided Biopsy in Biopsy-naive Men with Elevated Prostate-specific Antigen: A Large Prospective Multicenter Clinical Study, Eur Urol 75, 570-578.
[2] Liu, C., Liu, S. L., Wang, Z. X., Yu, K., Feng, C. X., Ke, Z., Wang, L., and Zeng, X. Y. (2018) Using the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System version 2 (PI-RIDS v2) to detect prostate cancer can prevent unnecessary biopsies and invasive treatment, Asian J Androl 20, 459-+.
[3] Rouviere, O., Puech, P., Renard-Penna, R., Claudon, M., Roy, C., Mege-Lechevallier, F., Decaussin-Petrucci, M., Dubreuil-Chambardel, M., Magaud, L., Remontet, L., Ruffion, A., Colombel, M., Crouzet, S., Schott, A. M., Lemaitre, L., Rabilloud, M., Grenier, N., and Investigators, M.-F. (2019) Use of prostate systematic and targeted biopsy on the basis of multiparametric MRI in biopsy-naive patients (MRI-FIRST): a prospective, multicentre, paired diagnostic study, Lancet Oncol 20, 100-109.
[4] Padhani, A. R., Weinreb, J., Rosenkrantz, A. B., Villeirs, G., Turkbey, B., and Barentsz, J. (2019) Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System Steering Committee: PI-RADS v2 Status Update and Future Directions, Eur Urol 75, 385-396.
[5] Esses, S. J., Taneja, S. S., and Rosenkrantz, A. B. (2018) Imaging Facilities' Adherence to PI-RADS v2 Minimum Technical Standards for the Performance of Prostate MRI, Acad Radiol 25, 188-195.
[6] Kabakus, I. M., Borofsky, S., Mertan, F. V., Greer, M., Daar, D., Wood, B. J., Pinto, P. A., Choyke, P. L., and Turkbey, B. (2016) Does Abstinence From Ejaculation Before Prostate MRI Improve Evaluation of the Seminal Vesicles?, Am J Roentgenol 207, 1205-1209.
[7] Medved, M., Sammet, S., Yousuf, A., and Oto, A. (2014) MR Imaging of the Prostate and Adjacent Anatomic Structures before, during, and after Ejaculation: Qualitative and Quantitative Evaluation, Radiology 271, 452-460.
[8] Rosenkrantz, A. B., Kopec, M., Kong, X. T., Melamed, J., Dakwar, G., Babb, J. S., and Taouli, B. (2010) Prostate Cancer vs. Post-Biopsy Hemorrhage: Diagnosis with T2-and Diffusion-Weighted Imaging, J Magn Reson Imaging 31, 1387-1394.
[9] Sharif-Afshar, A. R., Fen, T., Koopman, S., Nguyen, C., Li, Q. L., Shkolyar, E., Saouaf, R., and Kim, H. L. (2015) Impact of post prostate biopsy hemorrhage on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging, Can J Urol 22, 7698-7702.
[10] Kustner, T., Gatidis, S., Liebgott, A., Schwartz, M., Mauch, L., Martirosian, P., Schmidt, H., Schwenzer, N. F., Nikolaou, K., Bamberg, F., Yang, B., and Schick, F. (2018) A machine-learning framework for automatic reference-free quality assessment in MRI, Magn Reson Imaging 53, 134-147.
[11] Esses, S. J., Lu, X. G., Zhao, T. J., Shanbhogue, K., Dane, B., Bruno, M., and Chandarana, H. (2018) Automated image quality evaluation of T-2-weighted liver MRI utilizing deep learning architecture, J Magn Reson Imaging 47, 723-728.
Figures