0474
Multiplexed Measurement of Multiple Nuclei (M3N) for integrated multi-nuclei imaging and parametric mapping in 23Na and 1H MRI1Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia, 2Melbourne Brain Centre Imaging Unit, University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia, 3MR Research Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Pty Ltd, Melbourne, Australia, 4Department of Medicine & Radiology, University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia, 5Department of Radiology, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Parkville, Australia, 6MR Research Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Pty Ltd, Brisbane, Australia
Synopsis
X-nuclei imaging like sodium MRI offers complementary information to 1H-based imaging. However, its clinical translation is hampered by the significant increase in scan time required for the acquisition of an additional nuclei. Addressing this challenge, this work introduces Multiplexed Measurement of Multiple Nuclei (M3N) sequences and proposes MERINA-MP2RAGE, a multi-nuclei sequence, that embeds sodium MRI in a 1H-MP2RAGE acquisition. The developed sequence was implemented on a 7T MRI and tested in phantom and human in vivo experiments. Merging 1H-MP2RAGE and 23Na-MERINA reduces the total scan time by 40% compared to sequential acquisitions while maintaining uncompromised image quality.
Introduction
Despite its potential in diagnosis and treatment monitoring[1], x-nculei imaging like sodium (23Na) MRI still faces challenges with regard to clinical implementation. Providing complementary information to 1H-based imaging protocols, x-nuclei images are usually acquired as an additional measurement at the end of a scan session, leading to a significant increase in total scan time and associated costs, particularly in clinical environments.Tackling this scan time issue, this work proposes the Multiplexed Measurement of Multiple Nuclei (M3N) for a seamless integration of x-nuclei acquisitions in 1H-sequences and provides the example of MERINA-MP2RAGE, a fully integrated acquisition scheme acquiring sodium MRI in the idle imaging windows of a 1H-MP2RAGE[2] sequence.
The conceptual design and technical considerations of multi-nuclei acquisitions have been discussed previously[3-5]. MERINA-MP2RAGE builds up on this and integrates sodium measurements in a clinically relevant imaging sequence. Ultimately, its imaging principle of ‘scan one, get one free’ has the potential to support clinical translation.
Methods
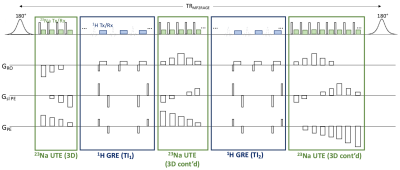
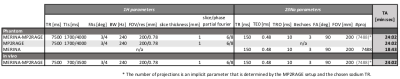
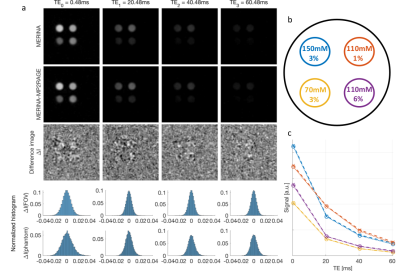
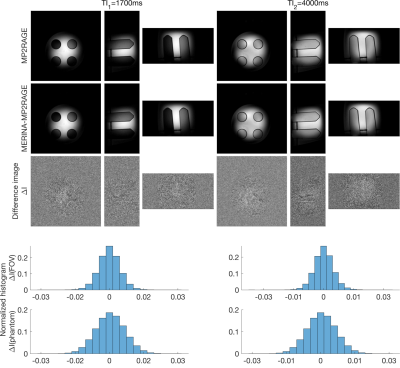
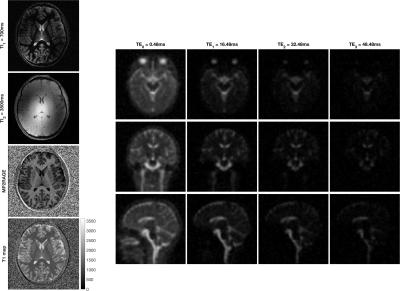
MERINA-MP2RAGE extends MP2RAGE to a multi-nuclei sequence by integrating 3D-multi-echo radial imaging of 23Na (MERINA[6]) in vacant imaging windows between the Cartesian GRE readouts (Figure 1). The multi-nuclei multi-trajectory concept was realized by adding the multi-echo sodium transmit and receive components to a 1H MP2RAGE prototype sequence and enabling decoupler pulse functionality to facilitate both 23Na and 1H RF excitation in a single scan. Imaging was conducted on a 7T research system (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) equipped with a transmit/receive dual-tuned 1H-23Na head coil (QED, USA). Phantom experiments were performed to compare image quality of the integrated sequence scheme with sequential acquisitions of stand-alone MP2RAGE and MERINA. The phantom consisted of 4 Falcon tubes filled with varying concentrations of sodium and agar (Figure 2b), submerged in a 2-litre cylindrical phantom filled with sucrose to match in vivo B1 characteristics[7]. Additionally, MERINA-MP2RAGE was tested on one healthy human volunteer (female, 27yr). Phantom and in vivo imaging sequence parameters of MERINA-MP2RAGE, as well as the stand-alone MP2RAGE and MERINA with identical setups are listed in Table 1. Sodium acquisitions were Hann-filtered and reconstructed offline in Matlab via Kaiser-Bessel regridding onto an isotropic 3.1mm grid.Results
The presented multi-nuclei MERINA-MP2RAGE sequence significantly improves scan time efficiency. In this study, the integrated sequence design facilitated a scan time reduction of more than 40% compared to a sequential acquisition (Table 1). Phantom experiments show no observable differences in the acquired MP2RAGE inversion images (Figure 3) and multi-echo sodium acquisitions (Figure 2) with difference images showing noise-like zero-mean Gaussian distributions. The mean sodium signal in different agar concentrations show comparable decay characteristics between the MERINA-MP2RAGE and the stand-alone MERINA acquisitions (Figure 2c). The human in vivo experiment confirms the findings showing 1H-based MP2RAGE and 23Na-based MERINA acquisitions of expected image quality.Discussion
M3N sequences address the integration of x-nuclei 1H-sequences for enhanced scan time efficiency, a core aspect for clinical translation. This work extends MP2RAGE with sodium MRI; however, the concept can be extended to many other MR-observable nuclei with resonance frequencies that are well separated from 1H-nuclei.Fast signal relaxation and concomitant low TR of sodium MRI make it a great candidate for vacant scan time filling. The number of integrated sodium projections depends on the MP2RAGE sequence parameters. However, the long TR of MP2RAGE and fast GRE acquisitions entail considerable scan time windows for the integration of sodium MRI.
The employed dual-tuned single-channel bird cage coil comprises signal acquisition. Advanced multi-channel coil designs have the potential to further improve image quality and signal homogeneity and enable parallel imaging capabilities for a reduction in total acquisition time.
SAR considerations are the main concern for M3N acquisitions, especially at higher fields. In this study, SAR limits were maintained by extending the sodium pulse length. SNR-enhanced sodium acquisition schemes[8-10] can be employed to maintain image quality with a reduced number of sodium excitations.
MP2RAGE is an information-rich acquisition scheme that provides access to multiple images, e.g. enhanced tissue contrast, T1-map, QSM[11]. Further enhancing the information content, the combined acquisition of two nuclei, sodium and hydrogen, extends this and offers to measure two complementary information sources with 1) 1H providing highly detailed anatomical data and 2) 23Na giving insight into physiological processes. The joint acquisition further offers the advantage of inherent image registration. Co-registration of 1H and 23Na images is a standard post-processing step for advanced image analysis and partial volume correction of 23Na images in quantitative estimation. The implicit registration allows to omit this post-processing step and further increases clinical translatability.
MERINA-MP2RAGE integrates multi-nuclei measurements in a clinically relevant imaging sequence. MP2RAGE is often a routinely acquired structural scan, particularly at high fields, and as such offers a great gateway for the ‘free’ acquisition of sodium MRI, ultimately providing a pathway for its clinical translation.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the facilities, and the scientific and technical assistance of the Australian National Imaging Facility at the Melbourne Brain Centre Imaging Unit. The Australian National Imaging Facility is funded by the Australian Government NCRIS program. The work was also supported by a research collaboration agreement with Siemens Healthineers.References
[1] Thulborn, K. R. (2018). Quantitative sodium MR imaging: a review of its evolving role in medicine. Neuroimage, 168, 250-268.
[2] Marques, J. P., Kober, T., Krueger, G., van der Zwaag, W., Van de Moortele, P. F., & Gruetter, R. (2010). MP2RAGE, a self bias-field corrected sequence for improved segmentation and T1-mapping at high field. Neuroimage, 49(2), 1271-1281.
[3] Lee, S. W., Hilal, S. K., & Cho, Z. H. (1986). A multinuclear magnetic resonance imaging technique-simultaneous proton and sodium imaging. Magnetic resonance imaging, 4(4), 343-350.
[4] de Bruin, P. W., Koken, P., Versluis, M. J., Aussenhofer, S. A., Meulenbelt, I., Börnert, P., & Webb, A. G. (2015). Time-efficient interleaved human 23Na and 1H data acquisition at 7 T. NMR in Biomed, 28(10), 1228-1235.
[5] Meyerspeer, M., Magill, A. W., Kuehne, A., Gruetter, R., Moser, E., & Schmid, A. I. (2016). Simultaneous and interleaved acquisition of NMR signals from different nuclei with a clinical MRI scanner. Magn Reson Med, 76(5), 1636-1641.
[6] Blunck, Y., Josan, S., Taqdees, S. W., Moffat, B. A., Ordidge, R. J., Cleary, J. O., & Johnston, L. A. (2018). 3D-multi-echo radial imaging of 23Na (3D-MERINA) for time-efficient multi-parameter tissue compartment mapping. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 79(4), 1950-1961.
[7] Duan, Q., Duyn, J. H., Gudino, N., de Zwart, J. A., van Gelderen, P., Sodickson, D. K., & Brown, R. (2014). Characterization of a dielectric phantom for high‐field magnetic resonance imaging applications. Medical physics, 41(10), 102303.
[8] Boada, F. E., Gillen, J. S., Shen, G. X., Chang, S. Y., & Thulborn, K. R. (1997). Fast three dimensional sodium imaging. Magn Reson Med, 37(5), 706-715.
[9] Nagel, A. M., Laun, F. B., Weber, M. A., Matthies, C., Semmler, W., & Schad, L. R. (2009). Sodium MRI using a density-adapted 3D radial acquisition technique. Magn Reson Med, 62(6), 1565-1573.
[10] Riemer, F., Solanky, B. S., Stehning, C., Clemence, M., Wheeler-Kingshott, C. A., & Golay, X. (2014). Sodium (23 Na) ultra-short echo time imaging in the human brain using a 3D-Cones trajectory. Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics, Biology and Medicine, 27(1), 35-46.
[11] Sun, H., Cleary, J. O., Glarin, R., Kolbe, S. C., Ordidge, R. J., Moffat, B. A., & Pike, G. B. (2019). Extracting more for less: multi‐echo MP2RAGE for simultaneous T1‐weighted imaging, T1 mapping, mapping, SWI, and QSM from a single acquisition. Magnetic resonance in medicine.
Figures