0459
Characterization and Correction of Cardiovascular Pulsation Artifacts in Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of the Pancreas1Department of Radiology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3MR, GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI, United States
Synopsis
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) of the abdomen faces multiple challenges, particularly artifacts induced by respiratory, peristaltic, and cardiovascular-related motions. Effects of cardiovascular pulsation on pancreas DWI have not been previously characterized. This motion introduces artifactual signal voids and unreliable apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values across the pancreas in DWI, regardless of cardiac phases and diffusion directions. Importantly, these artifacts can be addressed by motion-compensated diffusion gradient waveforms. These findings may facilitate the development of reliable and reproducible DWI of the pancreas.
Introduction
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) of the abdomen faces multiple challenges, particularly artifacts induced by respiratory, peristaltic, and cardiovascular-related motion1. Both respiratory and peristaltic motions can be mitigated by existing techniques2-5. In contrast, cardiovascular-related motion is essentially unavoidable and has been shown to generate significant artifacts and inaccurate diffusion parameter measurements in organs such as the liver6. Motion-related artifacts, which occur throughout the cardiac cycle, may not be avoided by cardiac gating. These artifacts have been addressed using optimized motion-compensated, first-moment-nulled gradient waveforms7. Pancreas DWI has an important role in the detection8, diagnosis9,10, and treatment monitoring of pancreatic cancer9. However, the effects of cardiovascular pulsation on DWI of the pancreas have not been previously characterized. Therefore, in this work we characterize the effects of cardiovascular pulsation on pancreas DWI, and evaluate a motion-compensated DWI approach to mitigate these effects.Methods
After IRB approval and informed written consent, eight volunteers were scanned at 3T (GE Signa Premier) using flexible coils (AIR Technology, GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI).Visualization of cardiovascular-related pancreas motion
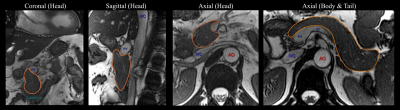
Cardiac-gated dynamic SSFP images of the pancreas in three orthogonal views were acquired in separate breath-holds to visualize the pancreas motion associated with cardiovascular-related motion.
Characterization and correction of motion artifacts in DWI
Characterization under various cardiac trigger delays
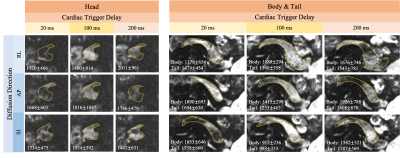
To maximally control the acquisition timing relative to the cardiac cycle, single-slice DWI was acquired using breath-holding and cardiac (peripheral) gating. DW images with b(#repetitions)=[0(1), 50(2), 500(6)]s/mm2 were acquired in a single end-of-expiration breath-hold. This acquisition was repeated at three cardiac trigger delays (20, 100, and 200ms), and in three diffusion directions using a standard monopolar waveform (TE=50ms). Reduced field-of-view (FOV=40%) was used with spatial resolution=1.25mm$$$\times$$$1.25mm$$$\times$$$5mm.
Correction using motion-compensated DW waveforms
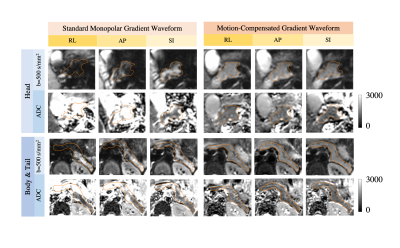
Single-slice DWI using a motion-compensated gradient waveform (TE=72ms)11 was tested using the same parameters as standard monopolar waveform with trigger delay=20ms.
Evaluating whole-pancreas respiratory-triggered DWI
Whole-pancreas DWI was acquired using respiratory-triggering with parameters similar to our local clinical protocol, with b(#repetitions)=[50(2), 500(6)]s/mm2 for three diffusion directions. Two separate acquisitions were performed, using standard monopolar and motion-compensated gradient waveforms, respectively.
Region of interest (ROI) measurements were taken on ADC maps derived from each combination of cardiac trigger delay and diffusion direction to characterize the effects of cardiovascular motion. ADC measurements were also performed in both single-slice and whole-pancreas data to assess the ability of motion-compensated acquisitions to address motion-related artifacts.
Results
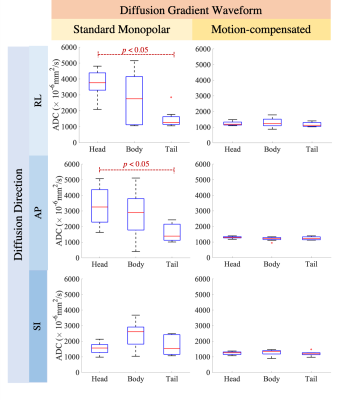
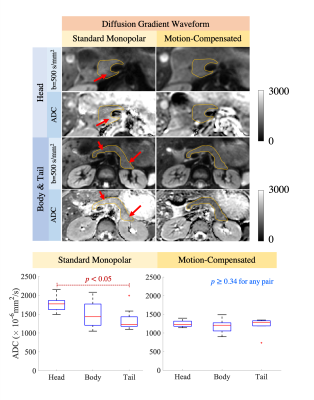
Cardiac-gated dynamic SSFP images of the pancreas in coronal, sagittal, and axial views are shown in Fig.1. Pulsation of the aorta, portal vein, inferior vena cava, and splenic vein cause substantial translational and elastic motion of the pancreas head and body. Bowel motion, or peristalsis, may also cause motion of the pancreas as demonstrated in the duodenum.In the breath-hold study, signal voids occurred in DWI images in all three parts of the pancreas, in all diffusion directions, and at all trigger delay times (Fig.2). As a result, biased ADC values with a large variation across volunteers occurred in all cases, which made avoiding the signal loss problem impossible by selecting a particular diffusion direction and trigger delay. With standard monopolar DW waveforms, heterogeneous DW signals and ADC values occurred across the pancreas in all diffusion directions (Fig.3). The measured ADCs had a large variability among volunteers and were significantly higher in head than in the tail (Fig.4). Using a motion-compensated DW waveform, DW signals and ADC values were uniform across pancreas (Fig.3), and the measured ADCs had a much lower variability among volunteers and were comparable in all three parts of pancreas (Fig.4).
In the respiratory-triggering study, the measured ADCs obtained with a monopolar waveform showed a reduction from pancreas head to tail with significant distinctions between the pancreas head and the tail. With motion-compensated waveforms, the measured ADCs did not show significant differences throughout the pancreas and had a lower variability among volunteers than for standard monopolar gradient waveforms (Fig.5).
Discussion
Cardiovascular pulsation induces complex elastic motion in the pancreas, leading to signal loss in head, body, and tail, at various phases in the cardiac cycle, and in various diffusion directions. Motion-compensated diffusion gradient waveforms can avoid this signal loss, resulting in more reproducible diffusion quantification.The reduction of ADC measurements from pancreas head to tail when using standard monopolar diffusion gradient waveforms replicated the results from various previous studies12-15. Furthermore, one study demonstrated that ADC values in the pancreas head were higher than in the tail, independently of gender, age and BMI16. Our results suggest that these differences may be artifactual and due to cardiovascular-related effects. In our study, this difference in ADC across different parts of pancreas disappeared using motion-compensated gradient waveforms. Confirmation of this finding in a larger volunteer and patient study is needed.
This study had several limitations. Susceptibility artifacts in DWI images may influence the accuracy of ADC measurements. Peristaltic motion was not controlled.
Conclusion
Cardiovascular pulsation introduces substantial artifacts and unreliable ADC measurements in pancreas DWI, which can be addressed by motion-compensated diffusion gradient waveforms. These effects may have important implications both for understanding current literature on DWI of the pancreas and for the design of improved DWI techniques in clinical and research applications.Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge research support from GE Healthcare and Bracco Diagnostics to the University of Wisconsin-Madison, help from undergraduate research assistant Zachary N. Schwartz, and technical support from Dr. Karl Vigen.References
[1] Balci, N. C., Perman, W. H., Saglam, S., Akisik, F., Fattahi, R., & Bilgin, M. (2009). Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas. Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 20(1), 43-47.
[2] Barral, M., Taouli, B., Guiu, B., Koh, D. M., Luciani, A., Manfredi, R., ... & Soyer, P. (2014). Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the pancreas: current status and recommendations. Radiology, 274(1), 45-63.
[3] Kwee, T. C., Takahara, T., Koh, D. M., Nievelstein, R. A., & Luijten, P. R. (2008). Comparison and reproducibility of ADC measurements in breathhold, respiratory triggered, and free‐breathing diffusion‐weighted MR imaging of the liver. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 28(5), 1141-1148.
[4] Kandpal, H., Sharma, R., Madhusudhan, K. S., & Kapoor, K. S. (2009). Respiratory-triggered versus breath-hold diffusion-weighted MRI of liver lesions: comparison of image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient values. American Journal of Roentgenology, 192(4), 915-922.
[5] Mochiki, E., Suzuki, H., Takenoshita, S., Nagamachi, Y., Kuwano, H., Mizumoto, A., & Itoh, Z. (1998). Mechanism of inhibitory effect of glucagon on gastrointestinal motility and cause of side effects of glucagon. Journal of gastroenterology, 33(6), 835-841.
[6] Liau, J., Lee, J., Schroeder, M. E., Sirlin, C. B., & Bydder, M. (2012). Cardiac motion in diffusion‐weighted MRI of the liver: artifact and a method of correction. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 35(2), 318-327.
[7] Zhang, Y., Peña‐Nogales, Ó., Holmes, J. H., & Hernando, D. (2019). Motion‐robust and blood‐suppressed M1‐optimized diffusion MR imaging of the liver. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 82(1), 302-311.
[8] Ichikawa, T., Erturk, S. M., Motosugi, U., Sou, H., Iino, H., Araki, T., & Fujii, H. (2007). High-b value diffusion-weighted MRI for detecting pancreatic adenocarcinoma: preliminary results. American Journal of Roentgenology, 188(2), 409-414.
[9] Kamisawa, T., Takuma, K., Anjiki, H., Egawa, N., Hata, T., Kurata, M., ... & Sasaki, T. (2010). Differentiation of autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer by diffusion-weighted MRI. The American journal of gastroenterology, 105(8), 1870.
[10] Fattahi, R., Balci, N. C., Perman, W. H., Hsueh, E. C., Alkaade, S., Havlioglu, N., & Burton, F. R. (2009). Pancreatic diffusion‐weighted imaging (DWI): comparison between mass‐forming focal pancreatitis (FP), pancreatic cancer (PC), and normal pancreas. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 29(2), 350-356.
[11] Peña‐Nogales, Ó., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., de Luis‐Garcia, R., Aja‐Fernández, S., Holmes, J. H., & Hernando, D. (2019). Optimized Diffusion‐Weighting Gradient Waveform Design (ODGD) formulation for motion compensation and concomitant gradient nulling. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 81(2), 989-1003.
[12] Schoennagel, B. P., Habermann, C. R., Roesch, M., Hahne, J. D., Arndt, C., Kleibeler, L., ... & Herrmann, J. (2011). Diffusion‐weighted imaging of the healthy pancreas: Apparent diffusion coefficient values of the normal head, body, and tail calculated from different sets of b‐values. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 34(4), 861-865.
[13] Dale, B. M., Braithwaite, A. C., Boll, D. T., & Merkle, E. M. (2010). Field strength and diffusion encoding technique affect the apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen. Investigative radiology, 45(2), 104-108.
[14] Yoshikawa, T., Kawamitsu, H., Mitchell, D. G., Ohno, Y., Ku, Y., Seo, Y., ... & Sugimura, K. (2006). ADC measurement of abdominal organs and lesions using parallel imaging technique. American Journal of Roentgenology, 187(6), 1521-1530.
[15] Ding, X., Xu, H., Zhou, J., Xu, J., Mei, H., Long, Q., & Wang, Y. (2019). Reproducibility of normalized apparent diffusion coefficient measurements on 3.0-T diffusion-weighted imaging of normal pancreas in a healthy population. Medicine, 98(14).
[16] Kiani Nazarlou, A.,
Faeghi, F., Abdkarimi, M. H., & Asghari JafarAbadi, M. (2015). ADC values
in diffusion-weighted MRI and their relationship with age, gender and BMI in
healthy people's pancreases. The British journal of radiology, 88(1047), 20140449.
Figures