0366
Rapid High-Resolution Mapping of Brain Metabolites and Neurotransmitters Using Hybrid FID/SE-J-Resolved Spectroscopic Signals1Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, United States, 2Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, United States, 3School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 4Med-X Research Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
J-resolved MRSI is a powerful tool for separating overlapping resonances in conventional MRSI, which is especially useful for mapping neurotransmitters like γ-aminobutyric acid and glutamate. A major practical limitation of J-resolved MRSI lies in its long data acquisition time required to sample the high-dimensional data space using spin-echo-based sequences. In this work, we present a novel hybrid FID/SE data acquisition scheme to accelerate J-resolved MRSI. The proposed method has been validated using phantom and in vivo experimental data, producing high-quality 3D spatial maps of brain metabolites and neurotransmitters within clinically feasible time.
Introduction
High-resolution mapping of metabolites and neurotransmitters, especially γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate (Glu), is of great interest to brain studies1-3. Unfortunately, mapping of GABA and Glu is rather difficult due to their low concentrations and spectral overlapping with other resonances4. J-resolved MRSI has the potential to separate overlapping resonances in the chemical shift spectrum by utilizing J-evolution information5,6. However, conventional J-resolved MRSI requires spin-echo-based acquisitions with many TE steps, often leading to a prohibitively long acquisition time. Several approaches have been proposed to accelerate J-resolved MRSI, including EPSI and spiral trajectories, compressed sensing and subspace/tensor-based approaches7-11. Nevertheless, the current capability of J-resolved MRSI is still rather limited, with spatial resolution on the order of centimeters and acquisition time on the order of 20 minutes, even for 2D imaging. In this work, we propose a novel method for highly accelerated J-resolved MRSI, with the following key features: a) utilizing both FID and SE signals to encode spatial, spectral and J-evolution information, b) large coverage of k-space for FID signals with short TR and relatively small coverage of k-space for SE signals, c) limited and sparse sampling of $$$(k,t_1,t_2)$$$-space, d) no water and lipid suppression for the FID signals and no lipid suppression for the SE signals. Phantom and in vivo experiments were performed to demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed method, generating impressive results. The method achieved $$$3.1\times2.2\times3.0\rm{~mm}^3$$$ resolution for metabolites and $$$7.5\times6.0\times4.5\rm{~mm}^3$$$ resolution for J-coupled neurotransmitters with 13 min scan time.Methods
FID and SE are two distinct acquisition methods often used separately in different MRSI experiments. FID acquisitions feature small-flip-angle excitation, ultrashort TE, short TR and high encoding efficiency, enabling rapid high-resolution MRSI. SE acquisitions can encode the J-evolution information but often suffer from poor trade-off between resolution and scan time due to the long TR required. To get the best of both worlds, we propose a hybrid FID/SE acquisition scheme, as illustrated in Fig. 1.In the proposed scheme, an FID acquisition was used to cover extended k-space to achieve high spatial resolution, while a multi-spin-echo acquisition12,13.was used to acquire two sets of J-resolved data with limited k-space coverage to save scan time. This data acquisition scheme allows us to take advantage of the high-resolution information encoded in the FID data, eliminating the needs for lipid suppression for both the FID and SE acquisitions. EPSI readouts were used to simultaneously encode spatial and spectral information for additional acceleration. This sampling scheme achieved higher data acquisition efficiency for the estimation of brain metabolites and neurotransmitters than conventional methods according to Cramér-Rao lower bound (CRLB) analysis.
We used a union-of-subspaces model to process the acquired data14. In this model, metabolite and neurotransmitter signals were represented using low-dimensional joint subspaces15, enabling effective use of the complementary information in the FID/SE data and incorporation of spatial and spectral prior information through a weighted regularization and pre-trained metabolite spectral basis. A more detailed description of the processing scheme is given in a companion ISMRM abstract.
Results
Simulation: A set of simulation results is shown in Fig 2. From CRLB analysis16,17, we can see that the proposed method can reduce the CRLB of GABA by a factor of 4.31 and 2.59, as compared with FID-only and SE-only acquisitions respectively, rendering the GABA concentration estimates much more reliable. Similar results were obtained for Glu and glutamine (Gln). From Fig. 2b we can see the steady-state magnetization decreased as the number of echoes increased. A comparison of the CRLB results indicates that for a fixed scan time, two spin-echoes can achieve the lowest CRLB for GABA (Fig. 2c). The two TE values optimal for GABA estimation were selected based on the results shown in Fig 2d.Phantom experiment: Phantom experiments were performed on a phantom with nine vials filled with solutions of NAA, Cr, Cho, myo-inositol, Glu and GABA at physiological concentrations on a 3T Siemens Prisma scanner. A set of hybrid FID/SE data was acquired using the parameters as follows: $$$\mathrm{FOV}=240\times240\times72\mathrm{~mm}^3,$$$$$$~\mathrm{FA}_{\mathrm{FID}}=27^{\circ},$$$$$$~\mathrm{TR}_{\mathrm{FID}}/\mathrm{TE}^{*}_{\rm{FID}}=160/1.6\rm{~ms},$$$$$$~\mathrm{FID~matrix~size}=78\times110\times24,$$$$$$~\mathrm{TR}_{\mathrm{SE}}/\mathrm{TE}_{\mathrm{SE},1}/\mathrm{TE}_{\mathrm{SE},2}=80/20/140\mathrm{~ms},$$$$$$~\mathrm{SE~matrix~size}=40\times40\times16,$$$$$$\mathrm{~and~}\mathrm{~total~acquisition~time}=14.0\mathrm{~min}$$$. As a comparison, a set of low-resolution conventional J-resolved SE data was also acquired with $$$\mathrm{TR}=800\mathrm{~ms},$$$$$$~20\mathrm{~TEs}$$$$$$~(\mathrm{starting~from~TE}_1=20\mathrm{~ms},$$$$$$~\mathrm{~with~}\Delta\mathrm{TE}=10\mathrm{~ms}),$$$$$$~\mathrm{data~matrix~size}=30\times30\times12,$$$$$$\mathrm{~and~total~acquisition~time}=96\mathrm{~min}$$$. A set of representative phantom results are shown in Fig. 3. As can be seen, the proposed method produced high-quality maps of GABA comparable to those from the conventional J-resolved MRSI experiments, but with a factor of 6.8 reduction in scan time and a noticeable improvement in spatial resolution.
In vivo experiment: A set of hybrid FID/SE data was acquired from a healthy volunteer. The acquisition parameters were the same as the phantom experiment, except for reduced $$$\mathrm{SE~matrix~size}=32\times40\times16,\mathrm{~and~total~acquisition~time}=13.1\mathrm{~min}$$$ . High-resolution maps of metabolites and neurotransmitters are shown in Fig. 4. With additional J-evolution information encoded in the SE data, high-quality neurotransmitter maps can be obtained. Representative 2D J-resolved spectra are shown in Fig. 5.
Conclusions
A novel hybrid data acquisition scheme has been proposed to synergistically integrate FID and SE MRSI acquisitions for rapid high-resolution mapping of brain metabolites and neurotransmitters. Experimental results demonstrated the feasibility of the proposed scheme, producing high-quality molecular maps. With further development, the proposed method is expected to make 3D high-resolution J-resolved MRSI experiments practically useful.Acknowledgements
This work reported in this paper was supported, in part, by NIH-R21-EB023413, NIH-P41-EB022544 and NIH-U01-EB026978.
References
[1] Schür RR, Draisma LW, Wijnen JP, et al. Brain GABA levels across psychiatric disorders: A systematic literature review and meta‐analysis of 1H‐MRS studies. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016; 37(9): 3337-3352.
[2] Sanacora G, Gueorguieva R, Epperson CN, et al. Subtype-specific alterations of γ-aminobutyric acid and glutamate in patients with major depression. JAMA Psychiatry. 2004; 61(7): 705-713.
[3] Simister RJ, McLean MA, Barker GJ and Duncan JS. Proton MRS reveals frontal lobe metabolite abnormalities in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Neurology. 2003; 61(7): 897-902.
[4] de Graaf RA, In vivo NMR spectroscopy: principles and techniques. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons, 2007.
[5] Aue WP. Bartholdi E and Ernst RR. Two‐dimensional spectroscopy. Application to nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Chem. Phys. 1976; 64(5): 2229-2246.
[6] Jensen JE, Frederick Bd, Wang L, Brown J and Renshaw PF. Two‐dimensional, J‐resolved spectroscopic imaging of GABA at 4 Tesla in the human brain. Magn Reson Med. 2005; 54(4): 783-788.
[7] Posse S, Ricardo O, Arvind C et al. Proton echo‐planar spectroscopic imaging of J‐coupled resonances in human brain at 3 and 4 Tesla. Magn Reson Med. 2007; 58(2): 236-244.
[8] Adalsteinsson E and Daniel MS. Spatially resolved two‐dimensional spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 1999; 41(1): 8-12.
[9] Wilson NE, Iqbal Z, Burns BL et al. Accelerated five‐dimensional echo planar J‐resolved spectroscopic imaging: Implementation and pilot validation in human brain. Magn Reson Med. 2016; 75(1): 42-51.
[10] He J, Liu Q, Christodoulou AG et al. Accelerated high-dimensional MR imaging with sparse sampling using low-rank tensors. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016 35(9): 2119-2129.
[11] Tang L, Zhao Y, Li Y et al. Accelerated J-resolved 1H-MRSI with limited and sparse sampling of (k, tJ)-space. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2019. 2486.
[12] Bax A, Mehlkopf AF and Smidt J. A fast method for obtaining 2D J-resolved absorption spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 1980; 40(1): 213-219.
[13] Herigault G, Zoula S, Rémy C, Décorps M and Ziegler A. Multi-spin-echo J-resolved spectroscopic imaging without water suppression: application to a rat glioma at 7 T. Magn Reason Mater Phy. 2004; 17(3-6): 140-148.
[14] Ma C, Lam F, Johnson CL and Liang Z-P. Removal of nuisance signals from limited and sparse 1H MRSI data using a union-of-subspaces model. Magn Reson Med. 2016;75(2):488‐497.
[15] Lam F, Cheng B and Liang Z-P. Accelerated J-resolved MRSI using joint subspace and sparsity constraints. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017. 1202.
[16] Bolliger CS, Boesch C and Kreis R. On the use of Cramér–Rao minimum variance bounds for the design of magnetic resonance spectroscopy experiments. NeuroImage 2013; 83:1031-1040.
[17] Ma C, Lam F, Ning Q, Johnson CL and Liang Z-P. High‐resolution 1H‐MRSI of the brain using short‐TE SPICE. Magn Reson Med. 2017; 77(2): 467-479.
Figures
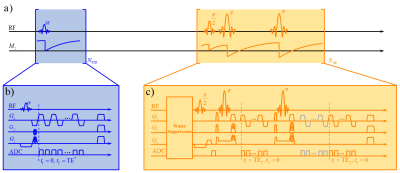
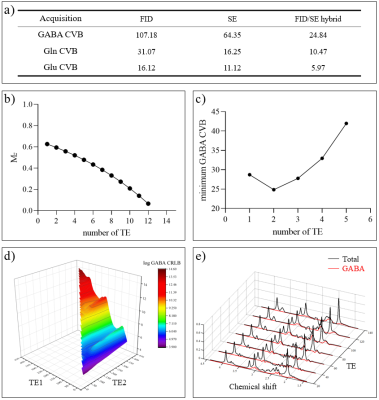

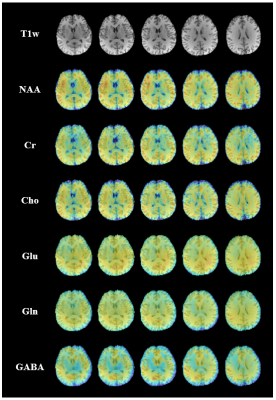
Figure 4. 3D metabolite and neurotransmitter maps obtained from in vivo data using the proposed method. The total acquisition time was 13.1 min.
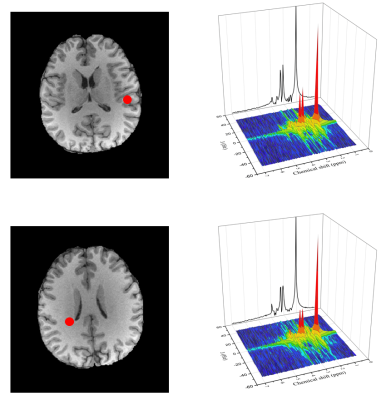
Figure 5. Representative spectra obtained from in vivo data (from the spatial locations marked by the red dots). As can be seen, the proposed method produced high-quality spectra using hybrid FID/SE J-resolved MRSI data.