0358
Feasibility of dynamic DTI exercise response and resistance dependence in quadriceps muscle1Radiology, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, United States
Synopsis
We describe measurement of resistance dependence diffusion metric exercise response in thigh muscle with a multiple echo diffusion tensor imaging (MEDITI) on a clinical 3 T scanner. With radial imaging, accelerated diffusion encoding, and compressed sensing reconstruction, spatial resolution of 3.4 mm and temporal resolution of 16 s was achieved. Using an MR-compatible ergometer with pneumatic resistance and force/displacement monitoring, post-exercise recovery of DTI metrics in the rectus femoris following quadriceps extension was monitored as a function of resistance. Significant dependences of response on resistance were observed.
Purpose
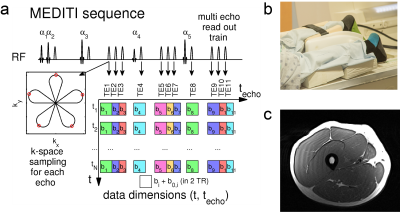
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of skeletal muscle probes myofiber architecture at rest, with extension, and in pathology. Exercise challenge has been widely employed with diffusion imaging for further diagnostic value (1-14). A key aspect of understanding exercise response of MR contrast is quantitative exercise control (15-18). A method (MEDITATE) for compressing directional encodings has been demonstrated using multiple echoes (19,20). A spatially-resolved variant (MEDITI) with a multi-spoke Single Trajectory Radial (STAR) k-space trajectory (21) and compressed sensing reconstruction, has shown dynamic DTI of calf muscle (8). In this work, we evaluated MEDITI in thigh muscle following in-scanner exercise in normal controls to probe the dependence of diffusion parameters on the level of exertion.Methods
In this HIPAA-compliant, IRB-approved study, 3 normal controls (2 M , 1 F, ages 25 ± 2 y) provided written informed consent for a thigh muscle MRI in a Siemens Prisma 3 T scanner. Subjects were positioned prone with one leg in an MR-compatible quadriceps extension ergometer (Ergospect Quadspect) (Figure 1) that provides real time control of pneumatic resistance and force / displacement measurement, with an anterior 4-channel flexible RF coil under the rectus femoris. Non-fat suppressed T1-weighted imaging was performed for localization and planning. Subjects first performed maximum voluntary contraction (MVC) against very high resistance. After 5 minute rest, subjects performed two bouts of repeated quadriceps extension for up to 3 minutes followed by 15 minute recovery. All subjects performed two bouts of resistance (23.7 ± 2.4 % and 37.4 ± 0.7 % MVC). Final MVC was determined from the larger of the pre-exercise measurement or the maximum achieved during exercise.MEDITI (Fig. 1a) captures 11 echoes with a 5-petal STAR-trajectory, with intershot angle increments according to the GRASP-scheme (Golden Radio Angle Radial Sparse Parallel), FOV = 220 mm, resolution 3.43 mm, total echo times TE=80-218 ms, isotropic b-values: 157-772 s/mm2, flip angles 61°/73°/85°/45°/85°, TR=2 s, and 10 mm slice thickness. A saturation band was used to suppress residual signal from the non-active leg. Image reconstruction was performed on a high performance computer cluster using custom-written code in MATLAB. Self-navigation corrected phase errors prior to dynamic reconstruction. Sparsifying transforms exploit the similarity between diffusion weighted images along the echo and the time dimensions to avoid undersampling artifacts(22) :
$$\hat X = \arg {\min _U}\left\{ {\left\| {E \cdot X - Y} \right\|_2^2 + {\lambda _{PCA}}{{\left\| {PC{A^{{t_{echo}}}}X} \right\|}_1} + {\lambda _{PCAt}}{{\left\| {PC{A^t}X} \right\|}_1} + {\lambda _{TV}}{{\left\| {T{V^{xy}}X} \right\|}_1}} \right\}$$
with X the time-series of images to be reconstructed, Y its k-space, E the multicoil encoding matrix, including coil sensitivities (23) and the NuFFT-transform, PCA the Principal Component Analysis transform, TVxy the in plane total variation transform and λPCA, λPCAt and λTV regularization parameters. Readouts from 4 TRs were combined for temporal resolution of 16 s. Time points during exercise were identified in a NuFFT reconstruction and edited out prior to final reconstruction. A cylindrical diffusion tensor model generated mean diffusivity (MD), axial (λ1), and radial (λrad) diffusion maps. Normalizing the post-exercise period by the average pre-exercise map generated diffusion response maps, which were temporally smoothed. Rectus femoris (RF) compartments were segmented on T2-weighted images (transverse / longitudinal weighting times 80 / 70 ms) and each recovery $$$nU\left( t \right)$$$ was fit to a gamma variate decay with baseline:
$$nU\left( t \right) = \frac{{U\left( t \right)}}{{{{\left\langle {U\left( t \right)} \right\rangle }_{rest}}}} - 1 = {R_{0U}} \cdot {\left( {\frac{t}{{TTP}}} \right)^\alpha }\exp \left( {\alpha \left( {1 - \frac{t}{{TTP}}} \right)} \right) + {l_0}_U + {l_{1U}}t$$
Total response $$${R_{0U}} + {l_0}_U + {l_1}_UTT{P_U}$$$, time to peak (TTP), and exponent α were computed for diffusion/T2w metrics. Parameters were compared at the group level between exercise bouts and between parameters with two-sided Student’s t-tests.
Results
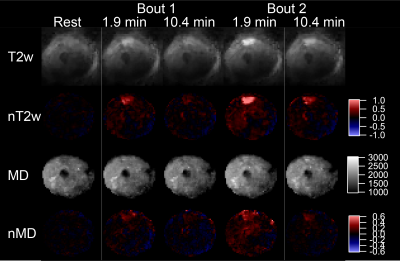
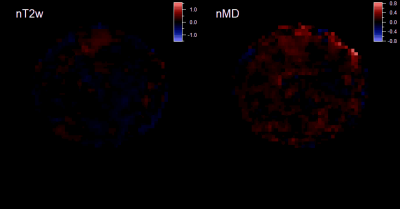
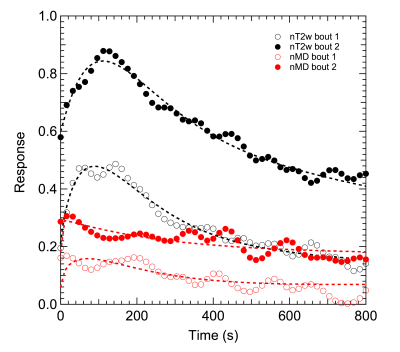
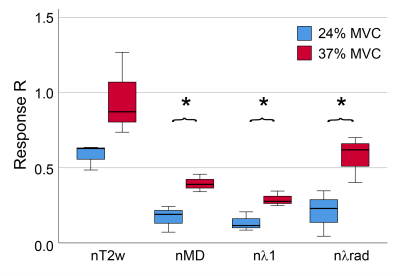
Average MVC was 561±96 N. Figures 2 and 3 show example MEDITI images from a volunteer thigh scan at rest and following each of 2 3-minute bouts of exercise 25% and 37% of MVC. Absolute T2-weighted (T2w) and mean diffusion (MD) maps are shown, as well as normalized maps (nT2w and nMD) highlighting changes from rest baseline. Activation in the rectus femoris is evident in nT2w and nMD maps, and at higher levels for the higher resistance. Temporal response curves for nT2w and nMD in the RF (Figure 4) illustrate the kinetics of exercise response at each resistance level and its representation by the gamma variate form. Figure 5 summarizes group results in which total response showed significant increases at higher resistance for all diffusion metrics. nT2w response was significantly greater than that of each of the diffusion metrics. TTP (64.4 ± 47.5 s) and α (2.8 ± 6.0) showed heterogeneity at the group level.Discussion
This study shows the feasibility of acquiring dynamic T2-weighted and DTI metrics in quadriceps muscle accompanying extension with a MR-compatible pneumatic resistance ergometer and the MEDITI sequence. Significant increases in diffusion metrics with increased normalized resistance were observed, and radial diffusion changes generally exceeded axial changes, consistent with DTI muscle exercise literature (7-11). This demonstration allows broader studies, both in sample size and range of exertion, to further scrutinize biological mechanisms of diffusion exercise response and their clinical application to neuromuscular disease.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the NIH (R21EB009435, S10OD021702).References
1. Ababneh ZQ, Ababneh R, Maier SE, Winalski CS, Oshio K, Ababneh AM, Mulkern RV. On the correlation between T(2) and tissue diffusion coefficients in exercised muscle: quantitative measurements at 3T within the tibialis anterior. Magma 2008;21(4):273-278.
2. Morvan D, Leroy-Willig A, Malgouyres A, Cuenod CA, Jehenson P, Syrota A. Simultaneous temperature and regional blood volume measurements in human muscle using an MRI fast diffusion technique. Magn Reson Med 1993;29(3):371-377.
3. Filli L, Boss A, Wurnig MC, Kenkel D, Andreisek G, Guggenberger R. Dynamic intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of skeletal muscle at rest and after exercise. NMR Biomed 2015;28(2):240-246.
4. Rockel C, Akbari A, Kumbhare DA, Noseworthy MD. Dynamic DTI (dDTI) shows differing temporal activation patterns in post-exercise skeletal muscles. MAGMA 2016.
5. Adelnia F, Shardell M, Bergeron CM, Fishbein KW, Spencer RG, Ferrucci L, Reiter DA. Diffusion-weighted MRI with intravoxel incoherent motion modeling for assessment of muscle perfusion in the thigh during post-exercise hyperemia in younger and older adults. NMR Biomed 2019:e4072.
6. Nguyen A, Ledoux JB, Omoumi P, Becce F, Forget J, Federau C. Application of intravoxel incoherent motion perfusion imaging to shoulder muscles after a lift-off test of varying duration. NMR Biomed 2016;29(1):66-73.
7. Rockel C, Akbari A, Kumbhare DA, Noseworthy MD. Dynamic DTI (dDTI) shows differing temporal activation patterns in post-exercise skeletal muscles. Magma 2017;30(2):127-138.
8. Sigmund EE, Baete SH, Patel K, Wang D, Stoffel D, Otazo R, Parasoglou P, Bencardino J. Spatially resolved kinetics of skeletal muscle exercise response and recovery with multiple echo diffusion tensor imaging (MEDITI): a feasibility study. MAGMA 2018;31(5):599-608.
9. Edalati M, Hastings MK, Sorensen CJ, Zayed M, Mueller MJ, Hildebolt CF, Zheng J. Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Calf Muscles in Subjects With and Without Diabetes Mellitus. J Magn Reson Imaging 2019;49(5):1285-1295.
10. Okamoto Y, Kunimatsu A, Kono T, Nasu K, Sonobe J, Minami M. Changes in MR diffusion properties during active muscle contraction in the calf. Magnetic resonance in medical sciences : MRMS : an official journal of Japan Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2010;9(1):1-8.
11. Sigmund EE, Baete SH, Luo T, Patel K, Wang D, Rossi I, Duarte A, Bruno M, Mossa D, Femia A, Ramachandran S, Stoffel D, Babb JS, Franks AG, Bencardino J. MRI assessment of the thigh musculature in dermatomyositis and healthy subjects using diffusion tensor imaging, intravoxel incoherent motion and dynamic DTI. Eur Radiol 2018;28(12):5304-5315.
12. Hiepe P, Gussew A, Rzanny R, Anders C, Walther M, Scholle HC, Reichenbach JR. Interrelations of muscle functional MRI, diffusion-weighted MRI and (31) P-MRS in exercised lower back muscles. NMR Biomed 2014;27(8):958-970.
13. Jungmann PM, Pfirrmann C, Federau C. Characterization of lower limb muscle activation patterns during walking and running with Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) MR perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 2019;63:12-20.
14. Mastropietro A, Porcelli S, Cadioli M, Rasica L, Scalco E, Gerevini S, Marzorati M, Rizzo G. Triggered intravoxel incoherent motion MRI for the assessment of calf muscle perfusion during isometric intermittent exercise. NMR Biomed 2018;31(6):e3922.
15. Tschiesche K, Rothamel M, Rzanny R, Gussew A, Hiepe P, Reichenbach JR. MR-compatible pedal ergometer for reproducible exercising of the human calf muscle. Medical engineering & physics 2014;36(7):933-937.
16. Pesta D, Paschke V, Hoppel F, Kobel C, Kremser C, Esterhammer R, Burtscher M, Kemp GJ, Schocke M. Different Metabolic Responses during Incremental Exercise Assessed by Localized 31P MRS in Sprint and Endurance Athletes and Untrained Individuals. Int J Sports Med 2013;34(08):669-675.
17. Caterini JE, Elzibak AH, St Michel EJ, McCrindle BW, Redington AN, Thompson S, Noseworthy MD, Wells GD. Characterizing blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) response following in-magnet quadriceps exercise. MAGMA 2015;28(3):271-278.
18. Naimon ND, Walczyk J, Babb JS, Khegai O, Che X, Alon L, Regatte RR, Brown R, Parasoglou P. A low-cost Mr compatible ergometer to assess post-exercise phosphocreatine recovery kinetics. MAGMA 2017;30(3):281-289.
19. Baete SH, Cho G, Sigmund EE. Multiple-echo diffusion tensor acquisition technique (MEDITATE) on a 3T clinical scanner. NMR Biomed 2013;26(11):1471-1483.
20. Baete SH, Cho GY, Sigmund EE. Dynamic diffusion-tensor measurements in muscle tissue using the single-line multiple-echo diffusion-tensor acquisition technique at 3T. NMR Biomed 2015;28(6):667-678.
21. Sarty GE. Single TrAjectory radial (STAR) imaging. Magn Reson Med 2004;51(3):445-451.
22. Lustig M, Donoho D, Pauly JM. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 2007;58(6):1182-1195.
23. Otazo R, Kim D, Axel L, Sodickson DK. Combination of compressed sensing and parallel imaging for highly accelerated first-pass cardiac perfusion MRI. Magn Reson Med 2010;64(3):767-776.
Figures