0322
Utility of Stack-of-stars Acquisition for Arterial Phase Imaging without Breath-holding on Dynamic MRI of the Liver1Department of Radiology, University of Yamanashi, Chuo, Japan, 2MR Collaboration and Development, GE Healthcare, Hino, Japan, 3MR Collaboration and Development, GE Healthcare, Tucson, AZ, United States, 4MR Collaboration and Development, GE Healthcare, Madison, WI, United States
Synopsis
We compared arterial phase (AP) images using conventional (Cartesian) breath-hold liver acquisition with volume acceleration (LAVA) and stack-of-stars acquisition without breath-holding (LAVA-Star) on hepatic dynamic MRI. In Cartesian breath-hold LAVA group, 8.7% of patients showed inadequate scan timing of AP, while only 1 patient (4.0%) in LAVA-Star group (12 s/phase) showed inadequate scan timing. One advantage of LAVA-Star was that the adequate scan timing of AP can be obtained by using additional high frame rate reconstruction (3 s/phase) in the patient with inadequate scan timing in routine reconstruction. LAVA-Star was useful to obtain adequate scan timing in all patients.
Introduction
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) of the liver is typically obtained with breath-holding 3D gradient echo sequence. However, breath-holding for >10 seconds is sometimes difficult in some patients. Respiratory gating with navigator echoes is available to obtain 3D gradient echo sequence without breath-holding. However, respiratory gating prolongs the acquisition time leading to limited time resolution. A stack-of-stars is a technique which is robust for respiratory motion compared with Cartesian sampling1 and useful to obtain breath-hold-free DCE-MRI using information of respiratory motion in the data set. Up to now, it has not been systematically investigated if the stack-of-stars acquisition for breath-hold-free arterial phase (AP) imaging of the liver in terms is useful in the clinic. Thus, the aim of this study was to investigate the utility of AP imaging using the prototype pulse sequences of stack-of-stars acquisition (LAVA-Star) compared to conventional (Cartesian) breath-hold LAVA.Methods
This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board and the requirement for informed patient consent was waived. One hundred seventy-four patients (male: female, 110: 64; mean age, 69.0 ± 9.6 years) who underwent gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI with a 3-T MRI system were enrolled (Cartesian breath-hold LAVA group (between October 2014 and January 2015, n = 149) and LAVA-Star group (October 2019, n = 25)). Gadoxetate disodium (0.025 mmol/kg body weight) was administered at a rate of 1 mL/s followed by a 20-mL saline flush by using a power injector. Imaging parameters of Cartesian breath-hold LAVA and LAVA-Star were shown in Fig.1. In LAVA-Star sequence, total of 1500 radial spokes were acquired in 4 minutes continuously and for routine frame rate reconstruction, 20 phases with 150 spokes per phase were reconstructed using 75 spokes offset between phases, which was equivalent to 12 s/phase. In each phase reconstruction, auto-calibrating reconstruction for Cartesian sampling (ARC) algorithm was used before Fourier transformation in kz direction and conjugate gradient-sensitivity encoding (CG-SENSE) algorithm was used for in-plane reconstruction2. The soft-gating, a retrospective gating technique, was used to suppress the image blur due to respiratory motion3. Visual assessment of the scan timing of AP (adequate or inadequate) was performed for each group, and in case of inadequate scan timing in LAVA-Star group, retrospective reconstruction with high frame rate (80 phases, 3 s/phase) was added. Adequate scan timing of AP was defined as when the hepatic artery and portal vein are enhanced but the hepatic vein is not yet enhanced by antegrade flow (Fig. 2). Artifact (3-point visual score: 3, no/mild; 2, moderate; 3, severe), overall image quality (5-point visual score: 5, excellent; 4, good; 3, adequate; 2, poor; 1, non-diagnostic), and acceptable image quality (≥3) were also assessed for each group and compared with Chi-square test.Results
Patients demographics of two groups are shown in Fig. 3. There is no significant difference on patients’ background between two groups (P = 0.1749-0.7388). Inadequate scan timing of AP was observed 13 patients (8.7%, 13/149) in Cartesian breath-hold LAVA group, while only 1 patient (4.0%, 1/25) in LAVA-Star group showed inadequate scan timing of AP. In remaining 24 patients, the adequate scan timing of AP was observed in the 3rd phase (25.0%, 6/24), 4th phase (70.8%, 17/24), or 5th phase (4.2%, 1/24). (Fig. 4). In the patient with inadequate timing of AP in LAVA-Star group, retrospective additional reconstruction with high frame rate offered images of adequate scan timing of AP (Fig. 5). LAVA-Star showed lower score of artifact and overall image quality (P < 0.0001) due to streak artifacts. However, there was no significant difference in the rate of patients with acceptable image quality between two groups (P = 0.7156).Discussion
Our results revealed that LAVA-Star showed a high performance to obtain AP images with adequate scan timing. Although routine frame rate reconstruction (12 s/phase) was not perfect, retrospective high frame rate reconstruction (3 s/phase) salvaged the AP images in case with inadequate scan timing of AP by routine frame rate. The AP is the most important phase in DCE-MRI of the liver. There are some drawbacks to obtain optimal AP images on gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI. Previous reports revealed that a high incidence (7–14%) of patients self-reported transient dyspnea after the administration of gadoxetate disodium4,5. The injection volume of gadoxetate disodium is half that of extracellular contrast agents that causes a short duration of adequate scan timing and truncation artifacts due to k-space inhomogeneity6,7. LAVA-Star without breath-holding is a good solution to obtain optimal AP images because there is no worry of missing scan timing of AP and it is not affected by respiratory motion artifacts. However, the streak artifact resulting from under-sampling is the major disadvantage of LAVA-Star. Our results revealed that there was not significant difference on acceptable image quality between LAVA Star and Cartesian breath-hold LAVA groups. However, degradation of image quality due to streak artifacts is a problem to be solved.Conclusion
The use of LAVA-Star is the good solution to obtain the adequate scan timing of AP images.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Peters DC, Korosec FR, Grist TM, et al. Undersampled projection reconstruction applied to MR angiography. Magn Reson Med. 2000;43(1):91-101.
2. Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Bornert P, et al. Advances in sensitivity encoding with arbitrary k-space trajectories. Magn Reson Med. 2001;46(4):638-651.
3. Johnson KM, Block WF, Reeder SB et al. Improved least squares MR image reconstruction using estimates of k-Space data consistency. Magn Reson Med. 2012;67(6):1600-1608.
4. Motosugi U, Bannas P, Bookwalter CA, et al. An Investigation of Transient Severe Motion Related to Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR Imaging. Radiology. 2016;279(1):93-102.
5. McClellan TR, Motosugi U, Middleton MS, et al. Intravenous Gadoxetate Disodium Administration Reduces Breath-holding Capacity in the Hepatic Arterial Phase: A Multi-Center Randomized Placebo-controlled Trial. Radiology. 2017;282(2):361-368.
6. Haradome H, Grazioli L, Tsunoo M, et al. Can MR fluoroscopic triggering technique and slow rate injection provide appropriate arterial phase images with reducing artifacts on gadoxetic acid-DTPA (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced hepatic MR imaging? J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;32(2):334-340.
7. Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sou H, et al. Dilution method of gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30(4):849-854.
Figures
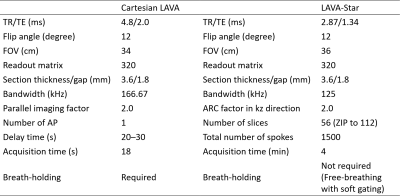
Fig. 1. Imaging parameters of Cartesian breath-hold LAVA and LAVA-Star.
In LAVA-Star sequence, total of 1500 radial spokes were acquired in 4 minutes continuously and 20 phases were reconstructed (12 s/phase) for routine frame rate reconstruction. The soft-gating, a retrospective gating technique, was used to suppress the image blur due to respiratory motion.
Abbreviations: LAVA, liver acquisition with volume acceleration; TR, repetition time; TE, echo time; FOV, field of view; ARC, auto-calibrating reconstruction for Cartesian sampling; AP, arterial phase.
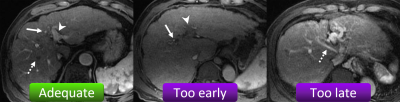
Fig. 2. Scan timing of the arterial phase (AP).
The adequate scan timing of the AP is when the hepatic artery and branches (arrow) and portal vein (arrowhead) are enhanced but the hepatic vein is not yet enhanced by antegrade flow (dotted arrow) (left image). If only the hepatic artery is enhanced (arrow), the scan timing is too early (middle image). If the hepatic vein is already enhanced (dotted arrow), the scan timing is too late (right image). Inadequate AP was defined as too early and too late scan timings.
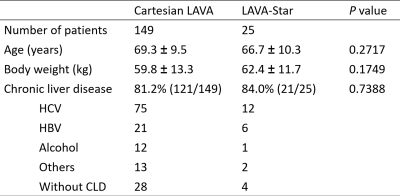
Fig. 3. Patients demographics.
There is no significant difference on patients’ background between two groups (P = 0.1749-0.7388).
Abbreviations: LAVA, liver acquisition with volume acceleration; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HBV, hepatitis B virus; CLD, chronic liver disease.
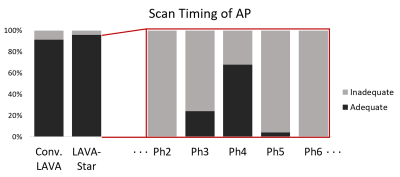
Fig. 4. The ratio of adequate scan timing of AP on each sequence and phase.
Inadequate scan timing of AP was observed 13 patients (8.7%, 13/149) in Cartesian breath-hold LAVA group, while only 1 patient (4.0%, 1/25) in LAVA-Star group showed inadequate scan timing of AP. In remaining 24 patients, the adequate scan timing of AP was observed in the 3rd phase (25.0%, 6/24), 4th phase (70.8%, 17/24), or 5th phase (4.2%, 1/24).
Abbreviations: AP, arterial phase; LAVA, liver acquisition with volume acceleration.
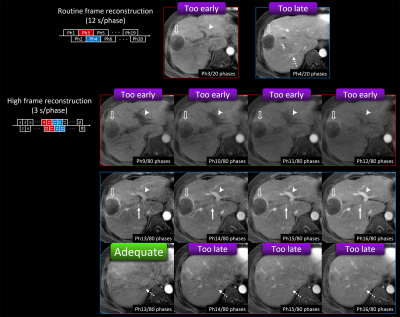
Fig. 5. Example of the utility of high frame rate reconstruction.
Adequate scan timing of AP was not observed on routine frame reconstruction (12 s/phase). Portal vein (arrowhead) was not enough enhanced in the 3rd phase and hepatic vein (dotted arrow) was already enhanced in the 4th phase. Optimal AP was obtained with high frame rate reconstruction (3 s/phase). Hepatic artery (arrow) and portal vein (arrowhead) were enhanced but the hepatic vein (dotted arrow) was not yet enhanced in the 13th phase only.
Open arrow shows metastatic liver tumor from pancreatic adenocarcinoma.