0279
Presurgical Mapping in Brain Tumors with High-Speed Resting-State fMRI: Comparison with Task-fMRI and Intra-Operative Mapping1Neurology, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM, United States, 2Neurosurgery, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM, United States
Synopsis
We investigated presurgical resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) in 9 patients with brain tumors using high-speed multiband-EPI (TR:400ms) with real-time data quality monitoring for seed-based localization of sensorimotor and language networks. The Euclidean distance between intra-operative electrocortical-stimulation (ECS) and rsfMRI connectivity and task-activation in motor cortex, Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas was 5-13mm, except for discordant rsfMRI localization of Wernicke’s area in one patient due to possible altered neurovascular coupling. A secondary objective was to accelerate encoding using echo-volumar-imaging. This study demonstrates the potential of high-speed rsfMRI for presurgical mapping and clinically-acceptable concordance with task-based fMRI and ECS localization.
Pre-operative task-based functional MRI (tfMRI) is often included in the battery of imaging studies for decision-making and operative planning to aid surgical resection of brain neoplasms, balancing long-term survival by maximizing the extent of resection while preserving the patient’s functional status1-4. However, dependence on patient’s task-compliance, which may be impaired due to disability, and the limited number of areas that can be mapped due to clinical time constraints impact the clinical utility of task-based fMRI (tfMRI). Resting state functional MRI (rsfMRI) is a promising task-free approach to delineate eloquent cortex5-11, which may complement and potentially replace tfMRI in patients who have difficulties performing required tasks12,13. However, rsfMRI is highly sensitive to head movement and physiological noise, and validation relative to tfMRI and intra-operative electrocortical mapping is still necessary14,15. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of presurgical mapping in patients with brain tumors comparing high-speed multi-band EPI (MB-EPI), which enables real-time rsfMRI analysis with online monitoring of data quality16, and recently developed high-speed multi-slab and multi-band echo-volumar imaging (MS-EVI, MB-EVI), which increases volume coverage and/or temporal resolution compared with multiband EPI. The objective was to map sensorimotor and language resting state networks in the vicinity of brain tumors and to validate this approach in comparison with tfMRI and intra-operative electrocortical-stimulation (ECS).
Methods
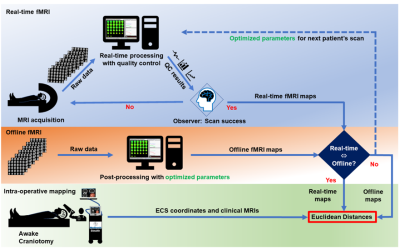
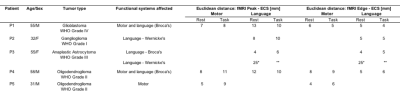
RsfMRI (eyes open, 5-10min) and tfMRI (3min per task) data were acquired in 9 patients (4F,5M) with brain tumors (2 glioblastomas, 2 gangliogliomas, 1 anaplastic astrocytoma, 3 oligodendrogliomas, 1 low grade glioma) as part of a multi-modal MRI protocol that included DTI and high-speed 3D proton-echo-planar-spectroscopic imaging using a 3T scanner equipped with 32-channel head coil. Informed written consent was obtained. Tasks were tailored to tumor location: motor (finger-tapping/fist-clenching), visual (eyes open/close), auditory (listening to syllables) and language (word/verb generation). Real-time fMRI was performed using MB-EPI (TR/TE: 400/35ms, multiband-acceleration:8, flip-angle:42o, voxel-size:(3mm)3, 32slices) and MS-EVI (TR/TE:246/30 ms, no.slabs:4, flip-angle:20o, voxel-size:(4mm)3, 29slices). MB-EVI (TR/TE:400/34ms, no.slabs:8, multiband-acceleration:2, flip-angle:40o, voxel-size:(3mm)3, 57slices) was reconstructed offline. Real-time and offline seed-based connectivity analysis (SCA) of 2 RSNs and task-based correlation analysis were performed using the TurboFIRE tool16,17. SCA was performed with 8s moving average temporal low pass filter, 15s sliding window correlation analysis with running mean, and sliding window regression of 6 rigid body motion parameters and signal time courses from WM and CSF ROIs. RSNs were mapped using unilateral Brodmann area (BA) based seed regions (sensorimotor: SMN–BA01-03, language: LAN-BA44,45 (Broca’s) and LAN-BA22,39,40 (Wernicke’s). Motion parameters, true/false positive connectivity, and task-activation were monitored online. Image guidance (Stealth Station Treon and S8; Medtronic Navigation, CO, USA) for the surgical approach was based on clinical task-based presurgical fMRI obtained separately. Intraoperative brain mapping was performed using electro-cortical stimulation (ECS) and continuous electrocorticography. ECS locations were mapped onto stereotactic MRI. The Euclidean distances between the peaks and edges of rsfMRI connectivity and task-activations with respect to intra-operative ECS were measured in motor and language areas.
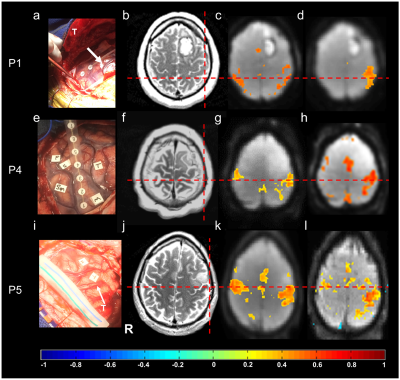
Results
Real-time monitoring of data quality enabled rapid optimization of scan protocols and seed selection, early identification of task non-compliance, and head movement related false-positive connectivity in white matter and at slice edges in all patients (Figure 1). Sensorimotor and language resting-state networks stabilized within 3-4 mins. A unilateral seed in BA1-3 contra-lateral to the tumor showed bilateral connectivity in primary motor areas with correlations ranging from 0.5 to 0.7 and in supplementary motor area (SMA) with correlations ranging from 0.3 to 0.5 (Figure 2). Resting-state language connectivity in Broca’s area was detected in all patients, predominantly left-lateralized and usually weaker than motor connectivity, necessitating a lower threshold of 0.3. Connectivity in Wernicke’s area was not detected in all patients, which may in part reflect cortical reorganization and/or impaired neurovascular coupling in these patients due to the proximity of the tumor. In patient 3, unexpected additional language connectivity in anterior insula was detected, which was retrospectively associated with a post-operative language deficit after resection. The Euclidean distance between the peaks of intra-operative ECS and rsfMRI connectivity and the peaks of ECS and task-activation in motor cortex, Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas in the first 5 patients was 5-13mm, except for discordant rsfMRI localization of Wernicke’s area in patient 3 due to possible altered neurovascular coupling and/or cortical reorganization (Table 1). Data analysis in patients 6-9 is in progress. Preliminary results show increased BOLD sensitivity of MB-EVI compared with MB-EPI (Figure 3).
Discussion
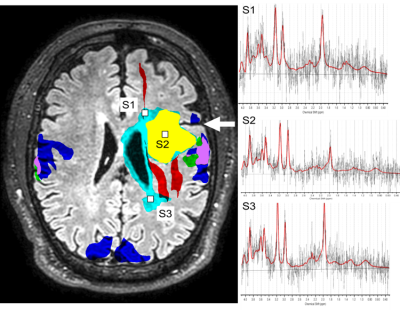
The data in patients show a high degree of consistency between resting state connectivity, task-based activation and ECS localization of motor cortex and Broca’s area. Localization of Wernicke’s area was more variable, both in rsfMRI and tfMRI, and in one case discordant with intra-operative ECS localization, which may in part reflect cortical reorganization. Limitations of this study include small number of patients studied and atlas-based seed selection, which needs to be adapted to possible cortical reorganization due to neuroplasticity. Future work will include integration of rsfMRI with tfMRI, DTI-based localization of peritumoral fiber tracts and MR spectroscopic imaging biomarkers of tumor borders to predict functional and oncological outcomes (Figure 4).
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge our patients for their time and effort participating in this study. Howard Yonas (Neurosurgery) graciously supported the initial phase of this project and provided guidance during the implementation of the research protocol. Dr. Brad Cushnyr conducted clinical fMRI scans. We thank Mona Chaney (Neurology) and Erin Semler (Neurosurgery) for their assistance with patient recruitment and Stacy Steadman (Neurosurgery) for facilitating data collection in the operating room. Kimball Malherbe (Medtronic Navigation, Inc) provided support for the Stealth workstation. We thank Catherine Smith and Diana South (Mind Research Network) for their expert support of MRI scanner operations.References
[1] D. J. Lee, N. Pouratian, S. Y. Bookheimer, and N. A. Martin, "Factors predicting language lateralization in patients with perisylvian vascular malformations. Clinical article," J Neurosurg, vol. 113, pp. 723-730, Oct 2010.
[2] A. Bizzi, V. Blasi, A. Falini, P. Ferroli, M. Cadioli, U. Danesi, D. Aquino, C. Marras, D. Caldiroli, and G. Broggi, "Presurgical functional MR imaging of language and motor functions: validation with intraoperative electrocortical mapping," Radiology, vol. 248, pp. 579-589, Aug 2008.
[3] J. J. Pillai and D. Zaca, "Relative utility for hemispheric lateralization of different clinical fMRI activation tasks within a comprehensive language paradigm battery in brain tumor patients as assessed by both threshold-dependent and threshold-independent analysis methods," Neuroimage, vol. 54 Suppl 1, pp. S136-145, Jan 2011.
[4] C. Giussani, F. E. Roux, J. Ojemann, E. P. Sganzerla, D. Pirillo, and C. Papagno, "Is preoperative functional magnetic resonance imaging reliable for language areas mapping in brain tumor surgery? Review of language functional magnetic resonance imaging and direct cortical stimulation correlation studies," Neurosurgery, vol. 66, pp. 113-120, Jan 2010.
[5] R. Li, K. Chen, A. S. Fleisher, E. M. Reiman, L. Yao, and X. Wu, "Large-scale directional connections among multi resting-state neural networks in human brain: a functional MRI and Bayesian network modeling study," Neuroimage, vol. 56, pp. 1035-1042, Jun 1 2011, 3319766.
[6] M. De Luca, C. F. Beckmann, N. De Stefano, P. M. Matthews, and S. M. Smith, "fMRI resting state networks define distinct modes of long-distance interactions in the human brain," Neuroimage, vol. 29, pp. 1359-1367, Feb 15 2006.
[7] M. D. Fox, A. Z. Snyder, J. L. Vincent, M. Corbetta, D. C. Van Essen, and M. E. Raichle, "The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks," Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, vol. 102, pp. 9673-9678, Jul 5 2005, 1157105.
[8] M. E. Raichle and A. Z. Snyder, "A default mode of brain function: a brief history of an evolving idea," Neuroimage, vol. 37, pp. 1083-1090; discussion 1097-1089, Oct 1 2007.
[9] V. Schopf, C. Windischberger, C. H. Kasess, R. Lanzenberger, and E. Moser, "Group ICA of resting-state data: a comparison," MAGMA, vol. 23, pp. 317-325, Dec 2010.
[10] A. Abou-Elseoud, T. Starck, J. Remes, J. Nikkinen, O. Tervonen, and V. Kiviniemi, "The effect of model order selection in group PICA," Hum Brain Mapp, vol. 31, pp. 1207-1216, Aug 2010.
[11] E. A. Allen, E. B. Erhardt, E. Damaraju, W. Gruner, J. M. Segall, R. F. Silva, M. Havlicek, S. Rachakonda, J. Fries, R. Kalyanam, A. M. Michael, A. Caprihan, J. A. Turner, T. Eichele, S. Adelsheim, A. D. Bryan, J. Bustillo, V. P. Clark, S. W. Feldstein Ewing, F. Filbey, C. C. Ford, K. Hutchison, R. E. Jung, K. A. Kiehl, P. Kodituwakku, Y. M. Komesu, A. R. Mayer, G. D. Pearlson, J. P. Phillips, J. R. Sadek, M. Stevens, U. Teuscher, R. J. Thoma, and V. D. Calhoun, "A baseline for the multivariate comparison of resting-state networks," Front Syst Neurosci, vol. 5, p. 2, 2011, 3051178.
[12] T. J. Mitchell, C. D. Hacker, J. D. Breshears, N. P. Szrama, M. Sharma, D. T. Bundy, M. Pahwa, M. Corbetta, A. Z. Snyder, J. S. Shimony, and E. C. Leuthardt, "A novel data-driven approach to preoperative mapping of functional cortex using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging," Neurosurgery, vol. 73, pp. 969-982; discussion 982-963, Dec 2013, PMC3871406.
[13] E. C. Leuthardt, M. Allen, M. Kamran, A. H. Hawasli, A. Z. Snyder, C. D. Hacker, T. J. Mitchell, and J. S. Shimony, "Resting-State Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent Functional MRI: A Paradigm Shift in Preoperative Brain Mapping," Stereotact Funct Neurosurg, vol. 93, pp. 427-439, 2015.
[14] K. R. Van Dijk, M. R. Sabuncu, and R. L. Buckner, "The influence of head motion on intrinsic functional connectivity MRI," Neuroimage, vol. 59, pp. 431-438, Jan 2 2012.
[15] T. D. Satterthwaite, D. H. Wolf, J. Loughead, K. Ruparel, M. A. Elliott, H. Hakonarson, R. C. Gur, and R. E. Gur, "Impact of in-scanner head motion on multiple measures of functional connectivity: Relevance for studies of neurodevelopment in youth," Neuroimage, vol. 60, pp. 623-632, 2012.
[16] S. Posse, E. Ackley, R. Mutihac, T. Zhang, R. Hummatov, M. Akhtari, M. Chohan, B. Fisch, and H. Yonas, "High-speed real-time resting-state FMRI using multi-slab echo-volumar imaging," Front Hum Neurosci, vol. 7, p. 479, 2013, 3752525.
[17] S. Posse, F. Binkofski, F. Schneider, D. Gembris, W. Frings, U. Habel, J. B. Salloum, K. Mathiak, S. Wiese, V. Kiselev, T. Graf, B. Elghahwagi, M. L. Grosse-Ruyken, and T. Eickermann, "A new approach to measure single-event related brain activity using real-time fMRI: Feasibility of sensory, motor, and higher cognitive tasks," Human Brain Mapping, vol. 12, pp. 25-41, Jan 2001.
Figures