0163
Model-based heterogenous transverse isotropic MR elastography inversion for brain tissue with aligned fiber tracts1Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH, United States, 2Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada, 3Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, MO, United States, 4University of Delaware, Newark, DE, United States, 5Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH, United States
Synopsis
An implementation of a transverse isotropic model with fiber directions defined by DTI was added to our finite element model-based nonlinear inversion MRE platform. The algorithm can recover accurate images of complex valued shear modulus, shear anisotropy, and tensile anisotropy from a realistic brain simulation. In vivo application to multi-excitation brain MRE data produced promising results, maintaining high quality images for the base shear modulus and damping ratio, while recovering additional images of anisotropy which may be useful for characterizing diseases affecting white matter tracts or muscle.
Introduction
MR elastography (MRE) produces images of mechanical properties, and has been successfully applied to many tissues, such as the liver [1] and brain [2]. Accurate treatment of heterogeneity has proven vital to successfully evaluate smaller brain structures such as subcortical grey matter [3]. While approaches which assume local homogeneity require excessive smoothing to overcome the model-data mismatch at tissue interfaces, model-based inversions such as nonlinear inversion can use heterogenous finite-element models and avoid these artifacts [4]. Another source of model-data mismatch comes from assuming mechanical isotropy in anisotropic tissues, such as aligned white matter tracts. Actuation direction-dependent artifacts of up to 26% have been demonstrated in white matter due to the isotropy assumption [5]. Although anisotropic MRE inversions have been proposed and demonstrated [6-10], local homogeneity assumptions limit performance of these techniques in the brain where heterogeneity is unavoidable. A heterogenous, anisotropic MRE approach is needed to accurately probe white matter tracts.Methods
The nearly incompressible transverse isotropic (NITI) model [10] for a fiber in the $$$x_1$$$ direction is described in Voigt notation by,$$\sigma_{i}=C_{ij} \epsilon_j$$,
$$c_{11}=\kappa+\frac{4}{3} \mu(1+\frac{4}{3}\zeta), c_{22}=c_{33}=\kappa+\frac{4}{3} \mu(1+\frac{1}{3}\zeta), c_{44}=c_{66}=\mu(1+\phi)$$
$$c_{12}=c_{13}=c_{21}=c_{31}=\kappa-\frac{2}{3} \mu(1+\frac{4}{3}\zeta), c_{23}=c_{32}=\kappa-\frac{2}{3} \mu(1+\frac{4}{3}\zeta), c_{55}=\mu$$
Important parameters in this model are the in-plane shear modulus, $$$\mu$$$ , shear anisotropy, $$$\phi$$$, and tensile anisotropy, $$$\zeta$$$. Transverse isotropic nonlinear inversion (TI-NLI) was created by incorporating the NITI model in a finite element based nonlinear inversion MRE algorithm [4], where spatially varying fiber directions are provided by the primary eigenvector from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). Heterogeneity of mechanical properties and defined fiber axes were supported on the finite element Gauss points to give the highest possible resolution of heterogeneity in the computational model. TI-NLI solves for four unknowns in the NITI model (complex-valued $$$\mu$$$ and real-valued $$$\phi$$$ and $$$\zeta$$$). MRE complex-valued 3D displacement amplitudes provide six measurements per voxel, which suggests that only one displacement set may be needed for TI-MRE at the data resolution; however, multiple displacement datasets provide more shear wave propagation and polarization directions which will help to accurately estimate $$$\phi$$$ and $$$\zeta$$$ [12]. A full-brain simulation with six subcortical grey matter regions and ten white matter tracts was used to demonstrate the inversion performance when the ground truth is available. Boundary conditions were assigned from MRE data to ensure realistic wavefields for the simulated data. Fiber directions were assigned from a DTI dataset, and the complex-valued shear modulus was assigned to each structure based on previous isotropic MRE studies. Grey matter structures were modeled as fully isotropic (), and $$$\phi$$$ and $$$\zeta$$$ for white matter tracts were assigned from DTI fractional anisotropy with a random multiplier between 0.9 and 1.1 to ensure the general case where $$$\phi$$$ and $$$\zeta$$$ are not equal. Two-excitation MRE data was collected in healthy subjects using a 3D multiband, multishot spiral MRE sequence [13] at 2 mm isotropic resolution, with 50Hz vibrations from the Resoundant actuator system applied separately at the back and the right of the head. The MRE scans were acquired sequentially with the same field-of-view, along with a co-registered DTI scan for determining fiber properties and T1-weighted anatomical image for structure localization. Repeat acquisitions on the same subjects were collected over three separate imaging sessions to gauge the repeatability of the anisotropic mechanical property estimates.
Results
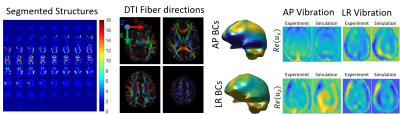
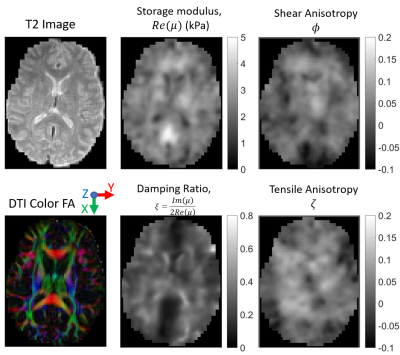
Figure 1 shows the simulated data used to test the TI-MRE algorithm has similar wavefields and geometry as experimentally-measured MRE brain data, so conclusions derived from this simulated model are applicable to in vivo MRE. Figure 2 shows TI-NLI inversions of simulated data, which demonstrate that spatially accurate images are recovered for all parameters, although the smoothing required for inversion stability limits the recovered contrast. An example case for in vivo TI-NLI is given in figure 3. Shear modulus and damping ratio images are similar to isotropic MRE. Reasonable values are recovered for the anisotropy parameters, and some symmetry and anatomic details are visible in the images. Repeatability of regional TI property estimates are shown in figure 4. The anisotropies have higher variation as they have lower sensitivity; however, it is promising that nearly all structures recovered positive values, which is expected as shear and tensile moduli should be larger along the fibers than transverse.Discussion
TI-NLI MRE was successfully implemented, validated in a realistic simulation, and tested in vivo. The approach has two potential advantages over isotropic MRE. First, reduction in model-data mismatch may improve standard shear stiffness and damping ratio images in aligned tissues such as white matter and muscle. Additionally, the mechanical anisotropy measurements may provide additional diagnostic parameters for disease that affect aligned tissue, analogous to the fractional anisotropy in DTI.Conclusion
TI-NLI MRE is a useful addition to the MRE toolbox with many potential applications. Future work will tune the regularization parameters to optimize resolution and repeatability for brain structures of interest, experimentally validate the recovered parameters in a phantom system compared to mechanical testing, and estimate the uncertainty in each parameter estimate based on the range of propagation and polarization directions in the displacement data.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grant R01-EB027577.References
[1] Kennedy, P., Wagner, M., Castéra, L., Hong, C.W., Johnson, C.L., Sirlin, C.B. and Taouli, B., 2018. Quantitative elastography methods in liver disease: current evidence and future directions. Radiology, 286(3), pp.738-763.
[2] Hiscox, L.V., Johnson, C.L., Barnhill, E., McGarry, M.D., Huston 3rd, J., Van Beek, E.J., Starr, J.M. and Roberts, N., 2016. Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) of the human brain: technique, findings and clinical applications. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 61(24), p.R401.
[3] Johnson, C.L., Schwarb, H., DJ McGarry, M., Anderson, A.T., Huesmann, G.R., Sutton, B.P. and Cohen, N.J., 2016. Viscoelasticity of subcortical gray matter structures. Human brain mapping, 37(12), pp.4221-4233.
[4] McGarry, M.D.J., Van Houten, E.E.W., Johnson, C.L., Georgiadis, J.G., Sutton, B.P., Weaver, J.B. and Paulsen, K.D., 2012. Multiresolution MR elastography using nonlinear inversion. Medical physics, 39(10), pp.6388-6396.
[5] Anderson, A.T., Van Houten, E.E., McGarry, M.D., Paulsen, K.D., Holtrop, J.L., Sutton, B.P., Georgiadis, J.G. and Johnson, C.L., 2016. Observation of direction-dependent mechanical properties in the human brain with multi-excitation MR elastography. Journal of the mechanical behavior of biomedical materials, 59, pp.538-546.
[6] Sinkus, R., Tanter, M., Catheline, S., Lorenzen, J., Kuhl, C., Sondermann, E. and Fink, M., 2005. Imaging anisotropic and viscous properties of breast tissue by magnetic resonance‐elastography. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 53(2), pp.372-387.
[7] Qin, E.C., Sinkus, R., Geng, G., Cheng, S., Green, M., Rae, C.D. and Bilston, L.E., 2013. Combining MR elastography and diffusion tensor imaging for the assessment of anisotropic mechanical propert ies: a phantom study. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 37(1), pp.217-226.
[8] Romano, A., Scheel, M., Hirsch, S., Braun, J. and Sack, I., 2012. In vivo waveguide elastography of white matter tracts in the human brain. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 68(5), pp.1410-1422.
[9] Namani, R., Wood, M.D., Sakiyama-Elbert, S.E. and Bayly, P.V., 2009. Anisotropic mechanical properties of magnetically aligned fibrin gels measured by magnetic resonance elastography. Journal of biomechanics, 42(13), pp.2047-2053.
[10] Guo, J., Hirsch, S., Scheel, M., Braun, J. and Sack, I., 2016. Three‐parameter shear wave inversion in MR elastography of incompressible transverse isotropic media: Application to in vivo lower leg muscles. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 75(4), pp.1537-1545.
[11] Tweten, D.J., Okamoto, R.J., Schmidt, J.L., Garbow, J.R. and Bayly, P.V., 2015. Estimation of material parameters from slow and fast shear waves in an incompressible, transversely isotropic material. Journal of biomechanics, 48(15), pp.4002-4009.
[12] Tweten, D.J., Okamoto, R.J. and Bayly, P.V., 2017. Requirements for accurate estimation of anisotropic material parameters by magnetic resonance elastography: a computational study. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 78(6), pp.2360-2372.
[13] CL Johnson, JL Holtrop, AT Anderson, BP Sutton, “Brain MR Elastography with Multiband Excitation and Nonlinear Motion-Induced Phase Error Correction,” 24th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Singapore, May 7-13, 2016, p. 1951.
Figures