1003
Whole lesion IVIM analysis in the diagnosis of thyroid tumor: Comparison with Conventional Diffusion-Weighted ImagingYunlong Yue1, Minghui Song1, Yanfang Jin1, Jinsong Guo1, Lili Zuo1, Queenie Chan2, and Zhenchang Wang3
1MR Department, Beijing Shijitan Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Hong Kong, China, 3Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Synopsis
To compare the diagnostic efficiency of IVIM parameters and conventional DWI (b=600 and b=990) derived from 3D whole-lesion (W-L ROI) delineation. Forty-three patients with 46 pathologically confirmed thyroid nodules were involved. According to ROC curve, D, f, ADC600 and ADC990 values showed diagnostic significance with the AUC values of 0.962, 0.756, 0.970 and 0.939 respectively. Furthermore, the Youden index of D value (0.871) was higher than that of ADC600 (0.826). IVIM is a more promising tool in the differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules using W-L ROI delineation than conventional DWI.
Introduction
Imaging examination methods for the thyroid include morphological and functional imaging; however, morphological evaluation lacks a single quantitative criterion, and multiple imaging features need to be considered. Of these functional imaging techniques, previous literature demonstrated the potential of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) to distinguish benign from malignant thyroid nodules, However, some recent meta-analyses have shown that the diagnostic threshold results have considerable variability (0.36–2.56 × 10-3 mm2/s) . Recently, some studies demonstrated interobserver reproducibility of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) using 3D whole-lesion (W-L) ROI was better than single slice analysis. Our previous research showed that W-L ROI IVIM analysis may aid in the differentiation of malignant and benign thyroid nodules1. To the best of our knowledge, the difference in diagnostic efficacy of IVIM and conventional DWI using W-L ROI delineation to distinguish thyroid nodules has not been reported.Purpose
This study aimed to compare the diagnostic performance of IVIM parameters with ADC from conventional DWI derived from W-L ROI in the differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid lesions.Methods
Forty-three patients (6 men, 37 women; mean age, 42 ± 11 years; age range, 18-68 years) with 46 pathologically confirmed thyroid nodules were involved. All patients underwent preoperative examinations (Philips 3.0T Ingenia, Philips Medical System, The Netherlands) with conventional imaging and reduced FOV DWI sequence using an 8-channel carotid coil. A reduced FOV DWI examination using a 2D RF excitation for shorter echo train length to decrease the distortion was scanned with following parameters: TE/TR 69/1400ms; FOV 160x47mm; acquisition matrix 108x30; slices thickness 5mm and 1mm gap; NSA 4. Eight b values (0, 20, 50, 100, 200, 400, 600, 990) were used for IVIM. The non-linear fitting of the bi-exponential model for IVIM analysis and mono-exponential fitting of the signal intensity using b = 0 s/mm2, 600 s/mm2, and 990 s/mm2 for ADC600 and ADC900 respectively were performed on Matlab. 3D W-L ROI was manually drawn on multiple slices to cover the whole nodule by two observers who were blinded to the clinical and histopathological data. The diffusion coefficient (D), pseudodiffusion coefficient (D*), and perfusion fraction (f) values derived from IVIM and ADC values derived from conventional DWI were measured. The mean values of all parameters in the malignant group and the benign group were compared by independent samples t-tests. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to evaluate the diagnostic performance of these parameters. All statistical analyses were performed using MedCalc Online, version 16.2 (Medcalc Software, Mariakerke, Belgium) and SPSS (18.0 for Windows, SPSS, Chicago, IL). A P value < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference.Results
The pathological findings confirmed 24 benign nodules and 22 malignant nodules. The D , f , ADC600 and ADC990 values showed significance difference between malignant and benign nodules, while D* values showed no significant difference (Table 1). D, f, ADC600 and ADC990 showed diagnostic significance with AUC of 0.962, 0.756, 0.970 and 0.939 respectively (Figure 1-3). D and ADC600 values achieved the highest AUC for differentiating malignant thyroid nodules from benign ones and there was no significant difference between them (Z=0.771, p>0.05). Furthermore, the Youden index of D value (0.871) was better than that of ADC600 (0.826) (Table 2).Discussion
Compared to conventional DWI model, IVIM with a biexponential model has the ability to separate tissue pure diffusion from microcapillary perfusion. Some studies have indicated that the IVIM model exhibits better diagnostic performance than ADC values using single slice ROI analysis2-4. This study demonstrated that quantitative analysis of conventional DWI and IVIM parameters could be helpful in discriminating benign and malignant thyroid lesions with the use of W-L ROI analysis. Additionally, compared with conventional DWI, the diagnostic accuracy of D was better than that of ADC value. No statistically significant between AUC of D and ADC may partly result from the smaller sample size of this study. The result also showed that ADC values were higher than D values, which might be related to the influence of internal perfusion factors and is consistent with the findings of other studies involving the head and neck.Conclusion
IVIM using W-L ROI delineation is a more promising tool in the differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid lesions than ADC from conventional DWI, and it still needs larger prospective studies to further validate them.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
- Song M, Jin Y, Guo J, et al. Application of whole-lesion intravoxel incoherent motion analysis using iZOOM DWI to differentiate malignant from benign thyroid nodules. Acad Radiol, in press, 2018.
- Tan H, Chen J, Zhao YL, et al. Feasibility of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion for Differentiating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules. Acad Radiol. 2018 Jun 13. pii: S1076-6332(18)30250-2. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2018.05.011.
- Xiao Z, Tang Z, Qiang J, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging in the differentiation of benign and malignant sinonasal lesions: comparison with conventional diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2018;39(3):538–546.
- Wu H, Zhang S, Liang C, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI for the differentiation of benign, intermediate, and malignant solid soft-tissue tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;46(6):1611-1618.
Figures
Table
1.
Comparison of IVIM parameters and ADC value between
benign and malignant groups.

Figure
1. Images of a 36-year-old man with right lobe nodular goitre (central part
with cystic necrosis). a. Axial T2-weighted image. b. DWI with b = 0 s/mm2.
c-d ADC map with b = 600 s/mm2 and 990 s/mm2 respectively.
e-g. IVIM colour map (from left to right representing D, f, and D*).
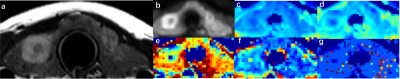
Figure 2: Images of a
27-year-old man with right lobe papillary thyroid cancer. a. Axial T2-weighted
image. b. DWI with b = 0 s/mm2. c-d. ADC map with b = 600 s/mm2
and 990 s/mm2 respectively. e-g. IVIM colour map (from left to right
representing D, f, and D*).
Figure 3. ROC curve analysis for discriminating
malignant from benign thyroid nodules with D, f, ADC600 and ADC990.
Table 2. Diagnostic performance of IVIM parameters and ADC value
for distinguishing benign
and malignant thyroid nodules.