5474
A support vector machine-based method to identify non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus with Regional Homogeneity1Medical Imaging Center, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 2Medical apparatus and equipment deployment, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China, 4Department of Dermatology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
Previous studies found that changes in brain function happened in default mode network beforeNeuropsychiatric involvement (NPSLE) development by using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI), highlighting the need for early evaluation and intervention in SLE patients. In this study, we proposed a valid Support Vector Machine (SVM) -based method to identify non-NPSLE using regional homogeneity (ReHo). The results demonstrate that ReHo parameter is an effective classification feature for the SVM-based method to identify SLE patients from healthy subjects.
Introduction
Neuropsychiatric involvement (NPSLE) is the least understood manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and is associated with widespread of clinical presentations[1]. Diagnosis of NPSLE focuses primarily on psychological manifestations, and the underlying mechanisms leading to neuropsychiatric complications remain unknown[2]. Previous studies found that changes in brain function happened in default mode network before NPSLE development by using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI), highlighting the need for early evaluation and intervention in SLE patients[3]. In this study, we proposed a valid SVM-based method to identify non-NPSLE using regional homogeneity (ReHo).Method
Forty-five non-NPSLE patients were recruited from the Inpatient Units of the Development of Rheumatology. In addition, 36 age- and gender-matched healthy subjects were recruited as the healthy controls with no history of neurologic or psychiatric disease. The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board and all participants provided signed informed consent . All MRI datasets were acquired on a 3.0 T Philips Medical Achieva Systems MR scanner with an 8-channel head coil. The rs-fMRI dataset was acquired with an EPI sequence (TR = 2,000 ms, TE = 35 ms, FA = 90°, FoV = 230 × 230 mm2, data matrix = 64 × 64, slice thickness/gap = 3.6 mm / 0.7 mm, 33 transverse slices covering the whole brain, and 240 volumes acquired in 8 min). The ReHo index of the pro-processed rs-fMRI was calculated using Kendall’s coefficient of concordance (KCC) firstly. Then all the ReHo mappings for all subjects were translated into zReHo mappings by using a z-transformation. Next, the average zReHo values of 90 regions of interest (ROIs) in automated anatomical labeling (AAL) atlas were compared between non-NPSLE and HC groups by using two-sample two-tailed-t test (P<0.05, uncorrected) and Fisher score criteria that indicated the identification ability of the feature to some degree by calculating its Fisher score value. At last, the abnormal zReHo values were adopted as the classification feature for a support vector machine (SVM)-based method, which utilized the radial basis function (RBF) as the kernel function, optimized two parameters of SVM with grid-search method, and estimated the classification performance with leave one out cross validation (LOOCV), to identify non-NPSLE patients from healthy subjects.Results
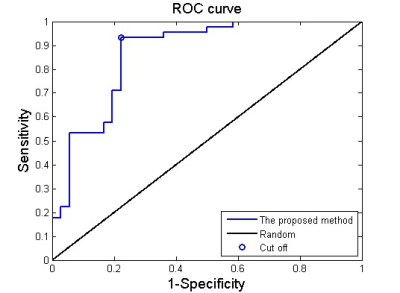
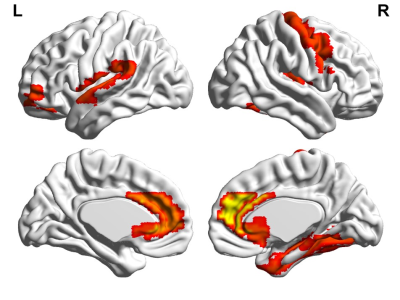
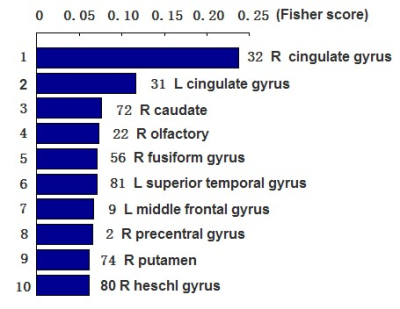
Our results obtained 86.2 % accuracy, 93.3% sensitivity and 77.8% specificity, and an area under curve (AUC) of 0.87 (Figure 1), suggesting that the proposed classification method could effective identify non-NPSLE patients from healthy subjects. Besides, the abnormal zReHo brain regions were predominately involved in bilateral cingulate gyrus, right caudate, right fusiform gyrus, right putamen, left middle frontal gyrus, left superior temporal gyrus, right olfactory, right precentral gyrus and heschl gyrus, and the detailed results are displayed in Figure 2. The Fisher score values of these abnormal features are shown in Figure 3.Conclusion
The ReHo parameter is an effective classification feature for the SVM-based method to identify non-NPSLE patients from HC subjects, which suggested that the proposed classification method is a promising approach for improving the clinical diagnosis of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus and revealing the underlying mechanism neuropsychiatric complications.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Mikdashi JA. Altered functional neuronal activity in neuropsychiatric lupus: A systematic review of the fMRI investigations. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2016; 45(4): 455-462.
2. Zardi EM, Taccone A, Marigliano B, Margiotta DP, Afeltra A. Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: tools for the diagnosis. Autoimmun Rev 2014; 13(8): 831-839.
3. Lin Y, Zou QH, Wang J, Wang Y, Zhou DQ, Zhang RH, Zhang YW, Lii HT, Fang YF. Localization of cerebral functional deficits in patients with non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Brain Mapp 2011; 32(11): 1847-1855.