5398
Diffusion weighted T2-mapping for the determination of tissue characteristics in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma1Hokkaido University Hospital, Sapporo, Japan, 2Philips Electronics Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Healthcare Korea, Seoul, Korea, Democratic People's Republic of
Synopsis
We investigated the utility of T2 mapping with the pre-pulse of diffusion gradient (DW T2-map) for the determination of tissue characteristics in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Significant difference in T2-value of tumor tissue between that with and without diffusion gradient was observed. In addition, DW T2-map was suggested to be one of the diagnostic tool for the prediction of tumor histological grade. DW T2-map can be useful tool for the assessment of tumor tissue characteristics with greater detail.
Purpose
The T2 relaxation time reflects numerous tissue characteristics1. Measurement of T2 value enables to quantitative evaluation for the property of numerous substances in the target tissue, including cancer. In general, T2 map can be obtained pixel by pixel basis. However, there are various components in each pixel such as the intracellular space, extracellular-extracellular space and perfusion fraction. Measured T2 value in each pixel by conventional pixel by pixel basis T2 mapping was considered to be obtained as a mixed and averaged value between various T2 values in multiple components in the tissue. In contrast, diffusion gradient as a use for pre-pulse can result in signal loss according to the degree of the water diffusivity in various components, introduced as diffusion weighted imaging. By using a certain degree of diffusion gradient (i.e. various b-value) as pre-pulse, roughly separation of diffusion based tissue component such as intracellular and extracellular space may be accomplished. Therefore, T2-map with the diffusion gradient pre-pulse is expected to provide component-selectively T2 value, and this can visualize the tissue characteristics with greater detail compared to the conventional method. The purpose of this study was to assess the utility of T2 mapping with the pre-pulse of diffusion gradient (=DW-T2 map) for the determination of tissue characteristics in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).Methods
1) Subjects
Fourteen patients with HNSCC were included in this study. Details of these volunteers were as follows; 12 males and 2 females (median 53 years, range 48–71 years), primary lesions of maxillary sinus in 1 patients, oral cavity in 7 patients and pharynx in 4 patients. The histopathological diagnoses were SCC in all patients. In all patient, tumor histological grade (well- or moderately-differentiated and poorly differentiated SCC) were determined from their tumor specimen.
2) MR scanning
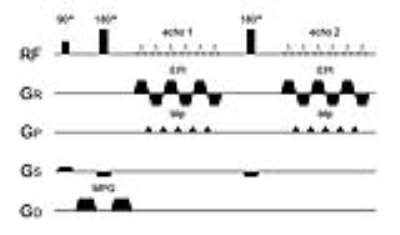
All patients were scanned on a 3 Tesla MR scanner (Achieva TX; Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) with a 16-channel neurovascular coil. DW-T2 map used spin-echo EPI with TR=5268 ms, TE1=42.5 ms, TE2=130ms, slice thickness=5mm, matrix=112 x 168 (reconstructed to 256 x 256), FOV=240 240mm. The scanning range of DW-T2 map acquisitions were planned to cover the whole tumor lesion. Two scans with various diffusion gradient (b-values of 0 and 1000 s/mm2) were acquired after the 90° excitation pulse and 180° refocusing pulse (Fig.1).
3) Data analysis
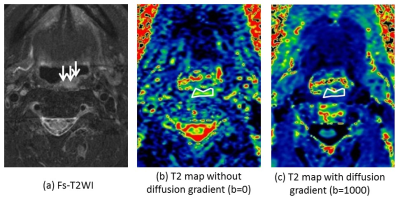
In each T2-map with b-value 0 and 1000, manual regions of interest (ROI) was placed corresponding to the tumor lesion manually by referring the conventional post contrast T1WI and fat-suppressed T2WI. After that, each T2 value in the tumor was determined as mean value in the ROI. Finally, T2-value with b=0 (T2b0) and T2-value with b=1000 (T2b1000) were respectively obtained in each patient. In addition, degree of difference between T2-values of two different b-values (i.e. absolute value of T2b0- T2b1000) was also calculated as ‘T2diff’. Example case was presented in Fig.2.
4) Statistical analysis
First, the comparison between T2b0 and T2b1000 in all tumor was performed by using paired t-test. Next, patients were divided into two groups based on their histological grade as well- or moderately-differentiated SCC group (well/mod-SCC group) and poorly-differentiated SCC group (poor-SCC group). The T2b0 value was compared between patients of well/mod-SCC group and poor SCC-group. T2b1000 value was also compared between patients of well/mod-SCC group and poor-SCC group. Finally, T2diff was compared between patients of well/mod-SCC group and poor-SCC group. All comparison between well/mod-SCC group and poor-SCC group was performed by Mann–Whitney U test.
Results
In all tumors, T2b0 (78.5±22.2 ms) was significantly higher than T2b1000 (72.3±18.8 ms). For the comparison of tumor histological grade, T2b0 was not significantly different between patient with well/mod-SCC group (79.7±18.5 ms) and poor-SCC group (77.8±16.2), and T2b1000 was not also significantly different between patient with well/mod-SCC group (73.6±14.9) and poor-SCC group (71.5±10.2). In contrast, T2diff was significantly larger in well/mod-SCC group (7.3±3.7 ms) than poor-SCC group (1.6±1.3 ms) (p<0.05).Discussion and conclusion
This study revealed the significantly difference between T2-values with and without diffusion gradient pre-pulse in the tumor tissue of the head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Such difference may reflect the tissue component selectivity by the diffusion gradient such as cellular space. This imaging technique can visualize the cancer cell characteristics such as degree of the cellular space ratio, intracellular viscosity and the degree of containing the polymer compound, etc in greater detail. In addition, tumor histological grade can be divided by the information of the degree of the decrease in T2 value between that with and without diffusion gradient. This information may be useful for the prediction of the histological grade in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Acknowledgements
NoneReferences
1. Herfkens R, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of the abnormal live rat and correlations with tissue characteristics. Radiology. 1981 Oct;141(1):211-8.Figures