5360
The diagnostic capability of diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in distinguishing cervical lymphoma from nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastases1Fujian Medical University Cancer Hospital, Fuzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
In our prospective study, We compared DKI and DWI related parameters in order to investigate the diagnostic capability of DKI in distinguishing cervical lymphoma from nasopharyngeal carcinoma(NPC) metastases. The ROC curve showed that K value of DKI had no significantly diagnostic capability, whlie D value of DKI had a better diagnostic performance than the ADC value of DWI in distinguishing the cervical lymphoma from the NPC metastases. Therefore, DKI may be a better noninvasive imaging biomarker for distinguishing the lymphoma and NPC metastases involving the head and neck.
Introduction & purpose
The performance of Lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) metastases involving the head and neck is non-specifical location, clinical manifestations and imaging appearances. Sometimes it is difficult to identify by morphological changes acquired from conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) is a functional MRI technique, which provides quantitative information of water motion using Gaussian distribution model. But the actual water diffusion in vivo follows non-Gaussian distribution due to the restriction of complicated microstructures. Therefore, using Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) model may more appropriate to descibe the real water diffusion behavior and provide additional information1. Our study aimed to investigate the diagnostic performance of DKI for distinguishing lymphoma and NPC metastases involving the head and neck, compared to the conventional DWI.Materials and Methods
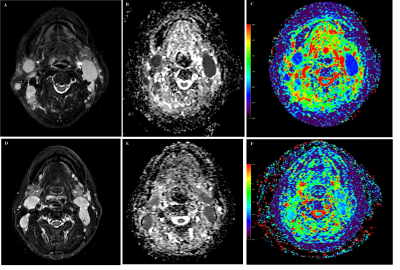
30 patients with lymphoma (mean age: 54±16 years) and 44 patients with NPC metastases (mean age: 47±12 years) were enrolled prospectively, all patients were pathologically confirmed. 37 volunteers were enrolled (mean age: 37±10 years) as the control group (benign lymph nodes). All subjects were accepted DKI and DWI scan at 3.0 Tesla MRI (Achieva TX, Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) using a 16-channel neurovascular head and neck coil (NV-16). Axial DWI and DKI was performed using a fat-suppressed single-shot echo-planar imaging (SS-EPI) sequence, scanning parameters for DWI were: echo time (TE) = 70 msec, repetition time (TR) = 6896 msec, field of view (FOV) = 240 mm, slice thickness = 5 mm, number of slices = 36, number of signal averages (NSA) = 2, b values = 0, 800 sec/mm2, scan time = 1:39 (min). For DKI were: TE = 69 msec, TR = 4190 msec, FOV = 250 mm, slice thickness = 5 mm, number of slices = 18, NSA = 2, b values = 0, 500, 1000, 1500, 2000 sec/mm2, scan time = 4:33 (min). The Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value, diffusion coefficient (D) value and kurtosis (K) were measured and compared among three groups. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was analyzed to evaluate the diagnostic capability of ADC, D and K.Results
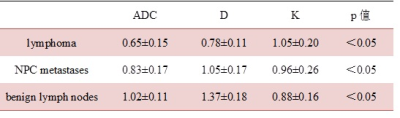
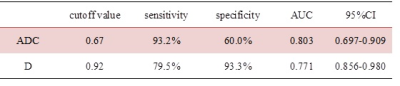
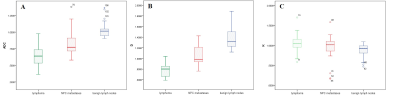
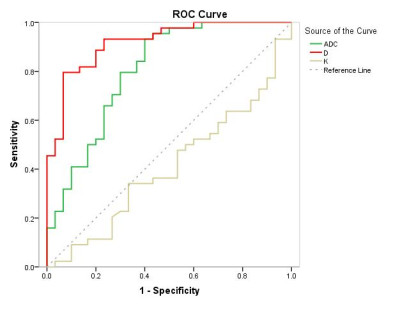
ADC and D values of lymphoma were significantly lower than in the NPC group (0.65±0.15 vs. 0.83±0.17×10-3mm/s2 and 0.78±0.11 vs. 1.05±0.17×10-3mm/s2, respectively, p<0.05), lower than benign lymph nodes (1.02±0.11×10-3mm/s2) (Table 1, Figure 1, 2). While the K values of lymphoma were significantly higher than in the NPC metastases (1.05±0.20 vs. 0.96±0.26, p<0.05), higher than benign lymph nodes (0.88±0.16) (Table 1, Figure 1). ROC curve indicated the area under the curve (AUC) of K value was 0.408. ROC curve analyses yielded a cutoff ADC value of 0.67×10-3mm/s2 for diagnosing of lymphoma, with a sensitivity of 93.2%, a specificity of 60.0%; a cutoff D value of 0.92×10-3mm/s2, with a sensitivity of 79.5%, a specificity of 93.3%. The AUC of D value was significantly larger than that of ADC value (0.918 vs. 0.803, P<0.05). ( Table 2, Figure 3).Discussion
Theoretically, DKI is more accurately to reflect the actual dispersion of water molecules in the body based on non-Gaussian distribution model2. Our results showed that the K value had no significantly diagnostic capability, whlie D value had a better diagnostic performance than the ADC value in distinguishing the lymphoma from the NPC and benign lymph nodes.Conclusion
The DKI model may be superior to conventional DWI as a noninvasive imaging biomarker for distinguishing the lymphoma and NPC metastases involving the head and neck.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Yuan J, Yeung D K, Mok G S, et al. Non-Gaussian analysis of diffusion weighted imaging in head and neck at 3T: a pilot study in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Plos One. 2014;9(1):e87024.
2. Minosse S, Marzi S, Piludu F, et al. Correlation study between DKI and conventional DWI in brain and head and neck tumors. Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2017;42:114.
Figures