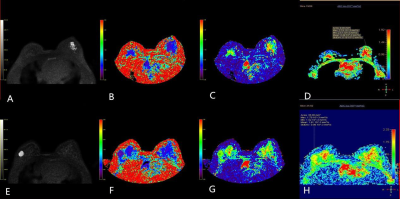
5358
Comparative study of DKI model and traditional DWI model in diagnosis of breast cancer1Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai, China, 2PhilipsHealthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
The aim of this study is to compare the value of diffusion kurtosis imaging model with traditional single-index diffuse weighted imaging model parameters in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions. The rusults showed that the parameters of DKI model and traditional DWI model can be used to differentiate benign and malignant breast lesions. The diagnostic value of MK value in DKI model is the largest. There is a certain correlation between DKI model parameters and prognostic factors.
Objective
To compare the value of diffusion kurtosis imaging model with traditional single-index diffuse weighted imaging model parameters in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions, and to explore the correlation between the parameters and molecular subtypes and prognostic factors of breast cancer.Methods
64 cases of breast lesions were examined by DKI (b = 0,500,1000,1500,2000,2500,3000 s / mm2) and traditional DWI (b = 0,1000 s / mm2). To compare the diagnostic efficacy of DKI parameters (MK and MD) and traditional DWI parameters (ADC) in benign and malignant breast lesions, and to analyze the correlation between MK, MD and ADC values and molecular subtypes and prognostic factors of breast cancer.Results
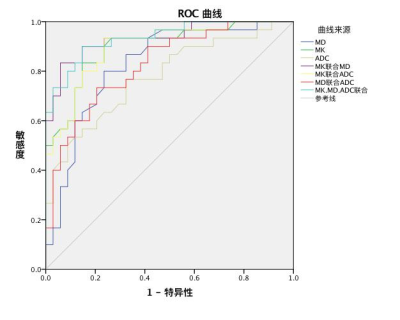
The difference of MK, MD and ADC between the benign and malignant groups was statistically significant (P <0.05). The area under the ROC curve of MK, MD and ADC was 0.897, 0.827 and 0.776, respectively. According to the Youden index, the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of the MK were 83.3%, 85.3% and 84.4% respectively. The combination of the three parameters could increase the AUC to 0.935. The MK of ER positive lesions were higher than negative (P = 0.024). The correlation analysis showed that ER was low positively correlated with MK (r = 0.417, P = 0.022), and there was no significant correlation between the other prognostic factors and the parameters (P> 0.05). There were no significant differences in DKI and DWI parameters between the subtypes (P> 0.05).Conclusion
The parameters of DKI model and traditional DWI model can be used to differentiate benign and malignant breast lesions. The diagnostic value of MK value in DKI model is the largest. There is a certain correlation between DKI model parameters and prognostic factors.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Partridge SC, McDonald ES. Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: protocol optimization, interpretation, and clinical applications. Magnetic resonance imaging clinics of North America 2013;21:601-24. PMID: 23928248
2. Kato F, Kudo K, Yamashita H, et al. Differences in morphological features and minimum apparent diffusion coefficient values among breast cancer subtypes using 3-tesla MRI. European journal of radiology 2016;85:96-102. PMID: 26724653
3.Bickelhaupt S, Laun FB, Tesdorff J, et al. Fast and Noninvasive Characterization of Suspicious Lesions Detected at Breast Cancer X-Ray Screening: Capability of Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging with MIPs. Radiology 2016;278:689-97. PMID: 26418516 4. Zaric O, Pinker K, Zbyn S, et al. Quantitative Sodium MR Imaging at 7 T: Initial Results and Comparison with Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Patients with Breast Tumors. Radiology 2016;280:39-48. PMID: 27007803
5.Nogueira L, Brandao S, Matos E, et al. Application of the diffusion kurtosis model for the study of breast lesions. European radiology 2014;24:1197-203. PMID: 24658871
6.Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic resonance in medicine 2005;53:1432-40. PMID: 15906300
7.Sun K, Chen X, Chai W, et al. Breast Cancer: Diffusion Kurtosis MR Imaging-Diagnostic Accuracy and Correlation with Clinical-Pathologic Factors. Radiology 2015;277:46-55. PMID: 25938679
8.Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, et al. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2009;101:736-50. PMID: 19436038
9.Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, et al. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology / ESMO 2013;24:2206-23. PMID: 23917950
10.Pang H, Ren Y, Dang X, et al. Diffusional kurtosis imaging for differentiating between high-grade glioma and primary central nervous system lymphoma. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI 2016;44:30-40. PMID: 26588793
Figures