5315
Meta-analysis of Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Major Depressive Disorder137#Guoxue lane, Huaxi Magnet Resonance Imaging(HMRRC),Department of Radiology,West China Medical School of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Synopsis
To investigate the most reliable resting-state functional connectivity(rsFC) abnormalities in adult dignosed as having major depressive disorder(MDD) with existing studies.After a comprehensive literature search of studies, meta analysis was conducted using Signed Differential Mapping(SDM) software package. We found dysfunction in large-scale brain regions in MDD patients, including hyperconnectivity in fronto-cingulate-parietal area and hypoconnectivity in bilateral superior temporal gyrus(STG). These findings paralleled to the core feature of MDD patients and may underlie the cognitive and affective abnormalities in depressive disorder.
Purpose
MDD is the second leading cause of disability worldwide.1 As reported by prior studies,MDD has been linked to abnormal rsFC in multiple brain regions. However, consistence among studies has not yet to come, so it’s significant to conduct a quantitative integration of rsFC studies to address the alteration of neural connectivity in MDD. Considering age would be a confounding factor and the developmental period of neural system would extend to 24 years old, thus, we conduct this meta analysis focusing on adult older than 24 but younger than 60.Materials and Methods
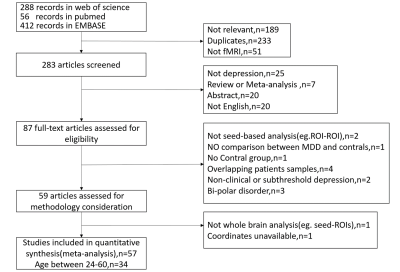
Study selection: We conducted a comprehensive literature search of studies comparing seed based rsFC difference between MDD adult and control participants published before November 2017 in Pubmed,Web of Science and EMBASE.The search key words were“depress*(-ion,ive)” , “seed*(s)”, “rest*(-ing)”,and “connect*(-ivity)”.We only keep the literatures that in coordinate with our criterias.( Figure1.)
Data extraction and synthesis:We use Signed Differential Mapping(SDM) software package to conduct meta-analytical differences calculation in global level. First,coordinates of brain regions exhibiting different rsFC in adult with MDD compared with control participants were extracted manually. Second, the difference in rsFC in each study map is recreated with a standard Talairach separately by means of a Gaussian kernel.Third,after a mean of these study maps by voxelwise calculation,the mean map is obtained.
Meta-regression and subgroup analysis: We also conducted meta-regression with Hamilton Depression Scale(HAMD) sores and subgroup analysis according to seeds regions.
Results
Included studies:57 studies assessed for eligibility after being selected and screened from 756 primary records. After limiting the range of age between 24 and 60,34 studies with 39 datasets, including 1123 MDD patients and 1092 controls were retained for this meta analysis.(Figure1.)
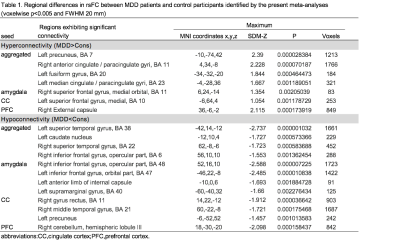
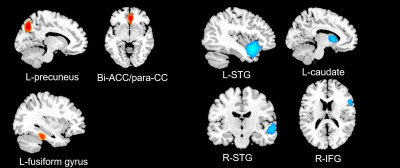
Aggregated seeds: In general, adult MDD patients were associated with hyperconnectivity in bilateral precuneus, orbital median PFC extending to median/anterior cingulate cortex(ACC),posterior cingulate cortex(PCC) extending to paracingulate gyrus and fusiform gyrus.MDD patients also demonstrated decreased rsFC in bilateral superior temporal gyrus(STG),besides,the right STG clusters were extended from right inferior frontal gyrus(R-IFG).In addition, decreased rsFC in left caudate was detected. (Table1. and Figure2.)
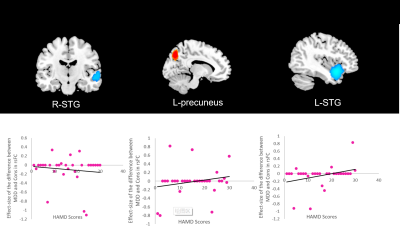
Meta-regression analysis:In 30 datasets of 868 MDD patients with available HAMD scores, a meta regression is performed to assess the correlation between HAMD scores and regions showing abnormal rsFC. HAMD scores positively correlated with rsFC in the left precuneus and L-STG and negtively correlated with rsFC in the R-STG. (Figure3.)
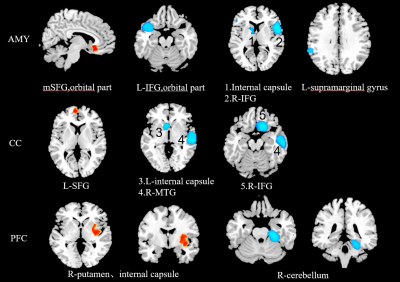
Subgroup analysis: subgroup analysis according to seed regions including amygdala, cingulate cortex(CC) and prefrontal cortex(PFC) revealed reduced rsFC in temperal gyrus(TG) and IFG when seeds were in amygdala and CC. In addition, seed with PFC showed significant increased connectivity in right striatum and internal capsule and declined connectivity from right median ITG extending to cerebellum.(Table1. and Figure4.)
Discussion&Conclusion
This meta analysis provides evidence that adult with MDD exhibit abnormal connectivity in fronto-cingulate-parietal areas, temporal lobe areas, as well as part of basal-ganglia areas.Those regions are implicated in executive control processes.Particularlly,IFG,mPFC,ACC and PCC within the fronto-cingulate-parietal areas are highly correlated with affective cognition;striatum within basal-ganglia areas is associated with reward processing. Besides,we found that HAMD scores are correlated with rsFC abnormalities in bilateral STG and left precuneus,which suggests that these regions are related to MDD symtoms.
Interestingly, consistent hyperconnectivity were found between amygdala and CC seeds and SFG,a region involved in self-awareness. Hypoconnectivity between amygdala and IFG(extremely important for language comprehension and production), anterior limb of the internal capsule(projecting fibers from frontal cortex to pons and thalamas) and supramarginal gyrus (part of the somatosensory association cortex) indicates decline of these functions.
PFC seeds FC shown hyperconnectivity with right striatum part and right cerebellum.The three regions form the frontal-striatum-cerebellum circuit that associate with reward mechanism.2 We infer dysfunction in this circuit may underlie the self-guilt and self-condemn of MDD.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.World Health Organization.Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2009.
2.Covington, H.E et al. Antidepressant effect of optogenetic stimulation of the medial prefrontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 2010;30, 16082–16090.
Figures