5301
Reduced White Matter Integrity Related with Elevated Inflammatory Cytokine Expression and Cognitive Impairments in First-episode Schizophrenia: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study Based on Tract-Based Spatial Statistics1Department of MRI Diagnosis, Shannxi Provincial People's Hospital, Xi'an, China, 2Department of Psychiatry, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China, 3Department of Diagnostic Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China, 4Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
This study aimed to investigate whether elevated inflammatory cytokine expression induced white matter integrity changes and cognitive impairments in first-episode schizophrenia patients. 27 first-episode schizophrenia patients and 16 healthy controls who underwent diffusion tensor imaging were enrolled. Tract-based spatial statistics analysis exhibited significantly decreased fractional anisotropy and increased radial diffusivity in widespread white matter tracts in patients. Of these tracts, anterior corona radiata (ACR), superior corona radiata, superior longitudinal fasciculus, the body of the corpus callosum, the splenium of the corpus callosum and fornix showed significant correlations with higher inflammatory cytokine expression. Moreover, ACR and fornix simultaneously showed reduced white matter integrity related to cognitive impairments in working memory and problem solving. These findings provides more evidence for supporting the role of neuroinflammation in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.
Introduction
Accumulating evidence from histological, genetic and immunochemical studies support neuroinflammatory mechanisms implicated in schizophrenia1. A recent study also suggests that peripheral immune mediators may underlie white matter dysconnectivity2. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether elevated inflammatory cytokine expression induced white matter integrity changes and cognitive impairments in first-episode schizophrenia patients by using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI).Methods
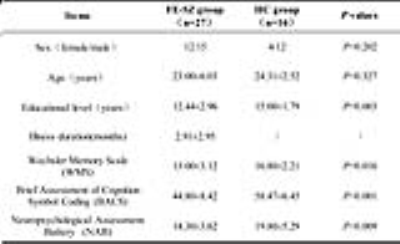
Subjects: 27 first-episode schizophrenia patients (FE-SZ group, 23.00±6.03 years old, 12 females) and 16 healthy volunteers (HC group, 21.31±2.52 years old, 4 females) who underwent DTI were enrolled. All subjects were right-handed. The MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB) was used to assess the cognitive levels. The severity of clinical symptoms was assessed using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS). Fasting blood samples were collected from each subject and processed for the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines including IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, CX3CR1, S100A8 and TGFA. MRI acquisition: Conventional MRI and DTI were performed on a 3.0T scanner. DTI protocols were: 30 directions; b value=0 and 1000 s/mm2; repetition time/echo time=16000/100.2-117.7 ms; slice thickness=2.5 mm; field of view=240×240 mm2; matrix=128 ×128. Image analysis: The analysis of DTI data was performed using the general linear model implemented in FMRIB's Software Library (FSL). After extracting brain images and eddy current correction, fractional anisotropy (FA), axial diffusivity (AD) and radial diffusivity (RD) were generated. Then tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS, part of FSL) 3 was used to compare group difference in above diffusional metrics with age and educational level as covariates. The results were corrected for multiple comparisons by controlling the family-wise error rate after threshold-free cluster enhancement (TFCE) and taken to be significant at P<0.005. The JHU ICBM-DTI-81 white-matter label atlas was used to label significant tracts and the FA, AD and RD were measured in these tracts. Partial correlation analysis was used to examine the relationship between alterations of diffusion measures and expression levels of inflammatory cytokines, cognitive tests or PANSS score in above tracts in patients with age, sex, illness duration and educational level as control variables.Results
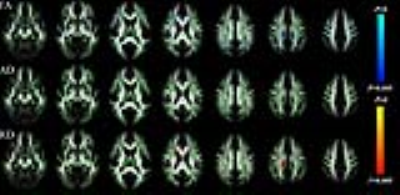
Demographic and clinical characteristics of all subjects were shown in table 1. The scores of Wechsler Memory Scale (WMS), Brief Assessment of Cognition Symbol Coding (BACS) and Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (NAB) in FE-SZ group were significantly lower than them in HC group (BACS: 44.80±8.42 vs. 58.47±6.45, P<0.001; WMS:13.00±3.12 vs. 16.80±2.21, P=0.002; NAB: 14.30±3.62 vs. 19.80±5.29, P=0.009). In TBSS analysis, FE-SZ group exhibited significantly decreased FA and increased RD in the genu of the corpus callosum (GCC), the body of the corpus callosum (BCC), the splenium of the corpus callosum (SCC), bilateral anterior corona radiata (ACR), superior corona radiata (SCR), posterior corona radiata (PCR), fornix, external capsule (EC), superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF), inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus/inferior longitudinal fasciculus (IFOF/ILF), uncinate fasciculus (UF), right posterior thalamic radiation (PTR) and left anterior limb of the internal capsule (ALIC) (as shown in Fig.1). AD showed no significant difference between the two groups. In FE-SZ group, lower FA in right ACR, BCC, right SCR, left SLF and higher RD in right fornix, SCC were significantly correlated with higher expression of IL-6, IL-1β, S100A8, IL-8, CX3CR1 and TGFA (r=-0.962, -0.967, -0.989, -0.990, 0.981, 0.958, P=0.038, 0.033, 0.011, 0.010, 0.019, 0.042 for above inflammatory cytokines expression respectively). Lower FA in right ACR was also significantly correlated with lower WMS score (r=0.995, P=0.005) with corresponding higher RD significantly correlated with higher PANSS G score (r=0.972, P=0.028). Furthermore, lower FA and higher RD in right fornix were significantly correlated with lower NAB score (r=0.991, -0.958, P=0.009, 0.042 respectively).Discussion
This study revealed widespread differences in FA and RD between the FE-SZ and HC groups, which demonstrated reduced white matter integrity in first-episode schizophrenia. Of these tracts, 6 of them showed significant correlations with higher expression levels of multiple inflammatory cytokine, which suggested that elevated expression of inflammatory markers contributed to impaired anisotropy of water diffusion in selected pathways including projection fibers (ACR, SCR), association fibers (SLF) and commissural fibers (BCC, SCC, fornix). Moreover, of the 6 tracts, ACR and fornix simultaneously showed reduced white matter integrity related to WMS and NAB score, which were also directly different between the two groups and reflected the cognitive impairment in working memory, reasoning and problem solving. All above findings seem to demonstrate the role of neuroinflammation in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.Conclusion
Our study reveals reduced white matter integrity in selected pathways closely related to elevated expression of inflammatory cytokines and cognitive impairments in schizophrenia, which provides more evidence for supporting the role of neuroinflammation in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81270416). We would like to thank Philips Applied Science Lab for their technical assistance. Finally, we thank all participants and their parents for their loyalty and cooperation.References
1. Howes, O.D. and R. McCutcheon. Inflammation and the neural diathesis-stress hypothesis of schizophrenia: a reconceptualization. Transl Psychiatry. 2017; 7(2): e1024.
2. Prasad, K.M., Upton, C. H., Nimgaonkar, V. L., et al. Differential susceptibility of white matter tracts to inflammatory mediators in schizophrenia: an integrated DTI study. Schizophr Res. 2015; 161(1): 119-125.
3. Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, et al. Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage. 2006;31(4):1487-1505.
Figures