5167
Quantitative Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging in Different Arterial Input Functions and Measurement Dimensions: Which Method Performs Best in differentiation of Malignant from Benign Soft Tissue Tumors?1Radiology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seocho-gu, Republic of Korea, 2Occupational and environmental medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seocho-gu, Republic of Korea, 3Pathology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seocho-gu, Republic of Korea, 4Orthopedics, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seocho-gu, Republic of Korea
Synopsis
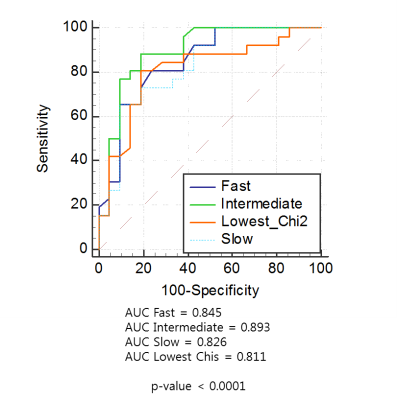
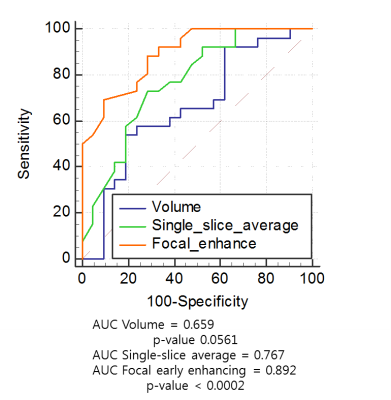
This study was designed to evaluate the reliability of quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) according to the different arterial input functions (AIF) at different measurement dimensions in differentiating malignant from benign soft tissue tumors at 3T. Quantitative DCE-MRI parameters of either benign or malignant tumors were obtained in three different measurement dimensions: focal early enhancing area, single-slice average, and whole tumor volume. They were calculated using three different population-averaged AIF (fast, intermediate and slow) and one of the three AIF of the lowest Chi-square, using SyngoVia software. The result showed quantitative DCE-MRI may be reliable and accurate in differentiating malignant from benign soft tissue tumors at 3T, particularly from focal early enhancing area using intermediate or fast AIF.
Purpose
To evaluate the reliability of quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) according to the different arterial input functions (AIF) and different measurement dimensions in differentiating malignant from benign soft tissue tumors at 3T.Materials and Methods
This study was approved by the institutional review board and informed consent was waived. 3T MR imaging including DCE-MRI of 47 patients with pathologically confirmed soft-tissue tumors were retrospectively analyzed. There were 21 malignant and 26 benign soft-tissue tumors. Quantitative DCE-MRI parameters were obtained in three different measurement dimensions: focal early enhancing area, single-slice average, and whole tumor volume. They were calculated using three different population-averaged AIF (fast, intermediate and slow) and one of the three AIF of the lowest Chi-square using SyngoVia software. The receiver operating characteristic curve with areas under the curve (AUC) was obtained.Results
Ktrans obtained in focal early enhancing area, using intermediate AIF, showed significantly higher AUC (0.892, 95% CI=0.767 to 0.964) than that of single-slice average (0.767, 95% CI=0.621 to 0.878) or whole tumor volume (0.659, 95% CI=0.507 to 0.791) in differentiating malignant from benign soft tissue tumors (P < .002). While analyzing three different AIFs, we encountered seven cases of fitting errors in calculating parameters using slow AIF. Among DCE parameters, Ktrans and Kep were reliable and accurate in all different AIF and measurement dimensions differentiating malignant from benign soft tissue tumors (P < .05). Ktrans and Kep were significantly higher in malignant soft tissue tumors: 0.44 min-1 vs 0.11 min-1; 1.91 min-1 vs 0.28 min-1 in focal early enhancing area (P =0.0006, P=0.0127, respectively). Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 89%, 71%, and 81%; 89%, 81%, and 85% with cutoff values of 0.18 min-1 in Ktrans and 0.47 min-1 in Kep of focal early enhancing area using intermediate AIF, respectively.Conclusion
Quantitative DCE-MRI may be reliable and accurate in differentiating malignant from benign soft tissue tumors at 3T, particularly from focal early enhancing area using intermediate or fast AIF.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Verstraete KL, Deene YD, Roels H, Dierick A, Uyttendaele D, Kunnen M. Benign and malignant musculoskeletal lesions: dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging--parametric "first-pass" images depict tissue vascularization and perfusion. Radiology. 1994;192(3):835-843.
2. Woude HJVD, Verstraete KL, Hogendoorn PC, Taminiau AH, Hermans J, Bloem JL. Musculoskeletal tumors: does fast dynamic contrast-enhanced subtraction MR imaging contribute to the characterization? Radiology. 1998;208(3):821-828.
3. Rijswijk CSPV, Geirnaerdt MJA, Hogendoorn PCW, et al. Soft-Tissue Tumors: Value of Static and Dynamic Gadopentetate Dimeglumine–enhanced MR Imaging in Prediction of Malignancy. Radiology. 2004;233(2):493-502.