5065
Effectiveness of fatty fraction by high-speed T2-corrected multi-echo SVS (HISTO) and multi-echo 3D DIXON (mDIXON) in rapid and robust acquisition for Duchenne Muscular DystrophyXiaolei Zhu1, Guijin Li2, and Zhiyong Li3
1MR SMK, Siemens Healthcare, NE Asia, Guangzhou, China, 2CS App, Siemens healthcare, NE Asia, Guangzhou, China, 3Department of Radiology, Shenzhen Children Hospital, Shenzhen, China
Synopsis
The purpose of this study is to assess a potential fat quantitative technique in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), one of High-Speed T2-corrected
Introduction
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a genetic disorder characterized by progressive muscle degeneration and weakness. The symptom Onset is between 3 and 5 years and the disorder progresses rapidly. An accurate marker of disease progression is to evaluate the amount of intramuscular fat[1]. But muscle biopsy is invasive and cannot be repeated. Single voxel MRS (SVS) is a non-invasive and potential method for fat quantification of liver, muscle and heart[2], however, there are many masking errors when MRS were performed with muscle, bone and marrow tissue due to the confounding effect.Purpose
In this study, a potential fat quantitative protocol containing High-Speed T2-corrected multi-echo SVS (HISTO) and Multi-echo 3D DIXON (mDIXON) were proposed to evaluate the intramuscular fat fraction of DMD. To assess its feasibility in DMD, a single voxel region-of-interest based MRS was performed with lesion. However, only one voxel-based MRS was limited with lipid heterogeneous in tissue or other confounds effect like phase error or multiple fat peaks. In order to demonstrate its accuracy and robustness, an accelerated 3D DIXON method with both multi fat peak robust lipid estimation and multi echo R2*-correction were also performed to further assess the reliability of HISTO.Methods
Muscular fatty infiltrations in the pelvic and thigh muscles of 21 boys with DMD (confirmed by DNA sequencing test) were assessed. Firstly 3D T1 TSE sequence was used to rank the lesion, then HISTO and mDIXON technique were succeeding performed on 3T MR scanner (Magnetom Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). For HISTO technique: a modified STEAM sequence (mixing time [TM] = 10 msec) with TR/TE1, 2, 3, 4, 5 = 3000/12, 24, 36, 48, 72 msec, single voxel region-of-interest 12 × 12 × 12 mm3, total of 1024 points was acquired at a bandwidth of 1085 Hz with 2 averages, duration time = 15 sec. Meanwhile, T2-correction was implemented by using repeatedly acquisitions with a total of five echo times, T1 effect was alleviated by long TR acquisition; for mDIXON technique: a 3D FLASH sequence with TR/TE1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 = 9/1.05, 2.46, 3.69, 4.92, 6.15, 7.38 msec, flip angle = 4°, bandwidth = 1085 Hz/pixel, matrix = 112 × 128 × 88, field of view = 260 × 298, slice thickness 3.5 mm, added with 4× CAIPIRINHA acceleration, duration time = 13 sec. In order to eliminate the most of confound components from muscle, lipid, R2* correction and multi lipid peak model were used to correct the mDIXON method. Furthermore, The fat fractions (FFs) of four muscles (gluteus maximus, adductor magnus, vastus laterlis, biceps brachii) were marked and measured with single voxel HISTO with inlined post process. In addition, fat quantification by mDIXON was also evaluated at a transversal position. Statistics analysis was used to demonstrate the consistency of fat fraction of between HISTO and mDIXON method. The whole protocol workflow could be seen as Fig.1.Result
16 boys with DMD were ranked as severity type while others were ranked as mild type of intramuscular fat infiltration by the non-quantitative T1 weighted imaging. Due to the relatively high fat concentration in DMD lesion, the fat fraction was at domination over other metabolite, see Fig.2. The severity type in DMD was observed with significantly increased FFs in comparison to mild type with 2 ROI HISTO (easpecially in biceps brachii 22.13±7.38% vs 4.19±1.46%, adductor magnus 42.69±15.52% vs 3.16±1.46%). To assess the reliability of 2 ROI HISTO, ROIs of adductor magnus and biceps brachii muscle were respectively compared at different methods. Fig3 shows a Bland-Altman plot and linear regression analysis result, which demonstrate its good consistency between FFs-HISTO and FFs-mDIXON, especially excellent agreement was found between HISTO and mDIXON (y=0.88x+0.005; R2=10e-5) in adductor magnus with DMD boys.Conclusions
HISTO and mDIXON technique can both reliably differentiate between DMD types with a rapid and robust acquisition, which can rapidly assess the degree of muscle fatty infiltration in boys with DMD. This quantitative protocol can be a potential biomarker for monitoring the DMD disease progression and treatment response in future clinical trials.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
- 1. Gaeta M. et. al. Muscle fat-fraction and mapping in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: evaluation of disease distribution and correlation with clinical assessments. Skeletal Radiol. 2012 Aug; 41(8): 955-961.
- 2. Pineda N.et.al. Measurement of hepatic lipid: high-speed T2-corrected multi echo acquisition at 1H MR spectroscopy -- a rapid and accurate technique. Radiology. 2009 Aug; 252(2): 568-576
- Liana G. et. al. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 22 (2014)
- Hu HH, Börnert P, Hernando D, Kellman P, Ma J, Reeder S, Sirlin C. ISMRM Workshop on Fat-Water Separation: Insights, Applications and Progress in MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012 Aug; 68(2): 378-388
Figures
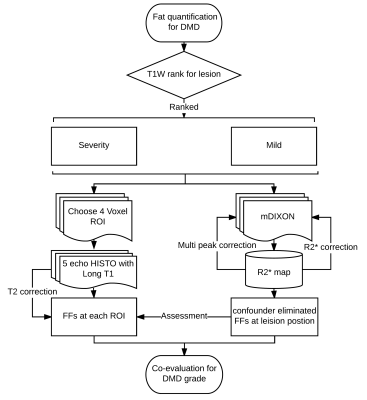
Fig.1 MR fat quantification in a rapid and robust acquisition protocol for
DMD patients
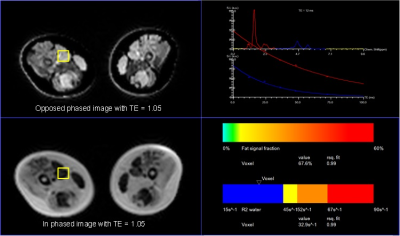
Fig.2 a rapid fat quantification with single ROI based HISTO technique
for DMD patients.
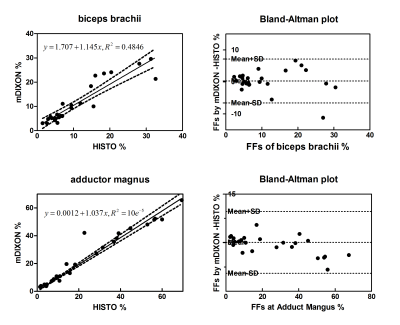
Fig.3. The analysis
of linear regression model and Bland-Altman plot shows good consistency between
FFs measured by HISTO and mDIXON methods.