4922
Epidermal Growth Factor's lowers Blood Brain Barrier leakiness in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model as detected using Diffusion Weighted Arterial Spin Labeling MR Imaging1Radiology, University of Illinois at Chicago Medical Center, Chicago, IL, United States, 2Anatomy and Cell Biology, University of Illinois at Chicago Medical Center, Chicago, IL, United States, 3Research Resources Center, University of Illinois at Chicago Medical Center, Chicago, IL, United States
Synopsis
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction is reemerging as a critical component of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Higher BBB leakiness is one of the mechanistic pathways through which AD risk factors induce cognitive decline. We have previously demonstrated that epidermal growth factor (EGF) prevents BBB leakiness in a model of two important AD risk factors: APOE4 and female sex (female E4FAD mice). The goal of this study was to use Diffusion Weighted Arterial Spin Labeling MRI to determine whether post-symptomatic EGF treatment, (during 8-10 months) can reduce BBB leakiness in EGF treated mice compared to vehicle controls.
Purpose
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction is reemerging as a critical component of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [1,2,3]. An important outcome of BBB dysfunction is higher BBB leakiness, as the extravasation of plasma components into the brain induces neuronal dysfunction. Indeed, BBB leakiness is observed in AD patients and models of AD-like pathology. Higher BBB leakiness is also a mechanistic pathway through which AD risk factors induce cognitive decline. Two important interactive AD risk factors are APOE and sex. APOE4 is the greatest genetic risk for sporadic AD, increasing risk up to 12-fold compared to APOE3. Further APOE4-induced AD risk is higher in women. Our previous data have demonstrated higher BBB leakiness in female mice that express APOE4 (female E4FAD mice) [1,2,3]. Importantly, we identified that there were low plasma levels of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) in female E4FAD mice [1,2,3]. EGF plays a key role in modulating BBB function, including leakiness. Importantly, we have demonstrated that EGF prevents cognitive decline and BBB leakiness in female E4FAD mice (6 to 8 months treatment) [1,2]. Based on this data, the goal of this study was to use Diffusion Weighted Arterial Spin Labeling (DW-ASL) MRI [4] to determine whether post-symptomatic EGF treatment (8-10 months), can reduce BBB leakiness in EGF treated mice compared to vehicle controls. Diffusion weighted arterial spin labeling (DW-ASL) at a b-value 50 s/mm2, which eliminates signal from water flowing within the capillaries and larger vessels, relative to rCBF unaltered by diffusion weighting provides a measure of the leakiness of the BBB [4].Methods
E4FAD female mice were treated (I.P, weekly) with EGF 50 μg/kg (n=17) or 300 μg/kg (n=20) or vehicle control (n=19) from 8 to 10 months of age.
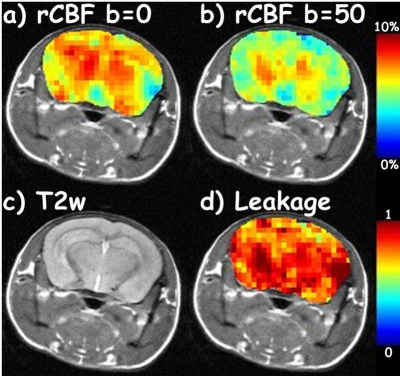
To assess BBB leakiness, DW-ASL datasets were acquired of each mouse at 10 months using a Diffusion Weighted spin echo Signal Targeting with Alternating Radio frequency (STAR) [5] sequence on a 9.4T small-animal scanner (TR/TE 2000/9.6 ms, post labeling delay 500 ms, FOV 25x25 mm2, slice thickness 1 mm, matrix 64x64, tagging gradient=0.4 G/cm, number of average = 1, tagging gaps of -15,-1,-1,0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,15 mm, b-values of 0 and 50 s/mm2). Relative CBF (rCBF) maps were processed using the TADZZ method [6]. The leakage maps were generated as the ratio of the rCBF map at b=50 to the rCBF map at b=0 s/mm2, rCBF(b=50)/rCBF(b=0) [4]. Pixels with abnormal leakage values (>1) were likely due to white noise or image artifacts and hence were not included in the analysis.
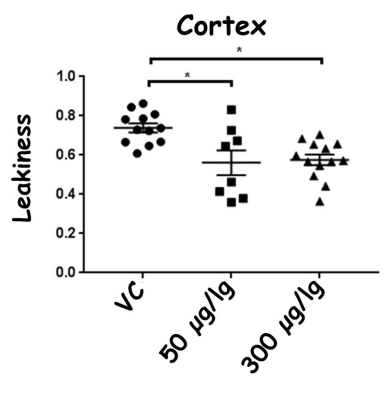
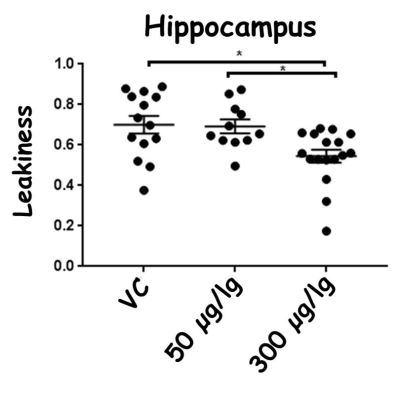
ROI analyses of BBB leakiness were performed on the hippocampus and cortex, the two brain regions that demonstrate higher BBB leakiness in female E4FAD mice. Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc (GraphPad Prism Software) with p < 0.05.
Results
Representative anatomical T2-weighted images, rCBF(b=0) map, rCBF (b=50) map, and leakage map are displayed in Figure 1.
There were no significant changes in rCBF due to EGF treatment compared to vehicle control treated female E4FAD mice. However, in the cortex, BBB leakiness values from highest to lowest were: vehicle control (0.74±0.08) > 50 μg/kg EGF treated mice (0.56±0.17) > 300 μg/kg EGF treated mice (0.57±0.09). Thus, both EGF treatments resulted in lower BBB leakiness compared to the vehicle controls (p<0.05, Figure 2). In the hippocampus, BBB leakiness was lower with 300 μg/kg EGF treatment (0.54 ±0.13) compared to the vehicle control (0.70±0.16) and 50 μg/kg EGF treatment (0.68±0.11) (p<0.05, Figure 3).
Discussion and Conclusion
Collectively, these demonstrate that post-symptomatic EGF treatment results in lower BBB leakiness in E4FAD female mice. Future studies dissecting the mechanistic pathways that underlie the beneficial effects of EGF on BBB function could lead to novel treatments for AD.Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge NIH grant supports (R21 EB023516 and R21 AG053876).References
1) Riya Thomas,Alan W.J. Morris, Leon M. Tai. Epidermal growth factor prevents APOE4-induced cognitive and cerebrovascular deficits in female mice. Heliyon 3 (2017) e00319. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2017. E00319
2) Riya Thomas, Paulina Zuchowska, Alan W. J. Morris, Felecia M. Marottoli, Sangeeta Sunny, Ryan Deaton, Peter H. Gann, Leon M. Tai, Epidermal growth factor prevents APOE4 and amyloid-beta-induced cognitive and cerebrovascular deficits in female mice. Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2016) 4:111; doi 10.1186/s40478-016-0387-3
3) Tai, L. M.,D. Balu, E. Avila-Munoz, L. Abdullah, R. Thomas, N. Collins, A.C. Valencia-Olvera, and M. J. LaDu. EFAD transgenic mice as a human APOE relevant preclinical model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Lipid Res. 2017. 58: 1733–1755. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R076315
4) Keith S. St. Lawrence, Daron Owen, and Danny J. J. Wang. A Two-Stage Approach for Measuring Vascular Water Exchange and Arterial Transit Time by Diffusion-Weighted Perfusion MRI. Magn Reson Med 67:1275–1284, 2012.
5) Edelman RR, Siewert B, Darby DG, Thangaraj V, Nobre a C, Mesulam MM, et al. Qualitative mapping of cerebral blood flow and functional localization with echo-planar MR imaging and signal targeting with alternating radio frequency. Radiology. 1994;192(2):513–20. 5)
6) Frederick C. Damen, Rong-Wen Tain, Weigo Li, Xiaohong Joe Zhou, Leon Tai, and Kejia Cai. Tagging distance dependent Z-spectrum (TADDZ) for ASL MRI free from B0-inhomogeneity induced errors. ISMRM 2017 #7429.
Figures