4910
Assessment of right ventricular functional recovery after acute myocardial infarction by cardiac magnetic resonance1west china hospital, sichuan university, chengdu, China
Synopsis
In order to clarify the assess the right ventricular (RV) function changes and recovery and the relationship with different culprit vessel for myocardial infarction (MI) patients on cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR). We prospectively recruited forty-nine MI patients and 20 healthy control, all them underwent CMR to analysis right ventricular (RV) function and global strain. Our results showed that, the RV function was related to whether the culprit vessel was RCA or not, and even RCA was obstructed the RV global strain can significantly recovery at chronic phase.
Introduction The right ventricular (RV) dysfunction after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and the functional recovery at the chronic phase are still controversial1-3. In previous studies, only a few studies focused on the assessment of RV dysfunction during both the acute and chronic phase for MI patients4-5. In addition, whether the culprit vessel was the right coronary artery (RCA) might cause different influence on RV myocardium. Now cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) as one of the effective criteria for evaluation of the RV function could analysis the global strain of ventricle. Compared with 2D speckle echocardiography, CMR might better avid the bias caused by interference factors. Thus, the purpose of this study was to assess the RV functional recovery and the relationship with different culprit vessel for MI patients by CMR strain analysis.
Methods Forty-nine MI patients who had received PCI and 20 healthy controls were prospectively enrolled in this study. Patients with history of organic heart disease were exclude. All patients underwent CMR using a 3.0 T whole-body scanner after PCI, and second examination after 3 months. The short-axis two-chamber view, long-axis four-chamber view and long-axis two-right-chamber view were performed for all individual to obtain global right ventricle strain (longitudinal strain (LS), global radial strain (RS) and global circumferential strain (CS)). According to culprit coronary artery, all MI patients were divided into group A (culprit vessel was RCA, n=37) and group B (culprit vessel was not RCA, n=12). Pairing-sample t test and independent-sample t test were performed for groups comparison.
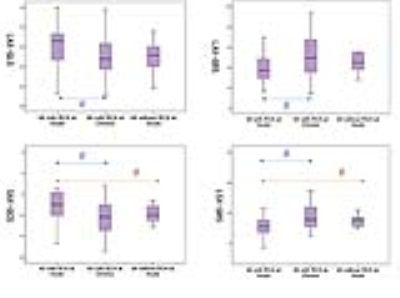
Results Both cardiac function and RV global strain showed significant differences between MI patients and controls (figure.1). For MI patients with RCA involvement, LVEF value at chronic phase was higher than acute phase (52.34 vs. 49.42; p<0.05) and the reminds cardiac function indications had no difference between the two phases. All the global strain analysis on these patients showed a significant difference between at two phases (Acute vs. Chronic, LAX-GLS, -19.57 vs-22.24.; LAX-GRS, 37.99 vs. 50.79; SAX-GCS, -7.55 vs. -10.61; SAX-GRS 11.38 vs18.07.; all p<0.05) (figure.2). For MI patients without RCA involvement, all cardiac function indications and global strain parameters had no difference between acute phase and chronic phase. Comparing the global stain for different culprit vessel at acute phase, the SAX-GCS and SAX-GRS had a significantly difference between two groups (RCA vs. non-RCA, SAX-GCS, -7.55 vs. -10.22; SAX-GRS, 11.38 vs. 15.45; all p<0.05) (figure.2& figure.3). As for chronic phase all the global strain had no difference between these two group.
Discussion Firstly, the global RV strain and cardiac function results showed the damage of myocardium at both acute and chronic for MI patients. Secondly, The RV strain in MI patients with RCA involvement had significantly improved at the chronic phase, which indicating that RV myocardium could still functionally recovery in the case of RCA obstruction. Only LVEF recovery at chronic phase of all cardiac function indexes, means RV strain might early reflect the improvement of RV myocardium. In terms of patients without RCA involvement, the RV myocardium which adjacent to the infarction area were still decreased in global strain, and the degree of strain reduction was less than the RCA involved patients.
Conclusion Whether the RCA was the culprit vessel or not, the RV global strain was decreased in different degrees at both acute and chronic stage. When RV myocardial infarction happened, the RV strain will recovery at chronic stage quickly than cardiac function.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81471721, 81471722, 81641169, 81771887 and 81771897), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (no: NCET-13-0386), and Program for Young Scholars and Innovative Research Team in Sichuan Province (2017TD0005) of China.References
1. Kakouros N, Cokkinos D V. Right ventricular myocardial infarction: pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Postgraduate Medical Journal. 2010; 86(1022):719-28.
2. Huttin O, Lemarié J, Di M M, et al. Assessment of right ventricular functional recovery after acute myocardial infarction by 2D speckle-tracking echocardiography. International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging. 2015; 31(3):1-9.
3. Hutyra M, Skála T, Horák D, et al. Echocardiographic assessment of global longitudinal right ventricular function in patients with an acute inferior ST elevation myocardial infarction and proximal right coronary artery occlusion. International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging. 2015;31(3):497-507.
4. Amin N H M, Seng K C, Chi Y V, et al. Comprehensive right heart systolic function assessment using cardiac magnetic resonance imaging after inferior ST elevation myocardial infarction. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. 2015;17(1):1-2.
5. Altiok E, Tiemann S, Becker M, et al. Prediction of global and segmental functional changes after acute myocardial infarction by 2D speckle-tracking echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. European Heart Journal. 2013; 34(1):3801-3801.
Figures