4842
Comparison of ASL-MRA and 3D TOF-MRA in patients with transit ischemic attackYan Wang1, Jing Chen1, Chuanchen Zhang1, Jianxun Qu2, and Mingzhen Wu1
1Radiology, Liaocheng People's Hospital, Liaocheng, China, 2GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
A comparison of ASL-MRA and TOF-MRA was performed for patients suffered from TIA. TOF-MRA is superior to ASL-MRA in morphological assessment of the stenosis arteries. However, ASL-MRA can reflect more hemodynamic information of the blood supply arteries for the hypoperfusion area.
Introduction
Arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance angiography (ASL-MRA) is a newly developed noninvasive MR angiography. Compared to conventionally used TOF-MRA, which bases on inflow enhancement, ASL-MRA utilizes flowing blood as endogenous contrast agent and has shown beneficial properties for high fidelity blood imaging, like exempt from over saturation, immune to turbulent flow[1]. The purpose of this study was to compare ASL-MRA and TOF-MRA in patients suffered from transit ischemic attack and to explore the properties of ASL based contrast mechanism.Methods
Sixty-eight patients diagnosed as transit ischemic attack underwent routine MR exam, 3D TOF-MRA, 3D ASL-MRA, and ASL perfusion imaging. The scan parameters of angiography and perfusion sequences are listed in Table.1. Patients with intracranial hemorrhage, vascular abnormalities were excluded. Circler region of Interest (ROIs) were placed in low perfusion area (grey matter) to measure CBF. Region with CBF < 30ml/100g/min were considered as hypoperfusion, region with CBF≥30ml/100g/min were considered as normal perfusion. The ASL CBF map and MRA images were assessed by two neuroradiologists at separate times in a random blinded fashion to determine the hypoperfusion area and degree of stenosis respectively. The time interval between ASL-MRA and TOF-MRA analyses was 2 weeks. Disagreements were resolved by consensus. The hypoperfusion region larger than 1/2 of the corresponding artery perfusion territory [2] was considered as large hypoperfusion area; the hypoperfusion region smaller than 1/2 of the corresponding artery perfusion territory was considered as small hypoperfusion area. The degree of stenosis is graded for arteries on ASL-MRA and TOF-MRA according to the TICI3 based criteria, where lower score means more severe stenosis (Table.2). Statistical analysis was carried out by SPSS22.0. Wilcoxon signed rank test was used to analyze the difference between TOF-MRA and ASL-MRA classification. Mann-Whitney U test was used to evaluate the difference of ASL-MRA classification between the large hypoperfusion area group and small hypoperfusion area group.Results
Hypoperfusion was detected in 39 patients, a total of 111 ROIs were measured. Stenosis classification of TOF-MRA and ASL-MRA was shown in Table.3. Among the hypoperfusion regions, 64.86% (72/111) were large hypoperfusion area, and 35.14% (39/111) were small hypoperfusion area. The stenotic score was significantly higher (P<0.001) in TOF-MRA than that in ASL-MRA (Figure.2). ASL-MRA stenotic score was significantly lower in the large hypoperfusion area group than that in the small hypoperfusion area group(P=0.004) (Figure.2).Discussion
In this study, the degree of stenosis was assessed based on ASL-MRA and TOF-MRA. ASL perfusion imaging was also acquired for hypoperfusion severity evaluation. Both ASL-MRA and TOF-MRA scores higher in small hypoperfusion area group. TOF-MRA is superior to ASL-MRA in showing distal branches of the stenosis arteries, as shown in Figure.1. While for large hypoperfusion area group, ASL-MRA has much less score than that of TOF-MRA, indicating that ASL-MRA is more sensitive to hemodynamic status variance. TOF-MRA builds its contrast based on the refreshing rate of inflowing blood. ASL based mechanism, on the contrary, reflects the total volume of inflowing blood during labeling period. The low signal intensity in ASL-MRA is a reflection of poor perfusion status in the corresponding blood supply region. When the distal branches were invisible in ASL-MRA, the hypoperfusion area was significantly larger.Conclusion
TOF-MRA is superior to ASL-MRA in morphological assessment of the stenosis arteries. However, ASL-MRA can reflect more hemodynamic information of the blood supply arteries for the hypoperfusion area, which is helpful in functional diagnosis and treatment guidance.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Robson PM, and etc. Radiology 257:507–515, 2010
[2] JVIR 2003; 14: 945-946.
[3] Higashida RT, and etc. Stroke, 34:109-137, 2003
Figures
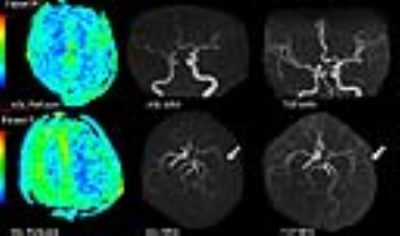
Figure.1 Patient
A, 84 years old male. Hypoperfusion in bilateral
hemispheres Patient
B, 55 years old male. Large area of
hypoperfusion in left MCA territory
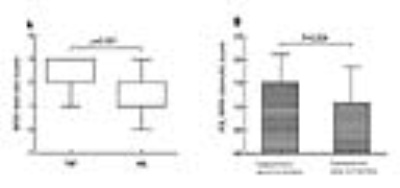
Figure.2 (A) Comparison of TOF-MRA and ASL-MRA stenotic score of blood
supply vessels in hypoperfusion areas. (B) Comparison
of ASL-MRA scores between small hypoperfusion area group and large
hypoperfusion area group.
Table.1 Parameters of angiography and perfusion sequences
Table.2 TICI Classification and MRA Score
Table.3 Stenosis Classification of TOF-MRA and ASL-MRA