4734
Feasibility of Assessing the Nonlinear Mechanical behaviors of Liver with MR Elastography (MRE)1Radiology, Mayo clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
Synopsis
This is a feasibility study for assessing the nonlinear mechanical behaviors of the liver while experiencing different degrees of mechanical preloads. The different loading conditions were induced by 1) diaphragm movement in a view-sharing free-breathing 2D-EPI-MRE acquisition; 2) end-expiration versus end-inspiration states in a breath-held 3D-EPI-MRE acquisition. We observed intriguing stiffness variation synchronized with the breathing pattern in the free-breathing MRE, and a difference between end-expiration and end-inspiration liver stiffness in the breath-held MRE. The promising results demonstrated that the free-breathing and/or breath-hold liver MRE at different breathing states can be useful for the assessment of nonlinear mechanical tissue behaviors.
Purpose
Nonlinear models have been used for distinguishing fibrosis from inflammation in biological tissues, such as bowel in Crohn’s disease [1-3]. However, characterization of this phenomenon in the liver is limited. In this study, we evaluated the feasibility of free-breathing and breath-held liver MRE acquisitions for assessing the nonlinear mechanical response of the liver under varying pre-stressed conditions. Recently, a free-breathing liver MRE acquisition strategy (0.8-second per slice) was developed to acquire 2D multi-slice MRE data without performing breath holds and with greatly reduced overall scan time [4]. During free-breathing, the liver is expected to experience low-frequency (0.1-1 Hz) cyclic strain variations due to respiration with varying amplitude (i.e., depth of breathing) and phase (i.e., state of breathing, such as end-inspiration or end-expiration). We hypothesize that the variation of the conventional 2nd order parameters (e.g., complex shear modulus) measured at standard MRE frequencies (e.g., 30-60 Hz) in response to varying preloads at lower frequency from different breathing states can be used to explore the 3rd order nonlinear mechanical behaviors of the liver tissue.Methods
With institutional review board approval, 4 healthy volunteers and 2 patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) were imaged on a 1.5T scanner with an 8-channel torso array coil. The standard 19-cm round rigid liver driver was used to delivery vibrations at 30 Hz or 60 Hz. The 2D free-breathing EPI-MRE scans were performed with the subject free-breathing (averaged respiratory rate of ~16-20 breaths per minute). The 3D EPI-MRE scans were performed with a breath hold at the end of expiration and inspiration. The imaging acquisition parameters and post-processing methods were as previously described [4-5]. ROIs were manually drawn in each slice for each acquisition and the distribution of free-breathing, slice-based stiffness estimates were compared to the breath-held results with a two-sample t-test (set P<0.05 as significance level).Results
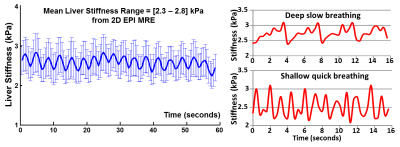
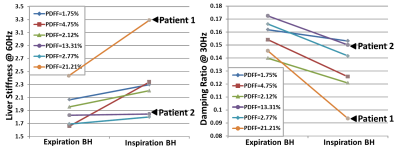
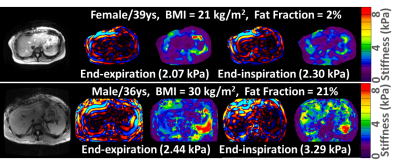
In this study, the diaphragm movement during free-breathing varied from 6 mm (shallow fast breathing) to 120 mm (deep slow breathing) across 4 volunteers. Fig.1 illustrates the 2D EPI-MRE results with the different respiration patterns. In the free-breathing acquisition in a healthy volunteer, we observed intriguing stiffness variation (2.3-2.8 kPa, 20%) synchronized with the breathing pattern from an anatomically registered ROI. Fig.2 shows the 3D EPI-MRE results measured at different breath-held positions. In subjects with no or mild steatosis (proton density fat fraction (PDFF) < 15%), the liver stiffness measured at end-inspiration was elevated by 0.25 ± 0.25 kPa (ranging from 0.11 to 0.68 kPa) compared to end-expiration, while the patient with moderate steatosis (PDFF = 21%) had substantially increased liver stiffness of 0.85 kPa (35% increase) compared to the normal stiffness (2.44 kPa) at end-expiration. Volunteers with no or mild steatosis had a decreased damping ratio at 30 Hz of -13.0% ± 4.8% (ranging from -5.4% to -18.4%), while the patient with moderate steatosis had a substantially decreased damping ratio of -35.8%, compared with the end-expiration results. Two representative examples are shown in Fig.3.Discussion and conclusion
Another collaborative study has confirmed this observation of a difference between end-expiration and end-inspiration liver stiffness using a breath-held 3D EPI MRE, with volumetric liver stiffness being 13% greater at end-inspiration in 9 healthy adults (P<0.05) [6]. Taken together, these findings suggest that inspiration transiently increases liver stiffness, which may augment systematically in diseased livers similar to the postprandial effect or other physiologic activities [7-13]. The promising results demonstrated in this preliminary study suggest that a free-breathing and/or breath-hold liver MRE at different breathing states can be useful for the assessment of nonlinear mechanical tissue behaviors.Acknowledgements
This research was funded by NIBIB grants EB017197 and EB001981.References
[1 ] Coelho R, Ribeiro H, Maconi G. Bowel Thickening in Crohn's Disease: Fibrosis or Inflammation? Diagnostic Ultrasound Imaging Tools. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017;23(1):23-34.
[2] Lei H, Johnson LA, Liu S, Moons DS, Ma T, Zhou Q, Rice MD, Ni J, Wang X, Higgins PD, Xu G. Characterizing intestinal inflammation and fibrosis in Crohn's disease by photoacoustic imaging: feasibility study. Biomed Opt Express. 2016;7(7):2837-48. PMCID: 4948634.
[3] Stidham RW, Xu J, Johnson LA, Kim K, Moons DS, McKenna BJ, Rubin JM, Higgins PD. Ultrasound elasticity imaging for detecting intestinal fibrosis and inflammation in rats and humans with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3):819-26 e1. PMCID: 4934420.
[4] Glaser K, Chen J, Ehman R. Fast 2D hepatic MR elastography for free-breathing and short breath hold applications. The 23rd Annual Meeting of International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM); May; Toronto, Ontario, Canada 2015. p. 6579.
[5] Yin M, Allen A, Glaser K, Venkatesh S, Mounajjed T, Shah V, Ehman R. Assessment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score (NAS) with MR elastography (MRE). The 25th Annual Meeting of International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM); Honolulu, Hawaii, USA 2017. p. 0370.
[6] Wang K, Manning P, Szeverenyi N, Wolfson T, Hamilton G, Middleton MS, Vaida F, Yin M, Glaser K, Ehman RL, Sirlin CB. Repeatability and reproducibility of 2D and 3D hepatic MR elastography with rigid and flexible drivers at end-expiration and end-inspiration in healthy volunteers. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017.
[7] Murphy IG, Graves MJ, Reid S, Patterson AJ, Patterson I, Priest AN, Lomas DJ. Comparison of breath-hold, respiratory navigated and free-breathing MR elastography of the liver. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;37:46-50.
[8] Jung C, Groth M, Petersen KU, Hammel A, Brinkert F, Grabhorn E, Weidemann SA, Busch J, Adam G, Herrmann J. Hepatic shear wave elastography in children under free-breathing and breath-hold conditions. Eur Radiol. 2017.
[9] Ipek-Ugay S, Tzschatzsch H, Braun J, Fischer T, Sack I. Physiologic Reduction of Hepatic Venous Blood Flow by the Valsalva Maneuver Decreases Liver Stiffness. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36(7):1305-11.
[10] Pellot-Barakat C, Chami L, Correas JM, Lefort M, Lucidarme O. Does motion affect liver stiffness estimates in shear wave elastography? Phantom and clinical study. Eur J Radiol. 2016;85(9):1645-50.
[11] Goertz RS, Egger C, Neurath MF, Strobel D. Impact of food intake, ultrasound transducer, breathing maneuvers and body position on acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastometry of the liver. Ultraschall Med. 2012;33(4):380-5.
[12] Yun MH, Seo YS, Kang HS, Lee KG, Kim JH, An H, Yim HJ, Keum B, Jeen YT, Lee HS, Chun HJ, Um SH, Kim CD, Ryu HS. The effect of the respiratory cycle on liver stiffness values as measured by transient elastography. J Viral Hepat. 2011;18(9):631-6.
[13] Hu X, Shao J, Bai J, Wang J, Qian L. New noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: maximal accumulative respiration strain. J Ultrasound Med. 2010;29(8):1213-21.
Figures