4729
PEG-FGF21 Variant Improves Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of NASH as Determined by Quantitative Water-fat MRI1Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lawrenceville, NJ, United States, 2Bristol-Myers Squibb, Hopewell, NJ, United States
Synopsis
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) ranges from simple fatty liver to steatohepatitis (NASH) to cirrhosis. In the present study, we implemented a water-fat MRI using the gradient-reversal technique to quantify the hepatic proton density fat-fraction (PDFF), for assessment of hepatic steatosis in a diet-induced mouse model of NASH. We compared the quantitative water-fat MRI technique with conventional Dixon method and single-voxel MR spectroscopy (MRS), and correlated the MRI-PDFF with histology and biochemical triglyceride (TG) content. Lastly, the effects of a PEGylated-FGF21 variant (PEG-FGF21v) on hepatic steatosis in the mouse model was evaluated using the water-fat MRI technique.
Purpose
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) ranges from simple fatty liver to steatohepatitis (NASH) to cirrhosis [1]. Analogues of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), a key regulator of lipid and glucose metabolism, improve insulin sensitivity, lipid profiles, steatosis, and fibrosis in preclinical and clinical studies of NASH [2]. In the present study, we employed an interleaved water-fat imaging using the gradient-reversal technique [3] to generate hepatic proton density fat-fraction (PDFF) mapping at 7T. Conventional Dixon method and single-voxel MR spectroscopy (MRS) were also performed for cross correlation to the MR fat measurements. The aim was to verify MRI-PDFF by histology and biochemical triglyceride (TG) content, and to apply the non-invasive MRI technique to evaluate the effects of a PEGylated FGF21 variant (PEG-FGF21v) on hepatic steatosis in a mouse model of NASH.Methods
In Vivo: During a natural history study, C57BL/6J mice were fed: 1) Control-diet (10% kcal fat, n=6); or 2) choline-deficient amino acid-defined high fat diet (CDAHFD, 60% kcal fat, n=10) [4] for 12 weeks, with longitudinal MRI/MRS performed at baseline, 4, 8, and 12 weeks on diet. Plasma and liver autopsy were performed in a subset of mice (n=2/6 Control/CDAHFD) at week 4 and 8, and in the study mice at week 12, following MRI/MRS. PEG-FGF21v efficacy study consists of three groups (n=12/group): 1) Control-diet+vehicle; 2) CDAHFD+vehicle; and 3) CDAHFD+PEG-FGF21v 0.6mg/kg. Animals were kept on the Control-diet or CDAHFD for 8 weeks. MRI was performed at: 1) 4 weeks on-diet (baseline, BL) prior to vehicle and PEG-FGF21v treatment (twice weekly subcutaneous administration); and 2) 8 weeks on-diet (4 weeks on treatment: Wk 4); followed by plasma and liver autopsy for biochemical and histological analysis.
Water-fat MRI: MRI was performed on a Bruker Biospec 7T 20cm system with a 86 mm quadrature whole-body coil for transmitting and a phase-array coil for receiving. Mice were anesthetized with a 1.5~2.5% isoflurane/O2 mixture. Temporally interleaved water-fat selective multi-echo spin-echo gradient-reversal technique was implemented [3]. The reversal of slice gradient during the refocusing pulses allows water and fat images from the identical slice location to be obtained in a single acquisition without increasing scan time. The duration of RF pulse was 1040Hz (water-fat chemical shift), to minimize water-fat contamination during slice selections. A multi-echo train was used to generate proton density fat-fraction. Spatially-corrected water-fat images were acquired with TR/TE=2000/8.5ms, 4 echoes at 8.5ms interval, 5 slices, slice-thickness 1mm, 1.5mm inter-slice distance, and respiratory-gating.
Dixon water-fat MRI: Spin-echo two-point Dixon images were acquired: fat in-phase without displacement of the refocusing RF; and fat opposed-phase with the refocusing RF shifted by 240 µs (π/2 at 7T), and TR/TE=1000/8ms.
MR spectroscopy: Localized MRS was acquired using PRESS with voxel size of (2mm)3, TR/TE=4000/10ms, NEX=36, and respiration-gating. Field-Map and localized shimming were performed to restrict the spectral linewidths <30Hz.
Tissue Analyses: Mice were anesthetized with 3% isoflurane/O2 and blood was collected by cardiac puncture. The entire liver was isolated and weighed, a piece of left lateral lobe was harvested for biochemical analysis of liver TG, and the medial and left lateral lobes were fixed for histology. H&E stained sections were analyzed for quantification of lipid content using HALO software (Indica Labs, Inc).
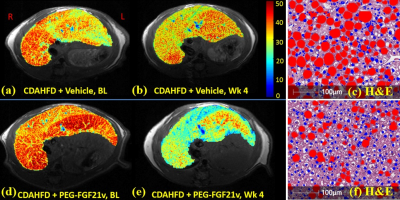
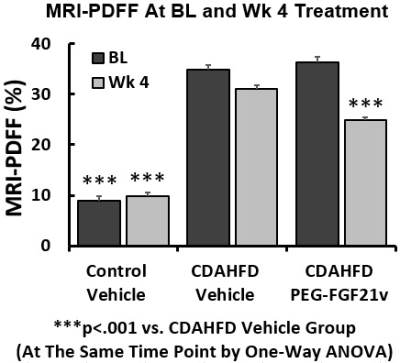
Results
In the 12-week natural history study, MRI-PDFF of the Control-diet group increased modestly from a baseline of 5% and peaked at 12 wks of 12.5%. MRI-PDFF increased significantly during the CDAHFD, peaking at 38.3% (4 wks) then declining to 35.5% (8 wks) and 30.9% (12 wks). MRI-PDFF (same region as MRS) highly correlated with MRS (r=0.99), biochemical TG (r=0.88), plasma ALT (r=0.85) and AST (r=0.82). In the PEG-FGF21v efficacy study, mice on CDAHFD developed liver steatosis as demonstrated in MRI-PDFF color maps (Fig. 1a&1d), treatment with PEG-FGF21v for 4 weeks decreased liver fat (Fig. 1e) compared to vehicle (Fig. 1b), which was confirmed by their H&E sections (Fig. 1f vs 1c, lipid in red). MRI-PDFF was averaged in 5 slices. One-way ANOVA showed MRI-PDFF significantly higher in CDAHFD+vehicle (35%) and CDAHFD+PEG-FGF21v (36.4%) groups at BL, compared to Control-diet group (8.9%, p<0.001). Four weeks of PEG-FGF21v treatment of CDAHFD mice resulted in a mean reduction of absolute MRI-PDFF of 11.6% from BL, compared to vehicle treatment (3.9%, p<0.001). PEG-FGF21v improved the CDAHFD-induced hepatic steatosis compared to vehicle treatment (Fig. 2). MRI-PDFF highly correlated with DIXON fat fraction (r = 0.97), liver TG (r = 0.97), and histological lipid content (r = 0.95).Conclusions
We implemented a water-fat MRI technique to assess hepatic steatosis in a mouse model of NASH. The MRI-PDFF demonstrated a beneficial impact of treatment with the PEG-FGF21 variant on hepatic steatosis. The quantitative nature makes the MRI technique a useful method to assess anti-NASH therapies.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Liu J, Xu Y, Hu Y, et. al. Metabolism 2015; 64(3):380-90. 2. Maratos-Flier E. Experimental Cell Research 2017; 360(1): 2-5. 3. Tang H, Wu EX, Kennan R, et al. J Magn Reson Imaging 2007; 26:1064–1070. 4. Machado MV, Michelotti GA, Xie G, et al., PLoS ONE 2015; 10(5): e0127991.