4713
Differentiation between Intestinal-type and Pancreatobiliary-type Periampullary Carcinoma and Prediction of Lymphatic Metastasis: Whole-Lesion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Histogram Analysis1Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, Wuhan, China
Synopsis
Pancreatobiliary versus intestinal histologic type of differentiation is an independent prognostic factor in resected periampullary adenocarcinoma. To differentiate these two histologic type proactively before surgery, we tried to use whole-lesion histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) derived from diffusion-weighted imaging . Entropy was significantly lower in pancreatobiliary-type periampullary carcinoma and achieved the best diagnostic performance. ADC value was relatively lower in pancreatobiliary-type. No significant difference was shown between lymph node metastasis positive and negative group. So we hypothesized that ADC histogram parameters might help to differentiate these two histologic type without the influence of lymph nodal involvement.
Purpose
To explore the usefulness of whole-lesion histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) derived from diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in differentiating the histologic type of periampullary carcinoma and predicting lymphatic metastasis.Materials and Methods
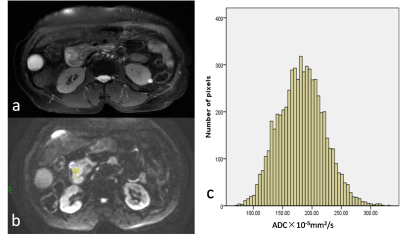
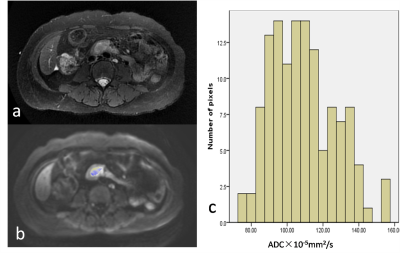
A total of 27 patients who underwent surgery and had histopathology available were included in this retrospectively study (5 with periampullary duodenal carcinoma, 15 with ampullary carcinoma, 2 with bile duct carcinoma, 5 with pancreatic head carcinoma; 10 with intestinal-type, 17 with pancreatobiliary-type; 12 with lymph node metastasis, 15 without lymph node metastasis). All patients underwent preoperative DWI at 3T and b values of 0 and 800 sec/mm2 were used in all three orthogonal diffusion directions. The whole-lesion ADC assessments were performed for each patient. Histogram-derived ADC parameters between different subgroups (histologic type, lymph node metastasis) were compared. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis was used to determine optimal histogram parameters in differentiating the histologic type of periampullary carcinoma and predicting tumor aggressiveness.Results
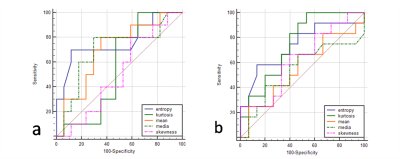
Mean ADC (P=0.112), median ADC (P=0.108) and entropy (P=0.039) were lower in pancreatobiliary-type periampullary carcinoma, and entropy achieved the highest AUC (0.762) with a cutoff value of 4.38 (Sensitivity, 0.70; Specificity, 0.88) in differentiating intestinal and pancreatobiliary-type periampullary carcinoma. Entropy (P=0.090) were higher in periampullary carcinoma with lymph node metastasis than those without. No significant difference was observed in all ADC histogram parameters. Entropy achieved the highest AUC of 0.733 (Sensitivity, 0.58; Specificity, 0.87; cut-off value, 4.40).Discussion
Several studies have reported that histologic phenotype is a better prognostic factor of survival in patients with periampullary carcinomas than tumor anatomic location. Intestinal-type periampullary carcinoma had longer median overall survival than those with pancreatobiliary-type 1, 2. Previous researches have tried various biomarkers which were only available after surgery to differentiate the two histologic types 3-5. In recent studies, investigators tried to differentiate pancreatobiliary and intestinal-type ampullary carcinomas at magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 6, 7 but no reliable diagnostic parameter was achieved. In our study, mean ADC and median ADC were lower in pancreatobiliary-type but no significant difference was shown, which is consistent with previous study 6. Entropy is a textural-based measure of the variation and predictability of individual values in the overall histogram distribution of values across the lesion. Entropy increase as the distribution of ADC values becomes more heterogeneous 8. Entropy of pancreatobiliary-type in our study was significantly lower than intestinal-type, which indicated higher heterogeneity in pancreatobiliary-type periampullary carcinoma. Since pancreatobiliary-type carcinoma has been reported to have poorer prognosis, lower entropy could suggest worse tumor outcome in periampullary carcinomas. It is worth noting that entropy was higher in lymph node metastasis positive group. In this study, 8 of 10 patients diagnosed with intestinal-type periampullary carcinomas had lymph node metastasis while in the pancreatobiliary-type group, only 4 of 17 patients had lymph node metastasis. Studies have been reported that although duodenal carcinomas have relatively high frequency of nodal involvement, the 5-year survival rate can approach 40%–50%9, indicating that histologic phenotype is a relatively independent prognostic factor of survival in patients with periampullary carcinomas and ADC histogram parameters might help to differentiate these two histologic type without the influence of lymph nodal involvement.Conclusion
Low entropy of ADC value indicates a pancreatobiliary-type periampullary carcinoma and whole-lesion ADC histogram might have limited value of predicting lymphatic metastasis in periampullary carcinomas.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Williams J L, Chan C K, Toste P A, et al. Association of Histopathologic Phenotype of Periampullary Adenocarcinomas With Survival[J]. JAMA Surg,2017,152(1):82-88.
[2] Westgaard A, Pomianowska E, Clausen O P, et al. Intestinal-type and pancreatobiliary-type adenocarcinomas: how does ampullary carcinoma differ from other periampullary malignancies?[J]. Ann Surg Oncol,2013,20(2):430-439.
[3] Sandhu V, Bowitz L I, Labori K J, et al. Molecular signatures of mRNAs and miRNAs as prognostic biomarkers in pancreatobiliary and intestinal-types of periampullary adenocarcinomas[J]. Mol Oncol,2015,9(4):758-771.
[4] Zhou H, Schaefer N, Wolff M, et al. Carcinoma of the ampulla of Vater: comparative histologic/immunohistochemical classification and follow-up[J]. Am J Surg Pathol,2004,28(7):875-882.
[5] Bronsert P, Kohler I, Werner M, et al. Intestinal-type of differentiation predicts favourable overall survival: confirmatory clinicopathological analysis of 198 periampullary adenocarcinomas of pancreatic, biliary, ampullary and duodenal origin[J]. BMC Cancer,2013,13:428.
[6] Bi L, Dong Y, Jing C, et al. Differentiation of pancreatobiliary-type from intestinal-type periampullary carcinomas using 3.0T MRI[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging,2016,43(4):877-886.
[7] Chung Y E, Kim M J, Park M S, et al. Differential features of pancreatobiliary- and intestinal-type ampullary carcinomas at MR imaging[J]. Radiology,2010,257(2):384-393.
[8] Umanodan T, Fukukura Y, Kumagae Y, et al. ADC histogram analysis for adrenal tumor histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient in differentiating adrenal adenoma from pheochromocytoma[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging,2016.
[9] Kim J H, Kim M J, Chung J J, et al. Differential diagnosis of periampullary carcinomas at MR imaging[J]. Radiographics,2002,22(6):1335-1352.
Figures