4685
Application of Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in the assessment of local aggressiveness of endometrial cancer1Department of Imaging Diagnosis, National Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Local aggressiveness of endometrial cancer (EC) including the quantification of myometrial invasion, the exclusion of cervical stromal infiltration, lymphovascular space invasion (LVSI), etc, are closely related to EC risk classification, development, prognosis and surgical procedures. The ADC and IVIM-derived parameters can quantitatively assess tumor microstructure which is correlated to tumor development and aggressiveness. Our results showed that ADC and some of IVIM parameters demonstrated good diagnostic performance in the identification of deep myometrial invasion, cervical stromal infiltration and LVSI. IVIM DWI could provide valuable information about local aggressiveness of EC preoperatively which contribute to clinical decision-making and prognosis prediction.
Purpose
To investigate the application of intravoxel incoherent motion(IVIM)-derived parameters in the assessment of local aggressiveness of endometrial cancer (EC) preoperatively.Methods
Sixty-six consecutive patients with EC confirmed by surgery and pathology underwent IVIM DWI with 12 b values (0, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100, 150, 200, 400, 800, 1000, 1500, 2000 s/mm2.,NEX=2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1 ,1, 1, 4, 6, 6, respectively) at 3.0T MR scanner(GE Discovery 750, USA) preoperatively. Apparent diffusion coefficient(ADC)was calculated using monoexponential analysis(b=0,800 sec/mm2 ). ADC values and IVIM parameters including true diffusivity (D), perfusion-related diffusivity (D*) and perfusion fraction (f) were measured by two radiologists using the postprocessing software in GE AW workstation independently. A single representative region of interest (ROI) was manually drawn along the margin of the tumor on the IVIM DWI images of b1000, on the section containing the largest tumor cross-section area avoiding areas of necrosis and hemorrhage with reference to conventional MRI imagesT2WI and DCE MRI. All ROIs were directly co-localized on all parameter maps, then the software automatically generated the values of IVIM parameters and ADC.Intraobserver reliability of these parameters was evaluated by using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The two-tailed independent samples t test or Mann-Whitney U test was performed to investigate the difference in the parameters between the deep (≥50%, n=16) and superficial ( <50%, n=50) of myometrial invasion, with and without cervical stromal infiltration (with, n=57; without, n=9), presence and absence of l lymphovascular space invasion (LVSI) (present, n=50; absence, n=16). ROC was performed to obtain the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), the predicted cutoff value, sensitivity, and specificity to compare the diagnostic capacities of IVIM-derived parameters and ADC in staging endometrial cancer preoperatively. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.Results
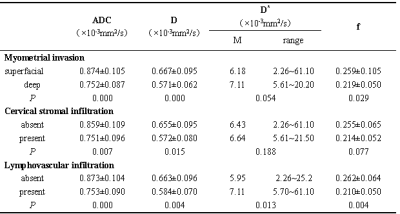
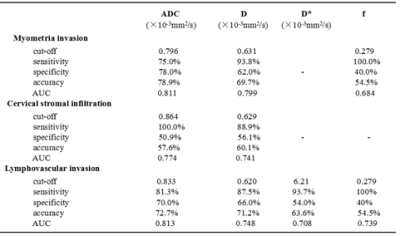
The interobserver agreement was highest for ADC (ICC, 0.989; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.983- 0.993) and lowest for D* (ICC, 0.954; 95% CI,0.926 - 0.972).. The ADC, D and f values were significantly lower in tumors that microscopically invaded ≥50% of the myometrial wall compared with tumors invading <50% of the myometrial wall (P=0.000, 0.000 and 0.029, respectively). There was a significant difference between with and without cervical stromal infiltration for the ADC and D values (P=0.007 and 0.015, respectively). There were no significant differences of D* values between the deep mymometrial invasion and the superfacial myometrial invasion(P=0.054),between the presence and the absence of cervical stromal invasion(P=0.188). The presence of lymphovascular invasion demonstrated significant lower of ADC, D, f values but higher of D* values compared with the absence of lymphovascular invasion (P=0.000, 0.004, 0.004 and 0.013, respectively)(Table 1). The ADC values showed the highest diagnostic performance in the identification of deep myometrial invasion, the presence of cervical stromal infiltration and lymphovascular invasion (AUC: 0.811, 0.774 and 0.813, respectively)(Table 2) .Discussion and conclusion
Discussion and conclusion
The deep myometrial invasion, the presence of cervical stromal infiltration and LVSI indicated more aggressive, poorer prognosis and higher risk of recurrence [1, 2]. Tumor microenvironment changed with the progression of tumor that can be partly reflected through tissue diffusion and perfusion by using the IVIM-derived parameters[3]. Our study showed that the IVIM-derived parameters demonstrated better sensitivity to the identification of the deep myometrial invasion, the presence of cervical stromal invasion and LVSI compared with ADC values meaning that IVIM DWI may have better ability to predict the local aggressiveness of EC preoperatively than ADC values which could be conducive to the pre-treatment risk classification to facilitate the selection of the optimal therapeutic approach and meet the demand for greater personalization of cancer care.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Colombo N, Creutzberg C, Amant F, et al. ESMO-ESGO-ESTRO Consensus Conference on Endometrial Cancer: Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up[J]. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2016, 26(1): 2-30.
[2] Solmaz U, Mat E, Dereli M, et al. Lymphovascular space invasion and cervical stromal invasion are independent risk factors for nodal metastasis in endometrioid endometrial cancer[J]. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2015, 55(1): 81-86.
[3] Ma C, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion DWI of the pancreatic adenocarcinomas: monoexponential and biexponential apparent diffusion parameters and histopathological correlations[J]. Cancer Imaging. 2017, 17(1): 1
Figures
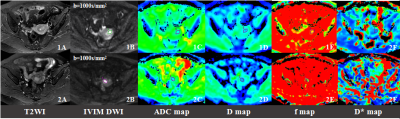
Fig1. Comparision of IVIM parameters and ADC values between the superfacial and deep myometrial invasion.
Images 1A-1F. Endometrial cancer with the superfacial myometrial invasion, FIGO IA. The ADC, D and f value were 0.826×10-3mm2/s, 0.615×10-3mm2/s and 0.264, respectively.
Images 2A-2F. Endometrial cancer with the deep myometrial invasion, FIGO IB. The ADC, D and f value were 0.705×10-3mm2/s, 0.548×10-3mm2/s and 0.248, respectively.
The myometrial invasion of the two tumor was showed similar on the T2WI images. But the ADC, D and f value demonstrated a statistically significant difference between the superfacial myometrial invasion and the deep myometrial invasion.
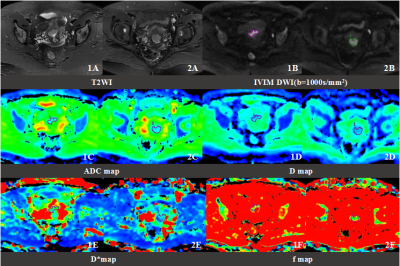
Fig2. Comparision of IVIM parameters and ADC between the presence of cervical stromal infiltration and the absence.Images 1A-1F. EC invaded the deep myometrium without the cervical stromal infiltration, IB.Images 2A-2D. EC invaded the deep myometrium with the cervical stromal infiltration, II.Both the two endometrial masses were located in the lower myometrium leading to the increased difficulty to make a definite diagnosis about the cervical stromal infiltration based on T2WI. The ADC and D value of the EC without the cervical stromal infiltration were significantely higher than the presence( ADC:0.903×10-3mm2/s vs. 0.734×10-3mm2/s;0.647×10-3mm2/s vs.0.565×10-3mm2/s ) , which can increase our confidence in the exclusion of cervical stromal infiltration preoperatively.
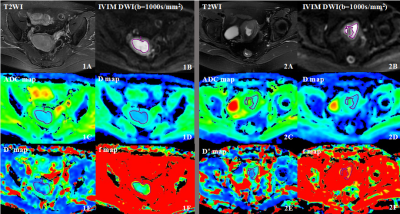
Fig3. Comparision of IVIM parameters and ADC values between the presence of LVSI and the absence of LVSI.
Images 1A-1F. EC invaded the deep myometrium with the lymphovascular invasion, FIGO IB. The ADC, D, D* and f value are 0.674×10-3mm2/s, 0.562×10-3mm2/s, 12.8×10-3mm2/s and 0.130,respectively.
Images 2A-2F. EC invaded the deep myometrium without the lymphovascular invasion, FIGO IB. The ADC, D, D* and f value are 0.863×10-3mm2/s, 0.671×10-3mm2/s, 5.12×10-3mm2/s and 0.305,respectively.
The ADC, D and f value of the presence of LVSI were significantly lower than the absence, while the D* value of the presence of LVSI were significantly higher than the absence.