4663
Effect of abstinent duration on brain function in heroin addicts: a resting-state fMRI study1Tangdu Hospital, Air Force Military Medical University, Xi'an, China
Synopsis
Heroin addiction is increasingly severe in China. Protracted abstinence is commonly used in China. However the effect of protracted abstinence treatment on brain function of heroin dependent patients remains unclear. Previous studies have demonstrated that resting state functional connectivity and amplitude of low frequency fluctuation (ALFF)is useful for studying function of brain.Using the above methods, we found that that prolonged abstinent duration is conducive to function restoring of brain network in heroin-dependent patients, which may be useful to reduce the risk of relapse of heroin addicts.
Purpose
To investigate the effect of abstinence duration on brain function of heroin dependent patients in use of ALFF[1] and functional connectivity (FC[2]) of heroin addicts in resting state, in order to formulate better therapy of abstinence and provide theoretical supports for the treatment program.
Methods
Fourteen heroin addicts abstinent for 6 months (PA6), sixteen heroin addicts abstinent for 11 months (PA11) and fifteen demographically matched healthy controls (HC) underwent this fMRI study. Using GE Signa Excite HD 3.0T MR imaging, the scan range covered the whole brain. The rest fMRI scans were performed using an EPI sequence with TR=2000 ms, TE=30 ms, flip angle=90 °, matrix=64 × 64, FOV=256 mm×256 mm, thickness=4 mm. Thirty-two axial images were taken at each time point, a total of 150 time points were collected and the scanning time was 5 min. The fMRI image datas were preprocessed using Matlab R2013a, BPABI_V2.3 and SPM12 software.The fMRI data weretime and head motion correced, resampled into voxels of 3 cm × 3 cm × 3 cm and normalized to the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) template,then smoothed, linear drifted and band filtered (filtering frequency of 0.01 ~ 0.08 Hz). finally ALFF values were analyzed. Difference in ALFF values among the above three groups were analyzed using one-way ANOVA. Differenc in functional connectivity among the above three groups were analyzed based on differential brain regions of the ALFF analysis.The Pearson correlation between the functional connectivity strength of differetial brain regions and abstinent time was analyzed .Results
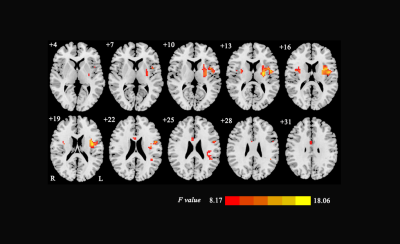
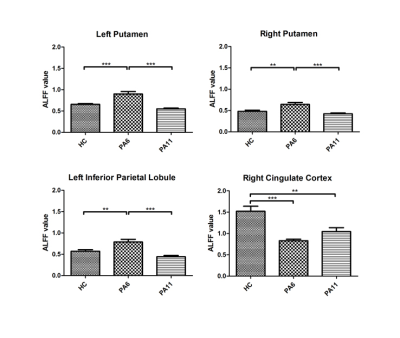
The results demonstrated statistically significant difference in ALFF values among three groups in the bilateral putamen, left inferior parietal lobule and right cingulate gyrus (Fig.1, 2). This study found that, with the extension of abstinent time, heroin addicts’ functional connectivity in left putamen and left island, left parietal lobule and left island, left parietal lobule and right upper frontal gyrus are close to normal, and the correlation between the functional connectivity strength of each brain region and abstinent time were negatively correlated(r=-0.71,P<0.0001)(Fig.3),(r=-0.67,P<0.0001)(Fig.4),(r=-0.59,P=0.0005)(Fig.4); functional connectivity in right anterior cingulate and left frontal gyrus, left precuneus are close to normal, while the correlation in right anterior cingulate and left frontal gyrus between the functional connectivity strength of each brain region and abstinent time was positively correlated (r = 0.55, P = 0.0018)(Fig.5).Discussion and Conclusion
In recent years, studies[3-4] have proposed that abnormal coupling among executive control network (including dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and posterior parietal cortex), salience network (including lateral prefrontal cortex and anterior island lobes) and default mode network (including cingulate cortex and part of the wedge anterior lobe and bilateral apical lobes) may be characteristics of mental and neurological disorders including addiction. We found that after long term abstinence, functional connectivity of heroin addicts’ brain regions involved in ECN, SN and DMN tend to returned to normal, suggesting that prolonged abstinent duration be conducive to function restoring of brain network, which may reduce the risk of relapse of heroin addicts.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants of National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671661, 81371532 and 81401393) and Technology Innovation Development Foundation of Tangdu Hospital (2013LCYJ003).References
[1] Zang YF, He Y, Zhu CZ, et al. Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI[J]. Brain & development. 2007, 29(2): 83-91.
[2] Sporns O, Chialvo DR, Kaiser M, et al. Organization, development and function of complex brain networks[J]. Trends in cognitive sciences. 2004, 8(9): 418-425.
[3] Sridharan D, Levitin DJ, Menon V. A critical role for the right fronto-insular cortex in switching between central-executive and default-mode networks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2008, 105(34): 12569-12574.
[4] Menon V. Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: a unifying triple network model[J]. Trends in cognitive sciences. 2011, 15(10): 483-506.
Figures