4640
Resting state default-mode network functional connectivity correlates with Glutamate +Glutamine/Creatine ratio of the medial prefrontal cortex in methamphetamine males : An fMRI-MRS study1Mental Health Institute of the Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
Synopsis
This study investigates the functional connectivity (FC) of medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) within default mode network (DMN) and the ratio of Glutamate+Glutamine/Creatine (Glx/Cr) in male methamphetamine-dependent subjects (MADs). We combined functional magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopy to investigate the altered FC and its relation with ratio of Glx/Cr in 54 male MADs and 52 healthy male controls. We found increased FC of mPFC with left posterior cingulate cortex and the ratio of Glx/Cr and their negative relation in male MADs. Our results may help with investigation of MADs pathophysiology.
Introduction
Methamphetamine use remains to be a significant social, economic and public health issue in China and worldwide. 1Studies about resting-state brain activity in healthy controls have found a default-mode network (DMN) and importance of differences in DMN connectivity have been reported in several psychiatric conditions.2-3No study to date, however, has investigated resting-state DMN using medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) as a region of interest (ROI) and ratio of Glutamate+Glutamine/Creatine (Glx/Cr) in methamphetamine-dependents subjects (MADs). In the present study, we used combined resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) methods to investigate the altered functional connectivity and its association with Glx/Cr ratio.METHODS
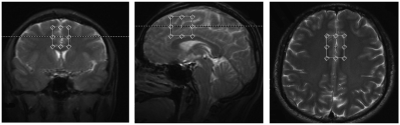
We investigated 54 male MADs met the DSM-IV criteria for lifetime MA dependence and 52 healthy male controls using a 3T Siemens MRI scanner while resting with eyes closed. ROI-wised functional connectivity analysis was used. A mPFC seed-region and Andrews-Hanna’s DMN ROIs were used to explore the FC between mPFC and DMN in Data Processing & Analysis of Brain Imaging (DPABI). 4With a specific interest in the mPFC area, we quantified the ratio of Glx/Cr using 1H-MRS technology. We conducted partial correlation analysis between the FC value and Glx/Cr ratio to find out the functional-biochemical relation in mPFC area.RESULTS
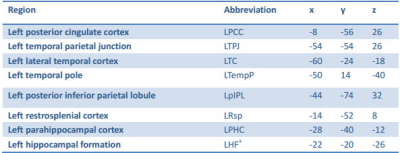
We found that the male MADs showed significant increased functional connectivity with left posterior cingulate cortex (LPCC) (0.21±0.21 VS 0.14±0.25, p=0.036, Bonferroni corrected) and left temporal parietal junction (LTPJ) (0.45±0.24 VS 0.38±0.18, p=0.022, Bonferroni corrected). The Glx/Cr ratio of mPFC (1.23 ±0.29 vs 1.03 ±0.25, p<0.001) was significant increased relative to healthy controls. The Glx/Cr ratio of mPFC was significantly negative related with the FC of mPFC with LPCC(r=-0.275, p=0.05), left temporal pole (LTempP)(r=-0.326, p=0.02) and left restrosplenial cortex (LRsp) (r=-0.372,p=0.007). No correlation was found in the healthy controls.DISCUSSION
In this study, we used fMRI-MRS approach to investigate the FC and its association with Glx/Cr in male MADs. We demonstrated that both the ratio of Glx/Cr in the mPFC and the FC of mPFC with PCC and TPJ were increased in male MADs. Moreover, we showed that Glx/Cr ratio in the mPFC significantly correlated with FC of the same area with LPCC, LTempP and LRsp. Greater brain connectivity in abstinent methamphetamine abusers was accompanied by glucose hyper-metabolism, which is consistent with the regional brain glucose utilization correlates strongly with localized intrinsic FC.6 Increased FC may suggest less efficient neural processing in MADs. The mPFC is thought to be an important site for the adjustment of glutamatergic agents because it is rich in glutamatergic neurons.7 Because most of the brain energy is used to supply glutamatergic signaling, the integration of glutamatergic neurons is supposed to have a direct impact on brain activity. Neuronal activities are primarily determined by the balance of excitation and inhibition in brain microcircuits.8 Glutamate is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. It is possible that the increased Glx/Cr ratio in mPFC is related with the excessive self-focus and thus hyperactivity in the MADs. The Glx/Cr ratio in the mPFC may predicte the degree of FC between this region and LPCC in male MADs. Combined fMRI-MRS is a useful tool for functional-chemical investigation of methamphetamine dependent pathophysiology.Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81371465 and 81671324 to TL, 81100996 and 81671325 to Y.L, 81371480 to J.T), and the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 2015JJ2180 to TL).References
1.United Nations Office On Drug and Crime. Word Drug Report 2016. United Nations publication, Sales No.E.16.XI.7
2.Buckner RL, Andrews-Hanna JR, Schacter DL. SchacterThe brain's default network: anatomy, function, and relevance to diseaseAnn. N Y Acad. Sci., 1124 (2008), pp. 1-38
3.Bluhm RL, Miller J, Lanius RA et al. Spontaneous low-frequency fluctuations in the BOLD signal in schizophrenic patients: Anomalies in the default network. Schizophr. Bull. 2007; 33: 1004–1012.
4.Andrews-Hanna JR, Reidler JS, Sepulcre J, et al.Functional-anatomic fractionation of the brain's default network. Neuron.2010; 65: 550-562.
5.Berman SM, Voytek B, Mandelkern MA, et al.Changes in cerebral glucose metabolism during early abstinence from chronic methamphetamine abuse. Mol Psychiatry.2008;13:897–908.
6. Aiello M, Salvatore E, Cachia A,et al. Relationship between simultaneously acquired resting-state regional cerebral glucose metabolism and functional MRI: A PET/MR hybrid scanner study. Neuroimage.2015;113:111–121
7.Duncan NW, Wiebking C, Tiret B,et al.Glutamate Concentration in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Predicts Resting-State Cortical-Subcortical Functional Connectivity in Humans.PLoS One. 2013; 8(6): 10.1371/annotation/8a1feb12-d70a-4fb2-8dcb-a9cad56c3afd
8.Zhang X, Tang Y, Maletic-Savatic M,et al.Altered neuronal spontaneous activity correlates with glutamate concentration in medial prefrontal cortex of major depressed females: An fMRI-MRS study.J Affect Disord. 2016 ;201:153-61.