4504
Histogram Analysis of monoexponential DWI, biexponential IVIM model and PI-RADS V2 for the Differentiation of Prostate Cancer from BPH in the Transition zone1the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China, 2Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Shanghai, China
Synopsis
In this study, we propose to evaluate histogram analysis of ADC derived by traditional DWI model, diffusion related parameters calculated by using intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model and PI-RADS V2 for the detection of the prostate cancer (PCa) in the transition zone (TZ). Our results show that the highest classification accuracy was achieved by the mean ADC (0.841) and mean D (0.809, acquired by the IVIM model). Our findings suggest that Monoexponential DWI and biexponential IVIM model could potentially improve the accuracy of the pathological grading of prostate cancer in TZ.
Synopsis
Synopsis:
In this study, we propose to evaluate histogram analysis of ADC derived by traditional DWI model, diffusion related parameters calculated by using intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model and PI-RADS V2 for the detection of the prostate cancer (PCa) in the transition zone (TZ). Our results show that the highest classification accuracy was achieved by the mean ADC (0.841) and mean D (0.809, acquired by the IVIM model). Our findings suggest that Monoexponential DWI and biexponential IVIM model could potentially improve the accuracy of the pathological grading of prostate cancer in TZ.
Purpose
It is clear that diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) is an important tool for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. However, the performance of diffusion parameters obtained by conventional DWI model and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model still need to be compared[1-3]. The purpose of this study is to evaluate histogram analysis of ADC, intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) and PI-RADS V2 for detecting the prostate cancer (PCa) in the transition zone (TZ).Methods
Methods :A total number of 63 patients underwent preoperative DWI (TR 3900ms, TE 95ms, slice thickness 2.0mm,gap between neighboring slice 0.24 mm,FOV 280 ×280 mm2,matrix 160×160, b=0、50、100、150、200、400、600、1000 s/mm2) were prospectively collected and processed by traditional monoexponential DWI (b = 0, 1000 were used) and biexponential IVIM model (b =0、50、100、150、200、400、600、1000 s/mm2 were used) to obtain apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) and IVIM parameters (i.e.diffusivity (D) and pseudo-diffusivity (D*) and perfusion fraction (f)). Histogram analysis was performed by outlining entire-tumor regions of interest (ROIs). These parameters (both individually and combined in a logistic regression model) were used to differentiate lesions depending on histopathological analysis of magnetic resonance/transrectal ultrasound (MR/TRUS) fusion guided biopsy. The diagnostic ability of differentiating the PCa from BHP in TZ was analyzed by ROC regression. p<0.05 was considered as statistically significant. The correlations between the Histogram analysis of quantitative parameters and Gleason score were assessed with Spearman correlation.Results
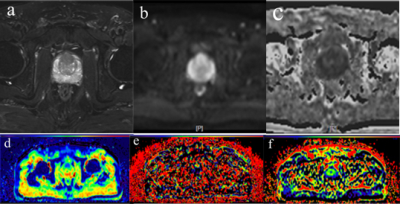
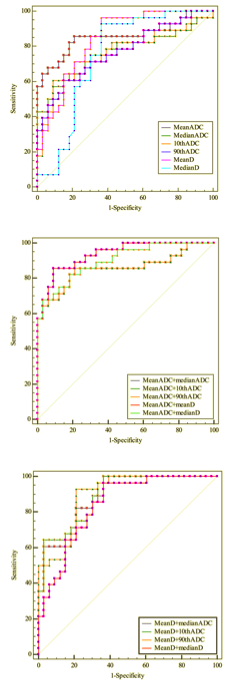
Results:Thirty (31 focus) cases of PCa in PZ and 33 (36 focus) cases of BPH were confirmed by pathology,there are 7 Gleason 6 areas,9 Gleason 7 areas,8 Gleason 8 areas, 5 Gleason 9 areas and 2 Gleason 10 areas detected from the 31 prostate cancer areas(figure 1). Mean ADC, median ADC, 10th percentile ADC, 90th percentile ADC, kurtosis, skewness of ADC, mean D and median D differ significantly between PCa and BHP in TZ. The highest classification accuracy is achieved by the mean ADC (0.841) and mean D (0.809). A logistic regression model based on mean ADC and mean D leads to an AUC of 0.873, however, the difference is not significant; the AUC of the combination of mean ADC and PI-RADS is significant higher the any single parameters(figures 2). The mean Gleason value is (7.5±1.2). The mean ADC, mean D and PI-RADS V2 have correlation with Gleason score (r=-0.522,-0.407 and 0.564, respectively, P<0.05).Conclusion
Our study found that monoexponential DWI and biexponential IVIM model could potentially improve the differentiation of prostate cancer in TZ. In addition, the combination of mean ADC and PI-RADS V2 do not perform better than only using each derived diffusion parameter alone. However, the diagnostic performance is significantly improved by combining mean ADC and PI-RADS V2 in the diagnosis of PCa in TZ. Lastly, it is feasible to confirm the pathological grade of prostate cancer in TZ by mean ADC, mean D and PI-RADS V2 individually.Acknowledgements
No Acknowledgement found.References
References 1. Zhang, Y.D., Q. Wang, C.J. Wu, X.N. Wang, J. Zhang, H. Liu, et al, The histogram analysis of diffusion-weighted intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging for differentiating the gleason grade of prostate cancer. Eur Radiol, 2015. 25(4): p. 994-1004. 2. Dopfert, J., A. Lemke, A. Weidner, and L.R. Schad, Investigation of prostate cancer using diffusion-weighted intravoxel incoherent motion imaging. Magn Reson Imaging, 2011. 29(8): p. 1053-8. 3. Polanec, S., T.H. Helbich, H. Bickel, et al., Head-to-head comparison of PI-RADS v2 and PI-RADS v1. European Journal of Radiology, 2016. 85(6): p. 1125-1131.Figures