4450
Quantitative evaluation of Diffusion tensor and Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) magnetic resonance imaging in cyclic mastalgia in premenopausal young womenQiuju Fan1, Hui Tan1, Nan Yu1, Yuxin Lei1, Shaoyu Wang2, and Yong YU1
1Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang, China, 2Siemens Healthcare, Scientific marketing, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Severe breast pain may significantly affect activities related to life quality, while its aetiology is still poorly understand. DTI and IVIM can provide valuable information on tissue microstructure, microcirculation and pathophysiology that has been extensively used on the breast cancer [1].
Introduction
This study aimed to investigate and evaluate the role of magnetic resonance (MR) diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) and Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in characterizing breast cyclic mastalgia throughout the menstrual cycle phases.Materials and method
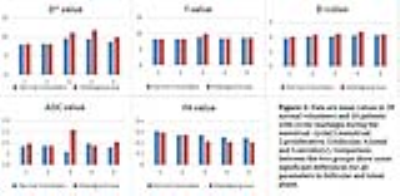
Sixteen premenopausal patients younger than 30 years old who presented to our hospital with a complaint of cyclic mastalgia were enrolled in this study. All with breast pain continuing throughout the day and lasting at least three months on both ends. Meanwhile, twenty-eight healthy female volunteers were enrolled. These patients and volunteers underwent MR imaging five times during one menstrual cycle: (menstrual, proliferative, follicular, luteal and secretory). All data were collected on a 3T MR scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with a receiving four-channel breast array coil. The imaging protocols included axial T2-weighted images. Axial DTI images with fat suppression is based on single-shot EPI imaging sequence, with 30 diffusion gradientsdirections, b values of 0 and 700 sec/mm2, acquisition time 10 minutes. Then IVIM sequences using single-shot spin-echo planar sequence, fat suppression techniques, b values of 0, 50, 100, 150, 200,250, 300, 400, 600, 800 sec/mm2, each b-value was acquired for each of three orthogonal directions.Results
Quantitative parameters including perfusion fraction (f), molecular diffusion coefficient (D), and microperfusion coefficient (D*). DTI related parameters is fractional anisotropy( FA) ,and ADC. Comparison between the two groups did not show any significant differences for all parameters during the menstrual and proliferative phase. In the follicular and luteal phase, IVIM related parameters and ADC values were higher of the mastalgia group compared to normal group, and extraordinary D* values have statistical significance difference (p=0.000). FA also show differences between the two groups in the last two phases (p=0.026 ,p=0.035). In the secretory phase, two Diffusion coefficient parameters of D value and ADC values in two groups respectively have different presence, (p=0.012, p=0.747), obviously, the formal one is statistical difference.Discussion and Conclusions
MRI parameters can indirectly reflected the abnormal high hormone levels in cyclic mastalgia patients , IVIM is more sensitive to this change than DTI, and could provide valuable information on the diffusion properties related to mastalgia microenvironment.