4449
Clinical Value of Reduced field-of-view Sagittal Delayed-Enhanced Breast MRI1Department of Radiology Diagnostics, Xijing Hospital, Xi’an, China
Synopsis
This study aimed to investigate the clinical value of reduced field-of-view (rFOV) sagittal delayed enhanced MRI in diagnosing of breast tumor. we assessed two groups with and without rFOV sagittal delayed enhanced scanning with a time interval of at least six months.In our study, the detection rate, specificity and positive predictive value of the test group with rFOV were significantly higher than that of the control group without rFOV. rFOV sagittal delayed enhanced scanning indicated clinical value in detecting and differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors.
Purpose
A large number of studies have shown that the pharmacokinetic characteristics of DCE-MRI improved the ability of differentiating benign and malignant lesions. Although breast MRI has been extensively applied in recent years, no widely accepted imaging acquisition strategy has been established. which resulted in uneven diagnostic efficiency. So far, there are only a few researches in studying the delay time for differentiating benign and malignant breast lesions. Meanwhile, because the scan time would affect the patient's comfort in the examination bed, too long scan time should be avoided. The appropriate delay time should be based on not affecting the accuracy of diagnosis.The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical value of reduced field-of-view (rFOV) sagittal delayed enhanced MRI in diagnosing of breast tumor.
Material and methods
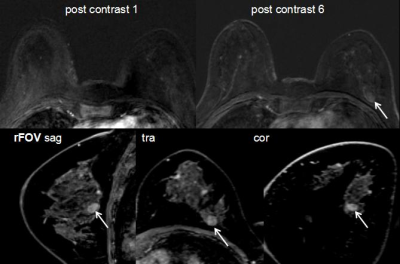
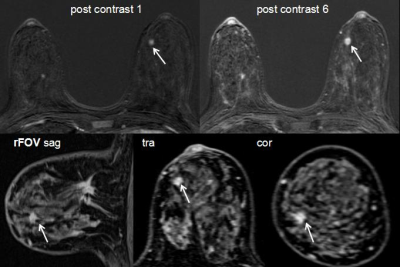
MRI was performed using a Siemens MAGNETOM Trio 3.0 T scanner (Siemens Healthcare Erlangen, Germany) and involved standard clinical sequences. Specifically, acquisitions included a bilateral T1 precontrast scan, a unilateral T2 turbo spin echo sequence with fat suppression, and a series of six bilateral T1 postcontrast scans spaced 53 s apart(TR/TE: 6/2 msec, flip angle 15°, FOV 340mmx340 mm, matrix 314x320, slice thickness 1mm). After DCE scanning, we performed the T1WI sagittal delayed enhanced scan on each unilateral mammary gland respectively with the sequence parameters as: TR/TE: 7/3 msec, Matrix 256x256, FOV: 160 mmx160 mm, slice thickness 0.9 mm. The MRI images of 200 histologically proven patients with breast tumors were retrospectively analyzed. The patients were divided into test and control groups with and without rFOV sagittal delayed enhanced scanning. The two groups were assessed with a time interval of at least six months.Results
There were totally 221 lesions in 200 patients. The detection rates in the test and control groups were 100% (221 lesions), and 95.48% (211 lesions). Among the 211 common lesions detected, pathologic results showed that 75 were malignant and 136 were benign.The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of the two groups were 89.33%, 91.91%, 85.90%, 93.98% and 78.67%, 83.09%, 71.95%, 87.60%, respectively. Differences of the detection rate, specificity and positive predictive value were significant between the two groups (P<0.05).Dissusion and conclusion
Our study employed delayed enhanced scanning and increased the spatial resolution by using small FOV in the sagittal plane, which not only guaranteed the shape of the TIC curve, but the details of the lesions were better shown as well, which improved the detection rate, diagnostic specificity and positive predictive value of the lesions. In addition, The lesions in the test group were more able to identify the boundary of the lesion. The differentiation of malignant and benign tumors mainly depended on morphological features. On this basis, the sagittal delayed scan provided improved detection rate and diagnostic efficiency, which have made up for the shortcomings of low spatial resolution during dynamic scanning.Under the premise of guaranteeing the time resolution, high spatial resolution delayed scanning with small field of view was more advantageous to show the morphological features of the lesions which had potencial clinical application value in the diagnosis and classification of benign and malignant breast masses.Acknowledgements
no acknowledgement found.References
[1] Rahbar H, Partridge S C. Multiparametric MR Imaging of Breast Cancer. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am, 2016,24(1):223-238.
[2] Schnall M D, Blume J, Bluemke D A, et al. Diagnostic architectural and dynamic features at breast MR imaging: multicenter study. Radiology, 2006,238(1):42-53.
[3] DeMartini W B, Rahbar H. Breast magnetic resonance imaging technique at 1.5 T and 3 T: requirements for quality imaging and American College of Radiology accreditation. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am, 2013,21(3):475-482.
[4] Rahbar H, Partridge S C. Multiparametric MR Imaging of Breast Cancer. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am, 2016,24(1):223-238.
[5] Kuhl CK, Schild HH, Morakkabati N. Dynamic bilateral contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the breast: trade-off between spatial and temporal resolution. Radiology. 2005;236:789–800.
[6] Partridge S C, Stone K M, Strigel R M, et al. Breast DCE-MRI: influence of postcontrast timing on automated lesion kinetics assessments and discrimination of benign and malignant lesions. Acad Radiol, 2014,21(9):1195-1203.
[7] Mahoney M C, Gatsonis C, Hanna L, et al. Positive predictive value of BI-RADS MR imaging. Radiology, 2012,264(1):51-58.
Figures