4438
Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Model with Dynamic Contrast Enhanced and Diffusion Weighted Imaging1Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Department of Biomedical Imaging and Image-guided Therapy, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Synopsis
To develop a multiparametric MRI model incorporating the ACR BI-RADS recommended descriptors for DCE-MRI, T2-weighted and DW imaging biomarkers for accurate breast cancer diagnosis. A multivariate logistic regression analysis of multiparametric MRI data from 210 breast tumors was performed to determine parameters that jointly predicted malignancy. A multiparametric MRI model incorporating quantitative and qualitative for DCE-MRI [mass margins (p=0.0012), initial EH (p=0.422) and delayed enhancement (0.0065)] and DW imaging biomarkers [ADCmean (p=0.0031)] enables an accurate breast cancer diagnosis. Results indicate that to maximize diagnostic accuracy a multiparametric MRI approach with DWI and DCE sequences must be considered.
Background
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) is an established valuable diagnostic tool in breast imaging with multiple indications. Although it boasts a high sensitivity of up to 98%, it is often criticized for its low specificity, ranging from 50-70%, due to the overlap of imaging features between benign and malignant lesions. Therefore, additional parameters are being explored for their ability to provide additional specificity; amongst them, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has emerged as the most valuable. DWI is a non-contrast robust MRI technique with high specificity that can easily be integrated into routine MRI protocols and performed as multiparametric MRI. Although previous studies have investigated combining DWI with DCE to improve diagnostic accuracy, none have addressed which of the individual descriptors recommended in the ACR-BI-RADS MRI lexicon including DCE and T2-weighted imaging and DW imaging biomarkers contribute to the compelling improvements in diagnostic accuracy.Purpose
To develop a multiparametric MRI model incorporating the ACR BI-RADS recommended descriptors for DCE-MRI, T2-weighted and DW imaging biomarkers for accurate breast cancer diagnosis.Materials and Methods
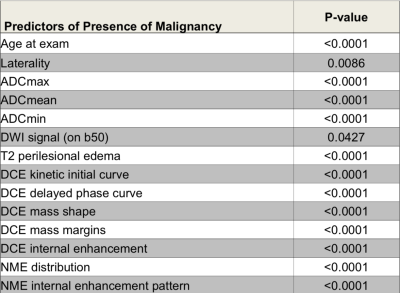
In this IRB approved study, a prospectively populated database was searched for patients with a BI-RADS 0,4,5 finding, who underwent multiparametric MRI of the breast with DCE-MRI and DWI between December 2010 and September 2014. 210 lesions in 188 patients were selected and mpMRI data were retrospectively evaluated by 3 experienced radiologists in consensus. For both mass (n=181) and non-mass (n=29) lesions, their location, size, signal intensity on T2-weighting, peritumoral edema and DCE BI-RADS descriptors [shape, margin, internal enhancement pattern, distribution, initial/delayed enhancement] were recorded. DWI signal intensity and pattern were qualitatively assessed on b0 images, and the mean, min and max ADC values were calculated. In a preliminary analysis, evaluation of the linear relationship between clinically related variables was calculated using Pearson correlation coefficient. Collinearity among the predictor variables was detected (tolerance threshold r ≤ 0.7). Variables that did not have correlation coefficient values within the tolerance threshold were excluded from the model. A multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to determine parameters that jointly predicted malignancy (Table 1). Two models were analyzed. Both models considered the same covariates for inclusion with the only difference being the inclusion of DWI ADC mean as either binary or continuous. Covariates were removed from the multivariate model using forward selection.Results
There were 136 malignant and 74 benign lesions (media 18mm, range 6-100mm). Average ADC mean, min and max were 1.430,0.682 and 2.133 x10-3/mm2 for benign and 0.903, 0.283 and 2.042 x10-3/mm2 for malignant tumors. Average ADC mean, min and max were statistically significantly lower compared to that of benign lesion (p<0.0001). In the multiparametric MRI model 1 incorporating significant univariate predictors and ADC as binary identified ADCmean (p=0.0031), mass margins with DCE (p=0.0016) and delayed enhancement with DCE (p=0.0016) to be significant independent predictors for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast tumors. In multiparametric MRI model 2 where ADC was incorporated as a continuous variable ADCmean (p=0.0031), mass margins with DCE (p=0.0012), initial EH with DCE (p=0.422) and delayed enhancement with DCE (0.0065) were identified to be significant independent predictors for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast tumors. An example of the predictors for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast tumors is provided in Figure 2.Conclusion
A multiparametric MRI model incorporating quantitative and qualitative for DCE-MRI and DW imaging biomarkers enables accurate breast cancer diagnosis. Results indicate that to maximize diagnostic accuracy a multiparametric MRI approach with DWI and DCE sequences must be considered.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
Pinker et al. Combined contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance and diffusion-weighted imaging reading adapted to the "Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System" for multiparametric 3-T imaging of breast lesions.
Baltzer A et al. Combined reading of Contrast Enhanced and Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging by using a simple sum score. Eur Radiol 2016
Mann et al. Eur Radiol 2013: Breast MRI; EUSOBI recommendations for women’s information. Eur Radiol. 2015
Bickel et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of breast lesions: Region-of-interest placement and different ADC parameters influence apparent diffusion coefficient values. Eur Radiol 2017
Pinker et al. Bilateral diffusion-weighted MR imaging of breast tumors with submillimeter resolution using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging at 7 T. Radiology 2015
Partridge et al. Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: protocol optimization, interpretation, and clinical applications. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 2013
Dorrius MD et al. Effect of b value and pre-admission of contrast on diagnostic accuracy of 1.5-T breast DWI: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 2014
Figures

Malignant: invasive ductal cancer grade 2 with a) spiculated margins, b) low ADC values and c) fast initial phase of kinetic curve with delayed phase washout
Benign: Fibroadenoma d) with circumscribed margins, e) high ADC values and f) slow initial phase of kinetic curve with persistent delayed phase.