4367
Multiparametric MRI Radiomic Signatures: Individual Prediction for Prostate Cancer and Benign lesions with same imaging findings1Imaging Center, Wuxi People’s Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi, China, 2CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing P.R. China; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing P.R. China., Beijing, China, 3Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Quantitative Radiomic features based on multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging have great clinical value in discriminating prostate cancer and benign lesions with same imaging findings. We extracted Radiomic features and compared the discrimination efficiency of the combined three types of images with each single type of images, then incorporated independent clinical risk factors and further developed an individual prediction model. The experimental results show that the individual prediction model achieved more accurate diagnosis results than only using Radiomic signatures or clinical factors
Background and purpose
According to the EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer, MRI examination is a crucial part in preoperative examination, along with PSA (prostatic specific antigen) level and other clinical manifestations, guiding further clinical treatment[1]. The Prostate Imaging – Reporting and Data System (version 2), T2WI, DWI and its derivative ADC maps take the leading role in prostate lesion diagnosis[2]. The malignant and benign prostate lesions could have the same image findings. Pathologic examination results used to be the ground truth in tumor discrimination, which is invasive and may leads to overtreatment that can have terrible side effects such as incontinence and impotence. As an emerging technique, Radiomics provide a noninvasive, efficient and reliable method in disease diagnosis and prediction[3]. In previous study, Radiomics has been mostly applied in oncology, such as colorectal cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer and so on. Experimental results showed that Radiomics connected imaging features with clinical manifestations and molecular gene level, which can obtain better recognition rates in tumor classification, tumor metastasis and recurrence[4,5]. The purpose of this study is to investigate the efficiency of multiparametric MRI (mp MRI) based Radiomic signatures in discriminating prostate cancer, and to develop and validate a noninvasive clinical individualized prediction model.Methods
Data was collected on a 3T MR scanners (MAGNETOM Verio, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) using 18-channel body coil. In total, 331 patients were identified and involved in this study: mean age, 71 years; range, 46 to 94 years. All the patients underwent two MRI sequences (T2WI, DWI) and were identified preoperative by pathological examination. For patients whose interval time between screening and pathological examination more than 2 months were excluded. The parameters of axial, coronal, and sagittal T2WI were :TR/TE, 4000/100ms; flip angle, 150°; section thickness, 3mm; intersection gap, 3mm; pixel spacing, 0.75/0.75; FOV, 216mm×240mm2; matrix, 288×320, and the parameters of the used readout segmentation of long variable echo-trains (RESOLVE) DWI were: the used b values, 0, 800 s/mm2; TR/TE, 3200/84 ms; flip angle, 90°; section thickness, 3mm; intersection gap, 3 mm; FOV, 250mm×250mm2; matrix, 192×192, readout segments, 7).
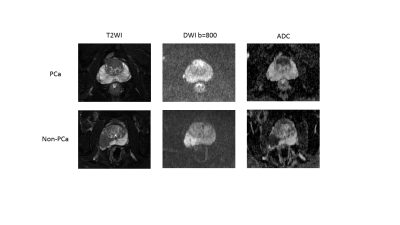
Peripheral zone (PZ), transition zone (TZ) and lesion area were segmented on the three types of MR images (T2WI, DWI and the corresponding ADC) and then extract Radiomic features respectively(Figure 1). The segmentation was carried out by using a free, open-source, and multi-platform image analysis software application for visualization and medical image computing (ITK SNAP version 3.6.0; available at: http://www.itksnap.org/). Intra-class correlation coefficients (ICCs) were used to evaluate the intra- and inter-observer agreement of the features extraction. An ICC greater than 0.8 was considered presenting good agreement. The predictive performance was calculated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and P <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
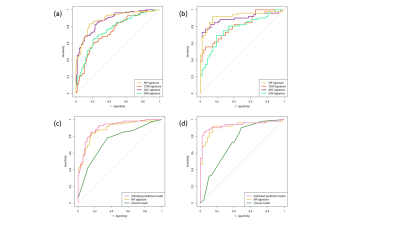
The predictive performance of Radiomic signatures based on multiparametric MRI show better discrimination performance (AUC, 0.920) than each individual MR images, as is shown in Figure 2(a) and 2(b). The discrimination efficiency were further improved when considering both the multiparamertic Radiomic signatures and independent clinical risk factors, which is shown in Figure 2(c) and 2(d) ROC curves (AUC, 0.933).Conclusion
Multiparametric Radiomic signatures based on three types of MR images (T2WI, DWI and ADC) performed better than only using each signal MR image. The individual prediction model including muiltiparametric Radiomic signatures and clinical factors manifested better preoperative diagnosis performance, which could provide an easy-to-use clinical tool for doctors.Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81271629)References
- Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent[J]. European urology, 2017, 71(4): 618-629.
- Weinreb J C, Barentsz J O, Choyke P L, et al. PI-RADS prostate imaging–reporting and data system: 2015, version 2[J]. European urology, 2016, 69(1): 16-40.
- Huang Y, Liang C, He L, et al. Development and validation of a radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer[J]. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2016, 34(18): 2157-2164.
- Aerts H J W L, Velazquez E R, Leijenaar R T H, et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach[J]. Nature communications, 2014.
- Gillies R J, Kinahan P E, Hricak H. Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data[J]. Radiology, 2015, 278(2): 563-577.
Figures