4340
Development and Validation of MR Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Breast Cancer1Radiology Department, Cancer Hospital Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, 2GE heathcare China, beijing, China, 3Huiying Medical Technology Co, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Axillary lymph node (ALN) status is an important prognostic factor for overall breast cancer survival. The number of axillary lymph node metastases is closely related to the risk of distant metastasis1. Accurate identification of axillary lymph node involvement in patients with breast cancer is crucial for prognosis and treatment strategy decisions. Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) is currently the standard procedure for determining ALN status. Sentinel lymph node biopsy was used to determine whether axillary lymph node dissection was needed, which is invasive2. Image based non-invasive predictors of axillary lymph nodes are highly desirable, and currently face challenges. The aim of this study was to develop and validate a radiomics nomogram that incorporates both the radiomics signature and clinicopathologic risk factors for individual preoperative prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer.
Introduction
Axillary lymph node (ALN) status is an important prognostic factor for overall breast cancer survival. The number of axillary lymph node metastases is closely related to the risk of distant metastasis1. Accurate identification of axillary lymph node involvement in patients with breast cancer is crucial for prognosis and treatment strategy decisions. Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) is currently the standard procedure for determining ALN status. Sentinel lymph node biopsy was used to determine whether axillary lymph node dissection was needed, which is invasive2. Image based non-invasive predictors of axillary lymph nodes are highly desirable, and currently face challenges. The aim of this study was to develop and validate a radiomics nomogram that incorporates both the radiomics signature and clinicopathologic risk factors for individual preoperative prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer.Methods
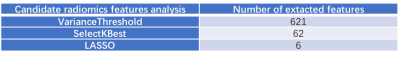
The prediction model was developed in a primary cohort that consisted of 95 patients who were diagnosed with breast cancer were enrolled from March 2016 to August 2016 (ALN Metastasis (+): 54/95; ALN Metastasis (-): 41/95). Radiomic features were extracted from the early stage of dynamic contrast MR imaging of breast cancer. A total of 1032 candidate radiomics features that were categorised as original classes. Variance threshold algorithm, the SelectKBest and lasso regression model were used for data dimension reduction, feature selection, and radiomics signature building. Four statistical analysis were used to develop the predicting model. The radiomics signature and independent clinicopathologic risk factors were incorporated, including T staging, the pathologic types and molecular subtypes. The performance of the nomogram was assessed with respect to its calibration, discrimination, and clinical usefulness. Internal validation was assessed.Results
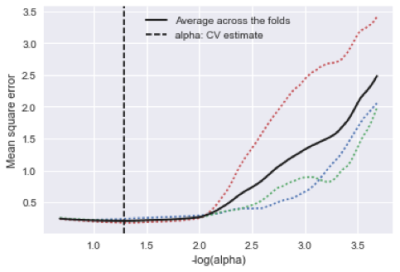
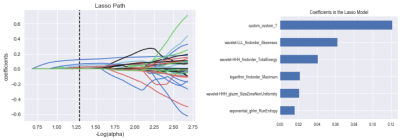
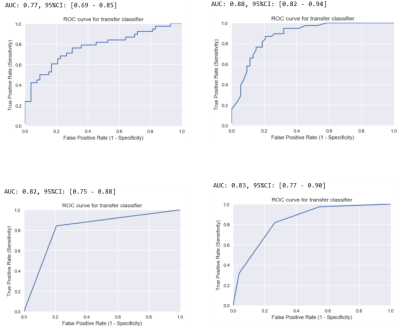
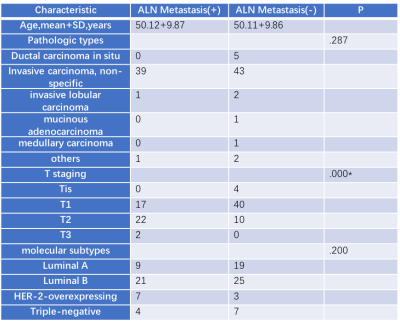
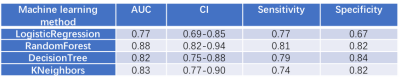
All 95 patients were randomly divided into ALN metastasis positive and ALN metastasis negative groups, the clinical and histopathological characteristics of the two groups were given in Table 1. There was significant differences between the ALN metastasis positive and ALN metastasis negative groups in T staging. The variance characteristics selection is higher than the threshold (0.8). The number of features decreased from 1032 to 621 using variance threshold algorithm. The SelectKBest single variable feature selection method was adopted to select the clinical information of the input, and the feature value was reduced from 621 to 62 (Table 2). The Lasso model that include the extracted features are shown in Fig 1 and Fig 2. All ROC curves of all 4 methods were shown in Fig 3, in comparison, Random Forest showed best diagnostic accuracy with AUC of 0.88 (95%CI: 0.82-0.94; sensitivity: 0.81; specificity: 0.82) and optimum results of four indicators (precision, recall, f1-score, support). The training model indicators of each image contrast are shown in Table 3.Conclusion
This study presents a radiomics nomogram that incorporates the radiomics signature and T staging, which could be conveniently used to facilitate the preoperative individualized prediction of ALN metastasis in patients with breast cancer.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Kohrt H E, Olshen R A, Bermas H R, et al. New models and online calculator for predicting non-sentinel lymph node status in sentinel lymph node positive breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer, 2008, 8(1): 66-66. 2. Esposito E, Micco R D, Gentilini O D. Sentinel node biopsy in early breast cancer. A review on recent and ongoing randomized trials[J]. Breast, 2017, 36:14.Figures