4291
Ophthalmic magnetic resonance imaging using a 7-channel receive-only phased array coil: Quantitative image evaluation of anatomical orbital structures at 3.0 T1Department of Biomedical Engineering and Research Institute of Biomedical Engineering, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2Department of Radiology, Research Institute of Radiological Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Synopsis
The surface coil which yields a higher signal-to-noise ratio only in small area can improve with multi-channel that each channel SNR is combined with a sum-of-squares method. This processing achieves an overall higher SNR in the region of interest (or field of view). In the present study, a 7-channel orbit array coil was developed for ophthalmic imaging. Image quality evaluation by using the designed orbit array coil was examined for imaging the eye, optical nerve, and ocular muscles with orbit.
Purpose
The orbit is complex and difficult area to obtain high quality magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with increase of artifacts (i.e., chemical shift artifacts, non-uniform magnetic field, and motion artifact).1 Therefore, high resolution is required for diagnostic assessment of ophthalmological disease because the orbit has detailed anatomical structures.2 The aim of this study is to improve image quality (with signal-to-noise ratio [SNR]) in anatomical orbit structures and to assess the feasibility of ophthalmic MRI by using designed 7-channel receive-only phased array coil.Materials and Methods
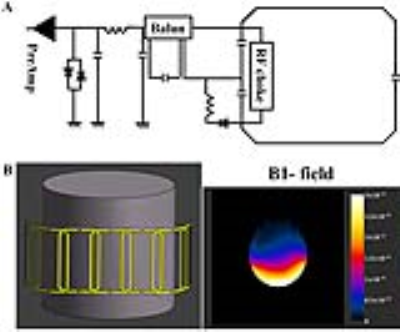
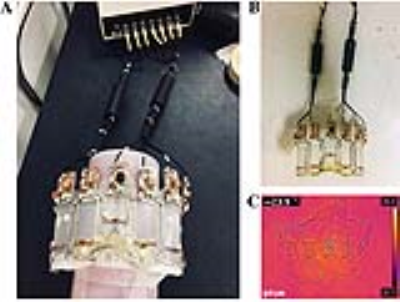
RF coil design and construction: 7-channel receive-only coil element was consist of matching, tuning, phase shifter circuits, and subdividing the conductor loops with two segments as shown by Fig 1. For providing sufficient RF depth penetration, the individual elements (loops; height, 80 mm; width, 41 mm) were attached on proton signal free plastic safety glasses to be able to cover up to the cheekbone. The inclination angle of 119~120° was used for the arrangement of element 1 (or element 7) versus element 2 (or element 6). For elements 4, a curved shape was used to acquire area for the nasal cavity. As prerequisite, the electromagnetic fields simulation (Sim4life, v3.2) was performed to quantify B1- field profile. A numerical cylinder shaped phantom (radius, 80 mm; length, 150 mm; electric conductivity, 0.55 S/m; relative permittivity, 52) was employed on B1- field simulation study. In Fig. 2, all dimensions with height, width, tuning capacitors, and detuning air inductor values were selected according to simulation study results (Sim4life, v3.2).3
MR imaging procedure: Acquisition of MR imaging was performed on a 3.0 T human MR scanner (Discovery MR750, GE healthcare, Waukesha, WI). Assembled array coil was connected to the scanner through a multi-port interface box including 8-low noise amplifiers (tuned at 127.7 MHz). As a scan protocol, we used the multi-slice T1-weighted FSE [TR, 500 ms; TE, 22 ms; FOV, 150 mm; NEX, 2; slice thickness, 2 mm; matrix size, 512×256; 20 slice; ETL, 3; bandwidth, 62.5]. MR images of both the silicon phantom and healthy volunteer were used to evaluate image quality with the estimated SNR (eSNR = mean SI in the region of interest/standard deviation air) and CNR (eCNR = [(mean SI region of interest) - (mean SI adjacent tissue)]/(standard deviation air)) of the retro orbital fat tissue, the globe, and the medial rectus muscle.
Results
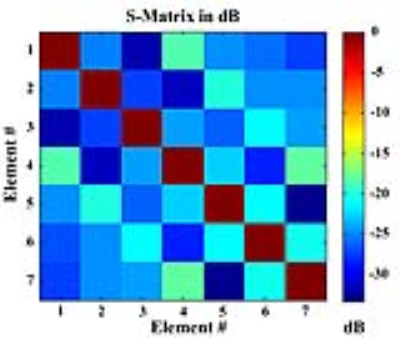
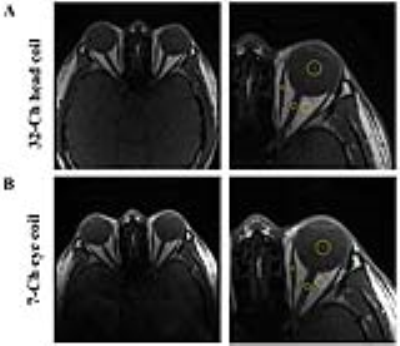
As shown in Fig. 3, reflection coefficient of the individual channels ranged between -26 and -33 dB (element coupling between -18 and -33.4 dB). Compared to the head coil, the images with the design coil indicate rather uniform signal intensity (mean, 140%) with lens and vitreous humor. The values of eSNR were calculated for phantom and healthy volunteer. As shown in Fig 4, the eSNR of the retro orbital fat tissue (>218.1%), the globe (>165.0%), and the medial rectus muscle (>156.8%) was higher in image of the designed coil than in 32-channel head coil. The eCNR of lens-vitreous humor was mean 9.4 at eye coil and 7.7 at head coil.Discussion and Conclusion
This work suggests that the designed coil can achieve improvements in SNR by utilizing closely attached receive only coil in a close-fitting goggle design. eSNR and eCNR comparisons between the designed 7-channel coil and 32-channel head coil on the orbit MR image were performed. The designed coil showed better eSNR and eCNR compared with images from a commercial 32-channel whole head coil. This work will greatly improve the quality of image on ROI for ophthalmic (with degenerative eye disease) imaging study.Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants (2012-007883) from the Mid-career Researcher Program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (MSIP) of Korea.References
1. Herrick RC., Hayman LA., Taber KH, et al. Artifacts and pitfalls in MR imaging of the orbit: a clinical review. Radiographics. 1997;17(3):707-724.
2. Townsend KA, Wollstein G, Schuman JS. Clinical application of MRI in ophthalmology. NMR Biomed. 2008;21(9):997-1002.
3. Sim4Life by ZMT, <http://www.zurichmedtech.com> www.zurichmedtech.com
Figures