3981
Effect of DRD4 receptor −616 C/G polymorphism on thalamic GABA levels in pediatric primary nocturnal enuresis patients1Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China, 2Philips Healthcare China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
The objective of this study is to explore the effect of DRD4 −616 C/G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) on thalamic GABA levels in with primary nocturnal enuresis (PNE). Results indicates the DRD4 −616 C allele is associated with increased thalamic GABA levels and higher arousal from sleep (AS) scores in PNE children. This research helps us understand the genetic susceptibility of the DRD4 −616 C allele to PNE.
INTRODUCTION
Studies have shown that
the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4)
promoter (−616; rs747302) associated with structural
and functional abnormalities in children suffer from primary nocturnal enuresis
(PNE). The effect of DRD4 −616 C/G SNP on GABA levels is important
but remained to unknown. Hence we carried investigation to explore the effect of DRD4 −616 C/G SNP
on thalamic GABA levels in PNE children.
METHODS
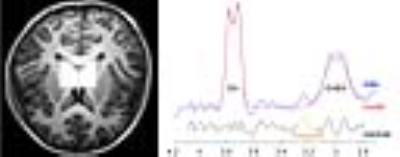
GABA MRS data were acquired from forty-seven pediatric PNE patients (9.1–13.8 years, with a median age of 11.2 years) and forty-four healthy controls (9.0–14.0 years, with a median age of 10.9 years) . The present sample was pre-stratified according to DRD4 −616 C/G SNP (24 C- allele and 23 G- allele PNE; 21C- allele and 23 G- allele controls ). Arousal from sleep (AS) was assessed on a scale of 1–8. MEGA-PRESS sequence was applied to measure GABA spectra (TR/TE=2000/68ms, Dynamic scans =320,Spectral BW (Hz) =2000,total scan time= 10 min 56 sec) using a 3T MRI scanner (Ingenia, Philips Healthcare) while subject was at rest. The 30×40×24 mm MRS voxel was placed in the bilateral thalamus. MRS data were post-processed using Gannet 3.0 software package. The GABA+ level (CSF-corrected) were calculated. Comparisons of AS scores and thalamic GABA levels were performed using the Mann–Whitney U test method: (1) between all PNE patients and controls; (2) between all the C-allele carriers and GG homozygotes; (3) between the C-allele carriers and GG homozygotes in PNE group; (4) between the C-allele carriers and GG homozygotes in control group. The Holm–Bonferroni method was used to correct for multiple comparisons.RESULTS
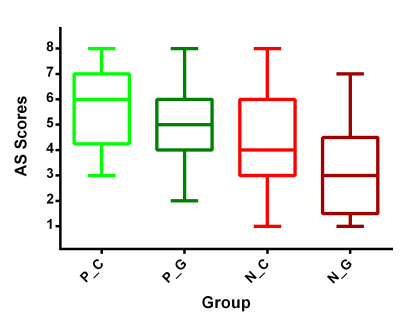
AS scores of the PNE group were significantly higher than those of the healthy control group (Z = 3.765, Pcorrected = 0.010); C-allele carriers exhibited significantly higher AS scores than GG homozygotes (Z = 2.024, Pcorrected = 0.042). The within-group comparisons showed that C-allele carriers exhibited higher AS scores than GG homozygotes in PNE group (Z = 2.053, Pcorrected = 0.040); however, no significant differences were found in AS scores between the genotypes within control group (Z =1.288, Pcorrected = 0. 350).
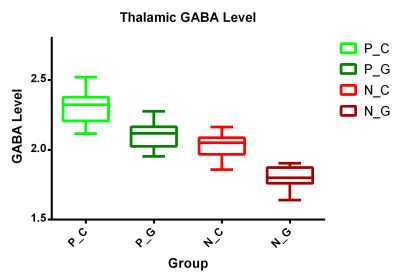
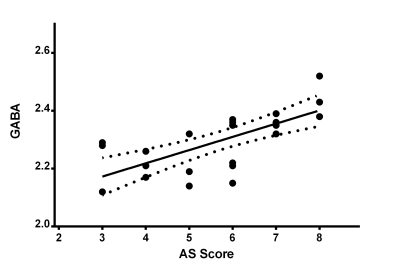
Thalamic GABA levels of the PNE group were significantly higher than those of the healthy control group (Z = 6.822, Pcorrected= 0.003). The GABA level of C-allele carriers were significantly higher than that of GG homozygotes both in PNE and control groups (Z =5.065 Pcorrected = 0.007; Z =4.970 Pcorrected= 0.009). The GABA level of the thalamus also showed a significant positively correlation with the AS scores in C-allele carriers within PNE group (r = 0.709, P < 0.001).
DISCUSSION
This research showed the C-allele carriers exhibit increased GABA
levels in thalamus. Hypothesis is raised that the C-allele may disrupt the
activator protein 2 (AP-2) binding site in the promoter region of the DRD4
gene. Since AP-2 is a sequence-specific mammalian transcription factor that can
activate gene transcription, the mutation may lead to down regulation of DRD4
transcription.
Thus, the C
allele-related decrease in the DRD4 receptor may weaken the inhibition of
depolarization evoked by Ca2+-dependent GABA release, causing increased GABA
concentrations in the thalamus. Therefore, the increased thalamic GABA may
affect the switching between sleep/waking and relaying of sensory afferent signals
from the bladder to cortex, therefore the risk of nocturnal enuresis maybe increased in C-allele carrying children.
The results also
demonstrated that thalamic GABA level of GG homozygotes in PNE children is higher
than that of controls, indicating that thalamic GABA levels may also be modulated by
other neurotransmitters which needs further investigation.
CONCLUSION
Our results suggested the DRD4 −616 C allele is associated with increased thalamic GABA levels, and more validation tests with more cases and other measurement aspects are needed. The effects of genetic variation of the DRD4 locus on GABA level in thalamus may help us understand the genetic susceptibility of the DRD4 −616 C allele to PNE.Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Edden, Richard A E and Mikkelsen, Mark for technical support.
Funding was provided by the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (grant nos. 81301204 and 81541058).
References
(1) Yu B, Chang N, Lu Y, Ma H, Liu N, Guo Q. Effect of DRD4 receptor -616 C/G polymorphism on brain structure and functional connectivity density in pediatric primary nocturnal enuresis patients. Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 27;7(1):1226
(2) Mikkelsen M, Barker PB, Bhattacharyya PK, Brix MK, Buur PF, Cecil KM, Chan KL, Chen DY, Craven AR, Cuypers K, Dacko M, Duncan NW, Dydak U, Edmondson DA, Ende G, Ersland L, Gao F, Greenhouse I, Harris AD, He N, Heba S, Hoggard N, Hsu TW, Jansen JFA, Kangarlu A, Lange T, Lebel RM, Li Y, Lin CE, Liou JK, Lirng JF, Liu F, Ma R, Maes C, Moreno-Ortega M, Murray SO, Noah S, Noeske R, Noseworthy MD, Oeltzschner G, Prisciandaro JJ, Puts NAJ, Roberts TPL, Sack M, Sailasuta N, Saleh MG, Schallmo MP, Simard N, Swinnen SP, Tegenthoff M, Truong P, Wang G, Wilkinson ID, Wittsack HJ, Xu H, Yan F, Zhang C, Zipunnikov V, Zöllner HJ, Edden RAE. Big GABA: Edited MR spectroscopy at 24 research sites. Neuroimage. 2017;159:32-45.
(3) Chandra, M., Saharia, R., Hill, V. & Shi, Q. Prevalence of diurnal voiding symptoms and difficult arousal from sleep in children with nocturnal enuresis. The Journal of Urology 2004; 172, 311-316.
(4) Okuyama, Y. et al. Identification of a polymorphism in the promoter region of DRD4 associated with the human novelty seeking personality trait. Molecular Psychiatry 2000; 5, 64-69.
(5) Gannet: https://github.com/richardedden/Gannet3.0/.